Reminiscence involves recalling past experiences with clarity, often leading to personal growth, while nostalgia evokes a sentimental longing for the past, sometimes idealizing memories. Explore the differences between reminiscence and nostalgia and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
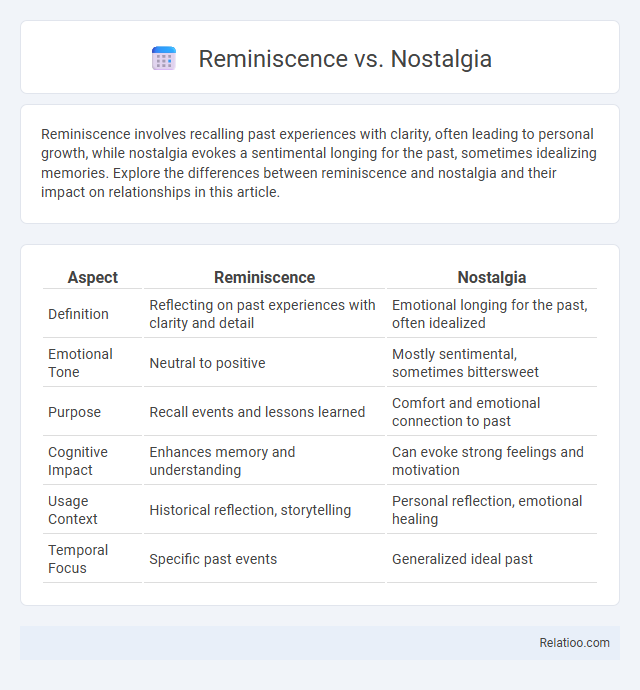
| Aspect | Reminiscence | Nostalgia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reflecting on past experiences with clarity and detail | Emotional longing for the past, often idealized |
| Emotional Tone | Neutral to positive | Mostly sentimental, sometimes bittersweet |
| Purpose | Recall events and lessons learned | Comfort and emotional connection to past |
| Cognitive Impact | Enhances memory and understanding | Can evoke strong feelings and motivation |
| Usage Context | Historical reflection, storytelling | Personal reflection, emotional healing |
| Temporal Focus | Specific past events | Generalized ideal past |
Understanding Reminiscence and Nostalgia
Reminiscence involves recalling past experiences with a neutral or positive emotional tone, often contributing to self-identity and memory consolidation. Nostalgia, by contrast, is a sentimental longing for the past, frequently evoking a bittersweet or idealized emotional response. Understanding how your mind differentiates between reminiscence and nostalgia can enhance emotional well-being and provide insight into how memories influence your present feelings.
Key Differences Between Reminiscence and Nostalgia
Reminiscence involves recalling past experiences with an objective or neutral tone, often used as a cognitive tool to remember detailed events, while nostalgia is an emotional longing for the past, typically idealizing those memories with warmth and sentimentality. Key differences highlight reminiscence as a reflective process focused on memory retrieval, whereas nostalgia emphasizes emotional connection and sentimental value attached to those memories. Understanding these distinctions clarifies how reminiscence serves as a mental activity, and nostalgia acts as an emotional experience linked to personal history.
Psychological Roots of Reminiscence
Reminiscence involves the recollection of past experiences, often serving as a cognitive process to consolidate memories and reinforce personal identity, rooted in the brain's hippocampus and frontal cortex activities. Nostalgia differs by triggering emotional warmth linked to longing for the past, often activated by affective brain regions like the amygdala, reflecting a deeper emotional engagement than mere reminiscence. The psychological roots of reminiscence emphasize its therapeutic potential in enhancing well-being, especially in aging populations, by fostering life review and self-continuity through intentional memory recall.
The Emotional Impact of Nostalgia
Nostalgia triggers complex emotional responses by blending joy and longing, often transporting you to cherished moments from the past. Unlike simple reminiscence, which involves recalling memories without emotional intensity, nostalgia creates a sentimental yearning that can boost mood and foster a sense of connection. The emotional impact of nostalgia plays a crucial role in mental well-being, providing comfort during times of stress or change.
Reminiscence in Memory and Aging
Reminiscence involves the intentional recall of past experiences, playing a crucial role in memory retention and cognitive health among aging individuals. Regular reminiscence sessions can enhance autobiographical memory, support emotional well-being, and delay cognitive decline in older adults. In contrast, nostalgia often evokes sentimental longing with emotional valence, while reminiscence centers on detailed recollection and reflection that reinforces identity and personal history.
How Nostalgia Shapes Identity
Nostalgia shapes identity by connecting Your past experiences with present emotions, fostering a sense of continuity and self-understanding. Unlike reminiscence, which is a neutral act of recalling memories, nostalgia invokes a sentimental longing that influences your emotional state and personal narrative. This emotional engagement helps solidify your identity through meaningful reflection on cherished moments.
Positive and Negative Sides of Reminiscence
Reminiscence involves recalling past experiences and can evoke both positive and negative emotions depending on the memories accessed, while nostalgia typically refers to a sentimental longing for the past often viewed positively. Positive sides of reminiscence include reinforcing your identity, providing comfort, and strengthening social bonds through shared memories. However, negative aspects may arise when reminiscing triggers regret, sadness, or a sense of loss, impacting your emotional well-being.
The Role of Nostalgia in Media and Culture
Nostalgia plays a significant role in media and culture by evoking emotional connections to past experiences, which deepens audience engagement and loyalty. Unlike reminiscence, which simply involves recalling memories, nostalgia carries an emotional longing that influences media content and consumer behavior. Your personal experiences trigger nostalgic responses that media creators strategically harness to foster cultural identity and collective memory.
Practical Benefits of Reminiscence Therapy
Reminiscence therapy, distinct from simple nostalgia or casual reminiscing, offers practical benefits by actively engaging patients in recalling past experiences to improve cognitive function and emotional well-being. It has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression, enhance self-esteem, and strengthen social connections among elderly individuals, particularly those with dementia. By fostering meaningful conversations, this therapeutic approach supports mental stimulation and helps maintain a sense of identity and continuity in aging populations.
Choosing Between Reminiscence and Nostalgia
Choosing between reminiscence and nostalgia depends on the emotional tone and purpose of your reflection; reminiscence involves fact-based, neutral recalling of past events, while nostalgia combines memory with a sentimental longing for those moments. Your choice should align with whether you want to simply remember experiences or evoke warm, emotional connections to past times. Understanding this distinction helps you communicate your memories more effectively, whether for personal reflection or storytelling.
Infographic: Reminiscence vs Nostalgia
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com