Legal custody grants a parent the authority to make major decisions about their child's welfare, education, and healthcare, while physical custody refers to the child's living arrangements and day-to-day care. Understanding the distinctions between legal custody and physical custody is essential for navigating family law; learn more about their implications in this article.
Table of Comparison
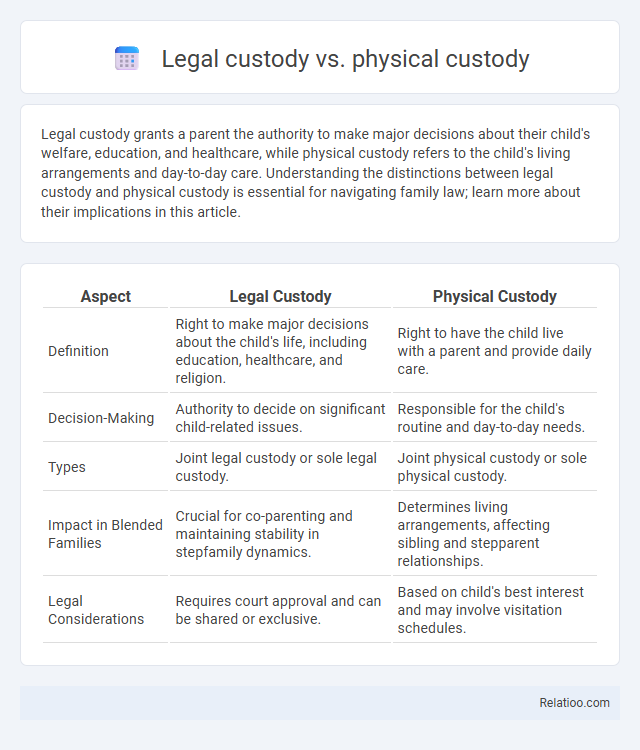
| Aspect | Legal Custody | Physical Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Right to make major decisions about the child's life, including education, healthcare, and religion. | Right to have the child live with a parent and provide daily care. |
| Decision-Making | Authority to decide on significant child-related issues. | Responsible for the child's routine and day-to-day needs. |
| Types | Joint legal custody or sole legal custody. | Joint physical custody or sole physical custody. |
| Impact in Blended Families | Crucial for co-parenting and maintaining stability in stepfamily dynamics. | Determines living arrangements, affecting sibling and stepparent relationships. |
| Legal Considerations | Requires court approval and can be shared or exclusive. | Based on child's best interest and may involve visitation schedules. |
Understanding Legal Custody
Legal custody refers to the right to make major decisions regarding a child's upbringing, including education, healthcare, and religious instruction, distinguishing it from physical custody, which concerns where the child resides. Legal custody can be sole or joint, impacting the level of decision-making authority each parent holds. Parenting agreements typically outline the specifics of both legal and physical custody, aiming to create a clear framework for parental responsibilities and decision-making.
Defining Physical Custody
Physical custody refers to the legal determination of where and with whom a child will live on a day-to-day basis, directly impacting their routine and environment. It differs from legal custody, which is about making major decisions on the child's welfare, such as education and healthcare. Your parenting agreement should clearly outline the terms of physical custody to ensure stability and clarity for the child's living arrangements.
Key Differences Between Legal and Physical Custody
Legal custody refers to the right to make important decisions about a child's upbringing, including education, healthcare, and religion, while physical custody determines where the child lives on a daily basis. Your parenting agreement outlines the arrangement between parents, specifying whether legal and physical custody are sole or joint, and detailing visitation schedules. Understanding the distinction between legal and physical custody is crucial for ensuring clear responsibilities and stable routines for your child.
Types of Legal Custody Arrangements
Legal custody arrangements include sole legal custody, where one parent holds decision-making authority, and joint legal custody, allowing both parents to share responsibilities regarding the child's education, health care, and welfare. Physical custody refers to the child's living arrangements and can be sole, where the child primarily resides with one parent, or joint, meaning the child splits time between both parents' homes. A parenting agreement often outlines the specifics of both legal and physical custody, detailing custody types, decision-making rights, visitation schedules, and other parental responsibilities to ensure clarity and reduce conflicts.
Types of Physical Custody Arrangements
Types of physical custody arrangements include sole physical custody, where one parent has the child living primarily with them, and joint physical custody, which involves the child splitting time between both parents' homes to maintain regular contact with each parent. Bird's nest custody, a less common form, keeps the child in one home while parents rotate living there according to the custody schedule. Parenting agreements typically outline these arrangements in detail to ensure clear expectations and promote the child's welfare.
Factors Courts Consider in Custody Decisions
Courts consider factors such as the child's age, emotional needs, and relationship with each parent when determining legal custody, which involves decision-making rights, and physical custody, which pertains to the child's living arrangements. Parenting agreements are evaluated based on the child's best interests, ensuring stability, continuity, and the ability of parents to cooperate effectively. The court also examines each parent's capacity to provide proper care, maintain a safe environment, and support the child's physical and emotional well-being.
Impact of Custody Types on Parental Rights
Legal custody determines Your right to make important decisions about a child's education, health, and welfare, while physical custody pertains to where the child lives and who provides day-to-day care. Parenting agreements outline the specific responsibilities and schedules agreed upon by both parents, facilitating cooperation and minimizing conflicts. The type of custody awarded directly impacts parental authority and decision-making power, influencing how Your relationship with the child is maintained and exercised.
Modifying Legal or Physical Custody
Modifying legal or physical custody requires demonstrating a significant change in circumstances that affects the child's best interests, such as shifts in parental fitness, relocation, or changes in the child's needs. Courts evaluate factors including stability, the child's welfare, and each parent's ability to provide care when considering custody amendments. Parenting agreements can be revised through court orders after substantiating these changes, ensuring that custody arrangements reflect the current needs and well-being of the child.
Common Misconceptions About Custody
Legal custody refers to the authority to make major decisions about a child's welfare, while physical custody involves where the child lives on a daily basis. A parenting agreement is a negotiation tool that outlines both types of custody but does not guarantee equal time or decision-making power. Common misconceptions include believing legal custody means equal parenting time and that a parenting agreement is legally binding without court approval.
Tips for Parents Navigating Custody Agreements
Understanding the distinction between legal custody, which grants decision-making authority, and physical custody, which determines where your child lives, is crucial for effective parenting agreements. Clear, detailed parenting agreements tailored to your child's best interests can reduce conflicts and provide stability. Open communication, flexibility, and willingness to prioritize your child's needs will help you navigate custody agreements successfully.
Infographic: Legal custody vs physical custody
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com