Disorganized attachment is characterized by inconsistent and confused behavior toward caregivers, often linked to trauma or neglect, whereas avoidant attachment involves emotional distancing and suppression of attachment needs to maintain independence. Explore this article to understand the key differences and implications of disorganized versus avoidant attachment styles in relationships.
Table of Comparison
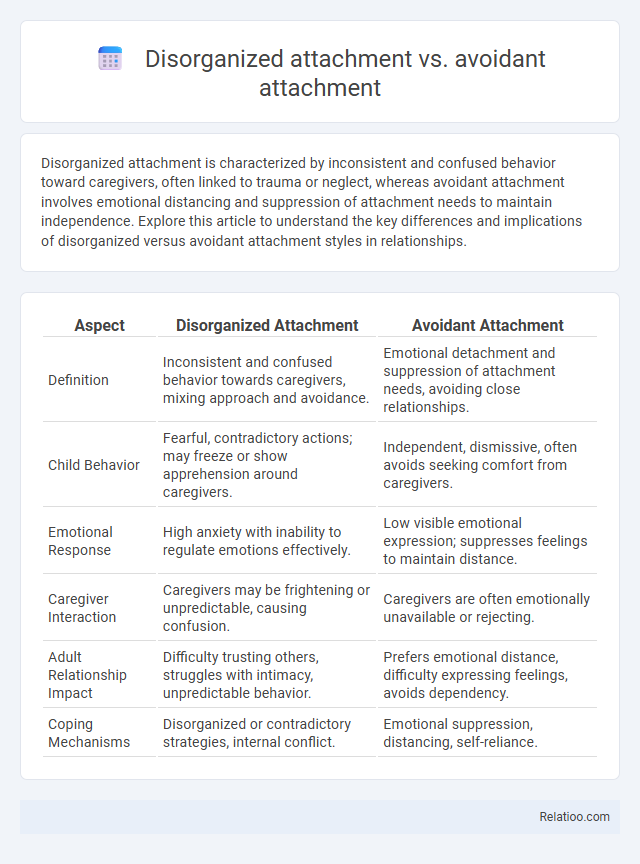
| Aspect | Disorganized Attachment | Avoidant Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inconsistent and confused behavior towards caregivers, mixing approach and avoidance. | Emotional detachment and suppression of attachment needs, avoiding close relationships. |
| Child Behavior | Fearful, contradictory actions; may freeze or show apprehension around caregivers. | Independent, dismissive, often avoids seeking comfort from caregivers. |
| Emotional Response | High anxiety with inability to regulate emotions effectively. | Low visible emotional expression; suppresses feelings to maintain distance. |
| Caregiver Interaction | Caregivers may be frightening or unpredictable, causing confusion. | Caregivers are often emotionally unavailable or rejecting. |
| Adult Relationship Impact | Difficulty trusting others, struggles with intimacy, unpredictable behavior. | Prefers emotional distance, difficulty expressing feelings, avoids dependency. |
| Coping Mechanisms | Disorganized or contradictory strategies, internal conflict. | Emotional suppression, distancing, self-reliance. |
Introduction to Attachment Theory
Attachment theory, developed by John Bowlby, explains how early relationships with caregivers shape emotional bonds and behavioral patterns in later life. Disorganized attachment is characterized by a lack of clear attachment behavior, combining contradictory actions like seeking and avoiding comfort simultaneously, often linked to trauma or inconsistent caregiving. Avoidant attachment reflects emotional distance and suppression of attachment needs, where individuals minimize closeness and prioritize self-reliance, contrasting with the unpredictable and confused responses seen in disorganized attachment.
Defining Disorganized Attachment
Disorganized attachment is characterized by a lack of a consistent strategy for dealing with stress or seeking comfort, often resulting from fear or confusion in relationships, particularly in early childhood caregiver interactions. Unlike avoidant attachment, where individuals tend to emotionally distance themselves, or secure attachment, where trust and reliability are present, disorganized attachment combines approach and avoidance behaviors, reflecting conflicting desires for closeness and fear of it. Understanding your own attachment style can provide critical insights into how you form relationships and manage emotional intimacy.
Understanding Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by a consistent desire to maintain emotional distance and minimize closeness in relationships, often stemming from early caregiving that was emotionally unavailable. Understanding avoidant attachment helps you recognize behaviors like suppression of feelings and a strong emphasis on independence as coping mechanisms. Differentiating avoidant attachment from disorganized attachment, which involves contradictory and confused behaviors, is crucial for addressing specific relationship challenges effectively.
Key Differences: Disorganized vs Avoidant Attachment
Disorganized attachment is characterized by inconsistent, contradictory behaviors and a lack of a coherent strategy to seek comfort, often linked to trauma or fear, whereas avoidant attachment involves emotional distancing and suppression of attachment needs to maintain self-reliance. Avoidant individuals typically minimize expressions of distress and avoid closeness, while disorganized individuals display confusion and apprehension in relationships, oscillating between approach and avoidance. The core difference lies in disorganized attachment's fragmented coping mechanisms versus avoidant attachment's controlled emotional detachment.
Childhood Origins and Contributing Factors
Disorganized attachment in childhood often results from frightening or chaotic caregiver behavior, leading to a lack of coherent strategies for comfort and safety. Avoidant attachment typically develops when caregivers consistently reject or dismiss a child's needs, encouraging emotional self-reliance and suppression of attachment behaviors. Your understanding of these attachment styles highlights the critical role early caregiving environments play in shaping emotional regulation and interpersonal relationships.
Behavioral Signs of Disorganized Attachment
Disorganized attachment is characterized by contradictory and confused behaviors such as approaching a caregiver while simultaneously displaying avoidance or fear, often resulting from inconsistent or frightening caregiving. Unlike avoidant attachment, where children consistently avoid closeness and suppress emotional expression, disorganized attachment manifests through erratic actions like freezing, dazed expressions, or apprehensive movements toward the caregiver. These behavioral signs indicate a lack of a coherent strategy for seeking comfort, reflecting deep emotional turmoil and attachment distress.
Behavioral Signs of Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by behaviors such as emotional distance, reluctance to seek comfort, and suppression of feelings in relationships. Individuals with avoidant attachment often appear self-reliant, avoid intimacy, and may struggle to express vulnerability. These behaviors contrast with disorganized attachment, which includes contradictory and erratic responses, and secure attachment, where individuals feel comfortable with closeness and dependence.
Long-Term Effects on Relationships
Disorganized attachment often leads to intense relational instability and fear of abandonment, causing unpredictable and confusing behaviors in long-term relationships. Avoidant attachment tends to result in emotional distance and difficulty with intimacy, as individuals prioritize self-reliance and suppress emotional expression. Both attachment styles can impair trust and communication, increasing the likelihood of challenges in forming secure, healthy adult relationships.
Therapeutic Approaches for Each Attachment Style
Therapeutic approaches for disorganized attachment prioritize trauma-informed care and stabilization techniques, often involving EMDR and attachment-based therapy to address unresolved trauma and improve emotional regulation. Avoidant attachment interventions focus on building trust and emotional awareness through cognitive-behavioral strategies and experiential therapies that encourage vulnerability and connection. Therapists working with secure attachment leverage strength-based methods to reinforce healthy relational patterns while addressing any specific challenges clients face.
Supporting Healing and Secure Attachment
Supporting healing from disorganized attachment involves creating consistent, predictable environments that foster safety and emotional regulation, while avoidant attachment requires gentle encouragement to express vulnerability and build trust. Your focus should be on reinforcing secure attachment through responsive caregiving, clear communication, and validating emotions to help restructure internal working models. Therapeutic approaches such as trauma-informed therapy and attachment-focused interventions are essential in guiding individuals toward resilience and healthier relational patterns.
Infographic: Disorganized attachment vs Avoidant attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com