Direct praise highlights specific behaviors, boosting confidence and reinforcing positive actions, while indirect praise subtly acknowledges efforts, fostering intrinsic motivation and self-reflection. Discover how these approaches impact relationship dynamics and communication effectiveness in this article.
Table of Comparison
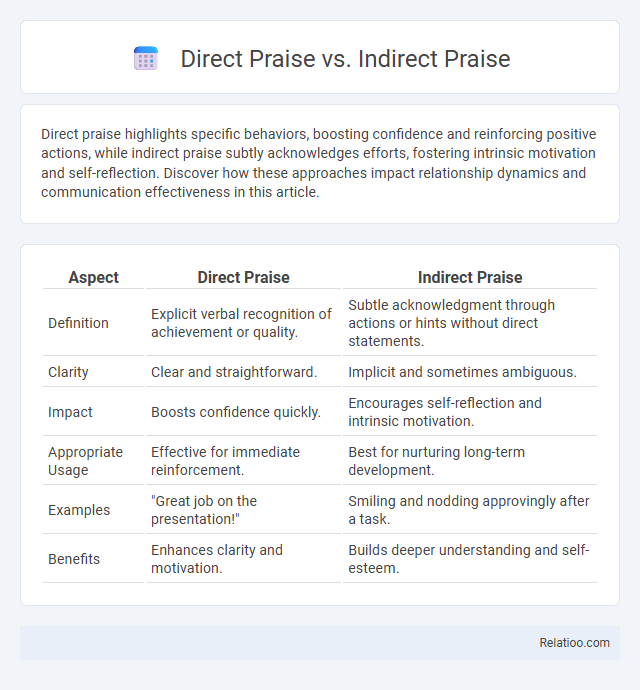
| Aspect | Direct Praise | Indirect Praise |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explicit verbal recognition of achievement or quality. | Subtle acknowledgment through actions or hints without direct statements. |
| Clarity | Clear and straightforward. | Implicit and sometimes ambiguous. |
| Impact | Boosts confidence quickly. | Encourages self-reflection and intrinsic motivation. |
| Appropriate Usage | Effective for immediate reinforcement. | Best for nurturing long-term development. |
| Examples | "Great job on the presentation!" | Smiling and nodding approvingly after a task. |
| Benefits | Enhances clarity and motivation. | Builds deeper understanding and self-esteem. |
Understanding Direct Praise: Definition and Examples
Direct praise explicitly acknowledges specific achievements or behaviors, such as saying, "You completed the project ahead of schedule," which reinforces positive actions and boosts motivation. Indirect praise, in contrast, uses subtle or implied compliments like, "That presentation really stood out," encouraging reflection without overt commendation. Understanding direct praise involves recognizing its clarity and impact in communication, making it a powerful tool for immediate and unambiguous positive feedback.
Exploring Indirect Praise: Meaning and Usage
Indirect praise involves recognizing someone's efforts or qualities subtly without explicitly stating commendation, often employing implication or context to convey appreciation. This form of praise enhances social interactions by fostering humility and encouraging intrinsic motivation, making it especially effective in cultures valuing indirect communication. Understanding indirect praise requires analyzing linguistic cues and situational factors that suggest approval without overt statements, distinguishing it from direct praise, which clearly articulates recognition.
Psychological Impact of Direct vs Indirect Praise
Direct praise explicitly acknowledges specific achievements or qualities, fostering increased self-esteem and motivation by providing clear, tangible feedback. Indirect praise, often subtle or implied, can encourage intrinsic motivation and self-reflection but may lead to ambiguity in self-assessment and reduced clarity regarding strengths. Understanding the psychological impact of direct versus indirect praise reveals that direct praise enhances confidence and goal-oriented behavior, while indirect praise supports autonomy and internalized motivation, highlighting the importance of context and individual differences in feedback delivery.
Cultural Influences on Praise Styles
Cultural influences significantly shape direct and indirect praise styles, reflecting varying communication preferences and social norms. Direct praise, often preferred in Western cultures, explicitly acknowledges individual achievements, enhancing your sense of personal accomplishment and motivation. In contrast, indirect praise, more common in collectivist societies like Japan and China, emphasizes group harmony and subtlety, where compliments are implied rather than overtly stated to maintain social cohesion and humility.
Effectiveness of Direct Praise in Motivation
Direct praise, highlighting specific achievements or behaviors, effectively boosts motivation by providing clear, unambiguous recognition that reinforces positive actions. Indirect praise, often vague or generalized, lacks the precision needed to connect feedback with particular efforts, resulting in weaker motivational impact. Understanding the value of directness allows you to foster a more encouraging environment where your efforts are explicitly acknowledged, driving sustained engagement and improvement.
Why Indirect Praise Can Encourage Growth Mindset
Indirect praise emphasizes efforts and strategies rather than inherent traits, fostering a growth mindset by encouraging learners to value improvement over fixed ability. Unlike direct praise, which often highlights innate qualities, indirect praise motivates persistence and resilience by reinforcing the process of learning. This approach supports adaptive mindset development, leading to increased motivation and long-term achievement.
When to Use Direct Praise in Communication
Direct praise is most effective when you want to clearly acknowledge specific achievements or behaviors, promoting immediate motivation and reinforcing positive actions. Use direct praise in situations where clarity and sincerity are essential to boost your audience's confidence and create a tangible connection to the compliment. Your direct communication style helps recipients understand exactly what they did well, making praise more impactful and meaningful.
Best Practices for Applying Indirect Praise
Indirect praise enhances motivation by emphasizing effort and process rather than inherent traits, fostering a growth mindset. Best practices for applying indirect praise include highlighting specific actions, such as perseverance or creativity, which encourages continuous improvement and resilience. Avoid vague compliments and instead use targeted feedback that subtly acknowledges achievements while promoting self-reflection.
Common Mistakes in Praising: Direct vs Indirect
Common mistakes in praising often arise when confusing direct praise, which clearly states the compliment, with indirect praise, which implies approval without explicit acknowledgment. Direct praise can sometimes seem insincere or overbearing if not genuine, while indirect praise may be overlooked or misunderstood by the recipient. Ensuring your praise matches the context and recipient's preferences helps avoid miscommunication and maximizes its positive impact on motivation and confidence.
Choosing the Right Praise Strategy for Positive Outcomes
Choosing the right praise strategy significantly influences motivation and self-esteem in learners, with direct praise explicitly recognizing specific behaviors or achievements, fostering clear reinforcement. Indirect praise subtly highlights positive traits or efforts without overt acknowledgment, promoting intrinsic motivation and humility. Understanding the balance between directness and subtlety helps tailor feedback to individual needs, enhancing engagement and encouraging continuous improvement.
Infographic: Direct Praise vs Indirect Praise
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com