Attachment disorder often results from early neglect or trauma, leading to difficulties in forming secure emotional bonds, whereas healthy attachment fosters trust, emotional regulation, and positive social relationships. Discover key differences and strategies for nurturing healthy attachment in this article.
Table of Comparison
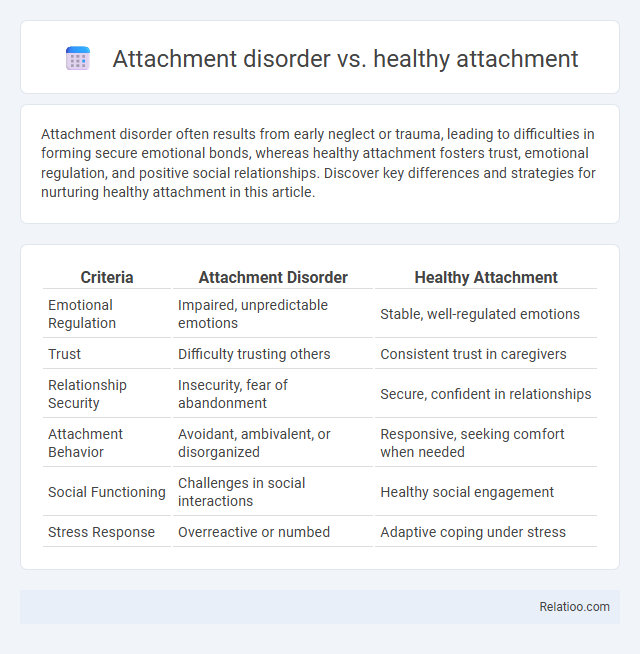
| Criteria | Attachment Disorder | Healthy Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Regulation | Impaired, unpredictable emotions | Stable, well-regulated emotions |
| Trust | Difficulty trusting others | Consistent trust in caregivers |
| Relationship Security | Insecurity, fear of abandonment | Secure, confident in relationships |
| Attachment Behavior | Avoidant, ambivalent, or disorganized | Responsive, seeking comfort when needed |
| Social Functioning | Challenges in social interactions | Healthy social engagement |
| Stress Response | Overreactive or numbed | Adaptive coping under stress |
Understanding Attachment: Definitions and Importance
Attachment disorder arises from inconsistent or harmful caregiving, leading to difficulty forming healthy emotional bonds, whereas healthy attachment involves secure, responsive interactions that foster trust and emotional regulation. Childhood trauma disrupts normal attachment development by creating fear, neglect, or abuse, impairing a child's ability to feel safe and connected. Understanding attachment is crucial for recognizing the lasting impact of early relationships on emotional well-being and guiding effective therapeutic interventions.
What is Healthy Attachment?
Healthy attachment is characterized by a secure emotional bond between a child and caregiver, providing a foundation of trust, safety, and consistent support. This secure connection enables Your child to develop emotional regulation, social skills, and resilience, promoting overall mental well-being. In contrast, attachment disorder results from disrupted bonding, often linked to childhood trauma, which can impair interpersonal relationships and emotional health.
Key Features of Attachment Disorders
Attachment disorders arise from early disruptions in the caregiver-child relationship, characterized by difficulty forming trusting bonds, emotional regulation issues, and social withdrawal. Healthy attachment involves secure, consistent, and responsive caregiving that fosters emotional security, resilience, and positive social interactions. Understanding the key features of attachment disorders helps you recognize signs such as avoidance of closeness, difficulty seeking comfort, and inappropriate social behaviors, often resulting from childhood trauma.
Causes of Attachment Disorders
Attachment disorders primarily stem from inconsistent or neglectful caregiving during early childhood, disrupting the development of secure emotional bonds. Childhood trauma, such as abuse or prolonged separation from primary caregivers, significantly increases the risk of attachment disorders by impairing trust and emotional regulation. In contrast, healthy attachment forms through responsive and sensitive caregiving, fostering emotional security and resilience in children.
Signs of Healthy Attachment in Children
Signs of healthy attachment in children include consistent responsiveness to caregivers, displaying comfort and security in their presence, and the ability to explore their environment while seeking reassurance when needed. Children with secure attachments typically show balanced emotional regulation, trust in relationships, and confidence in social interactions. Unlike children with attachment disorders or childhood trauma, they form stable bonds, exhibit empathy, and recover well from stress.
Symptoms and Red Flags of Attachment Disorders
Attachment disorders often manifest as persistent difficulty forming emotional bonds, marked by symptoms such as excessive clinginess, withdrawal, or aggressive behavior, indicating unhealthy attachment patterns. In contrast, healthy attachment features consistent emotional availability, secure bonds, and appropriate social interactions, crucial for your child's emotional development. Childhood trauma can exacerbate attachment disorders, triggering red flags like intense fear of abandonment, difficulty trusting others, and impaired social functioning, which require early intervention for better mental health outcomes.
Impact on Emotional and Social Development
Attachment disorder disrupts your ability to form secure emotional bonds, leading to difficulties in trust, empathy, and social interactions. Healthy attachment fosters emotional regulation, resilience, and positive relationships by providing a stable foundation during early childhood. Childhood trauma often impairs brain development related to emotions and social behavior, increasing the risk of anxiety, attachment disorders, and impaired social skills.
Risk Factors for Disrupted Attachment
Risk factors for disrupted attachment include inconsistent caregiving, neglect, abuse, and prolonged separation during early childhood, which significantly impact the development of healthy attachment bonds. Childhood trauma such as physical or emotional abuse disrupts the secure attachment necessary for emotional regulation and trust. You can foster healthier attachment patterns by addressing these risk factors early through supportive interventions and stable relationships.
Treatment and Support for Attachment Disorders
Treatment for attachment disorders involves therapy approaches such as Dyadic Developmental Psychotherapy (DDP) and Attachment-Based Family Therapy (ABFT), which help children and caregivers rebuild trust and emotional connection. Healthy attachment promotes emotional regulation and secure relationships, while childhood trauma can disrupt these bonds, necessitating specialized interventions focused on trauma resolution and attachment repair. Your involvement in consistent, supportive care and therapeutic guidance is crucial for fostering recovery and healthy emotional development.
Strategies to Foster Healthy Attachment
Strategies to foster healthy attachment include consistent emotional responsiveness, creating a secure environment, and encouraging open communication to build trust and safety. Understanding the impact of childhood trauma helps tailor approaches that address emotional regulation and promote positive bonding experiences. You can strengthen relationships by practicing empathy, validating feelings, and offering stable support, which counteracts attachment disorders and nurtures secure connections.
Infographic: Attachment disorder vs Healthy attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com