Step-parent rights vary significantly from biological parent rights, often requiring legal action to establish custody or visitation. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating family law; explore this article to learn more about your legal options and protections.
Table of Comparison
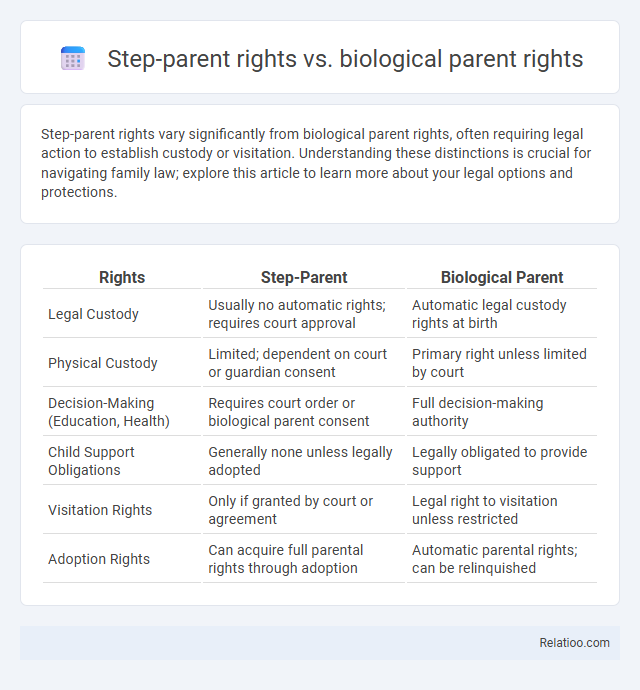
| Rights | Step-Parent | Biological Parent |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Custody | Usually no automatic rights; requires court approval | Automatic legal custody rights at birth |
| Physical Custody | Limited; dependent on court or guardian consent | Primary right unless limited by court |
| Decision-Making (Education, Health) | Requires court order or biological parent consent | Full decision-making authority |
| Child Support Obligations | Generally none unless legally adopted | Legally obligated to provide support |
| Visitation Rights | Only if granted by court or agreement | Legal right to visitation unless restricted |
| Adoption Rights | Can acquire full parental rights through adoption | Automatic parental rights; can be relinquished |
Introduction to Parental Rights
Parental rights define the legal responsibilities and privileges of both biological and step-parents in the upbringing of a child. Your rights as a step-parent typically depend on court rulings or agreements, which can be outlined in a parenting agreement to clarify custody, visitation, and decision-making. Parenting agreements serve to balance the interests of biological parents, step-parents, and the child, ensuring clear guidelines that protect the child's welfare.
Legal Definition of Step-Parent and Biological Parent
The legal definition of a biological parent typically includes individuals who have a genetic link or have legally recognized parental rights through birth or adoption. In contrast, a step-parent does not automatically possess parental rights unless granted by a court or through a formal parenting agreement. Your rights as a step-parent or biological parent can be clearly outlined and adjusted by a legally binding parenting agreement, which defines each party's responsibilities and visitation privileges.
Custody and Visitation Rights
Step-parent rights typically do not override biological parent rights unless legally established through adoption or court orders. Biological parents generally maintain primary custody and visitation rights, with courts prioritizing the child's best interests. Parenting agreements can modify these rights by outlining specific custody and visitation arrangements, often requiring court approval to ensure they serve the child's welfare.
Step-Parent Adoption: Process and Implications
Step-parent adoption grants the step-parent legal parental rights, often overriding biological parent rights when the non-custodial parent's consent is waived or terminated due to abandonment or incapacity. Your parenting agreement must explicitly address custody and visitation to avoid conflicts post-adoption, ensuring clarity in both legal responsibilities and child welfare decisions. This adoption process requires thorough legal and court approval, with significant implications on inheritance, decision-making authority, and the child's emotional stability.
Decision-Making Authority in Child’s Life
Biological parents typically hold primary decision-making authority in a child's life unless limited by a court order or legal agreement. Step-parents may gain certain rights through adoption or specific court rulings but generally lack inherent authority without a formal parenting agreement. Parenting agreements can outline shared decision-making responsibilities, clarifying roles and establishing legal boundaries between biological and step-parents.
Child Support Obligations
Step-parent rights typically do not extend to child support obligations unless a legal adoption or formal guardianship is established, whereas biological parents are generally responsible for financial support of their children by law. Parenting agreements can specify child support arrangements, ensuring both biological and, in some cases, step-parents contribute according to the agreed terms and legal requirements. Your understanding of these distinctions is crucial to navigating rights and obligations effectively in family law.
Educational and Medical Rights
Educational and medical rights are critical factors distinguishing step-parents from biological parents, especially within parenting agreements. Biological parents typically have automatic legal authority over their child's education and healthcare decisions, whereas step-parents must obtain legal recognition through adoption or court orders to secure similar rights. Your parenting agreement can specifically outline the extent of step-parent involvement in educational and medical choices, ensuring clarity and legal protection for all parties involved.
Rights After Divorce or Separation
After divorce or separation, biological parents retain fundamental legal rights regarding custody, visitation, and decision-making for their children, unless modified by a court order. Step-parents typically have limited rights, which may require formal adoption or court-issued custody agreements to establish legal parental responsibilities. Parenting agreements play a crucial role in defining the rights and obligations of all parties involved, ensuring clarity on custody, visitation schedules, and child support to protect the child's best interests.
Impact of Parental Rights on the Child’s Wellbeing
Parental rights, whether held by biological or step-parents, directly influence the child's emotional stability and access to essential resources, with legal agreements like parenting plans serving as tools to clarify responsibilities and reduce conflicts. Biological parents typically retain primary legal rights, but step-parents can gain specific rights through adoption or court orders, which can enhance the child's sense of security and continuity of care. Well-structured parenting agreements help balance these rights, ensuring decisions prioritize the child's wellbeing, consistency, and best interests in both household and legal contexts.
Resolving Disputes Between Step-Parents and Biological Parents
Resolving disputes between step-parents and biological parents requires careful consideration of legal rights, which often prioritize biological parent rights but can be influenced by parenting agreements that outline specific responsibilities and visitation arrangements. Parenting agreements serve as critical tools to clarify custody, visitation, and decision-making authority, reducing conflicts and providing a structured framework for collaboration. Courts may intervene when disputes escalate, balancing the best interests of the child with the established rights of both biological and step-parents.
Infographic: Step-parent rights vs biological parent rights
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com