Contrition involves genuine sorrow for wrongdoing driven by remorse, while repentance requires proactive steps to change behavior and make amends. Explore this article to understand how both elements uniquely impact relationship healing.
Table of Comparison
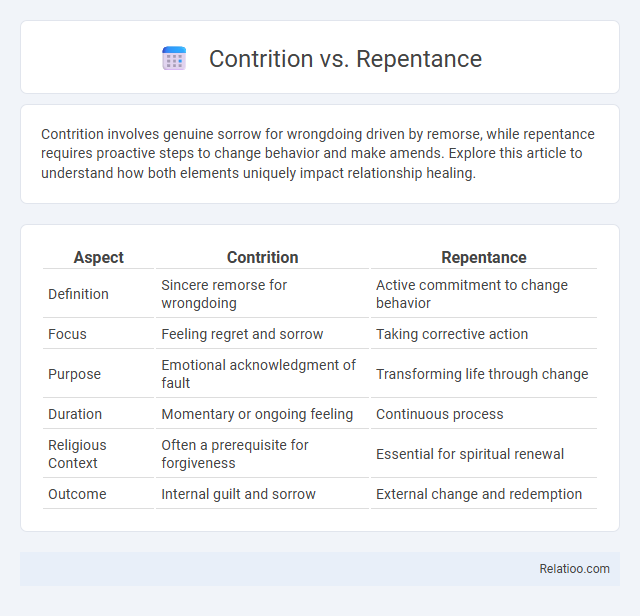
| Aspect | Contrition | Repentance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sincere remorse for wrongdoing | Active commitment to change behavior |
| Focus | Feeling regret and sorrow | Taking corrective action |
| Purpose | Emotional acknowledgment of fault | Transforming life through change |
| Duration | Momentary or ongoing feeling | Continuous process |
| Religious Context | Often a prerequisite for forgiveness | Essential for spiritual renewal |
| Outcome | Internal guilt and sorrow | External change and redemption |
Understanding Contrition: Definition and Meaning
Contrition is a deep, sincere remorse for committing a wrongdoing, often characterized by heartfelt sorrow and regret for one's sins or moral failings. Unlike repentance, which involves a commitment to change behavior and make amends, contrition centers on the emotional and spiritual acknowledgment of guilt. Understanding contrition is crucial in many religious and ethical contexts as it forms the foundation for true repentance and moral growth.
Repentance Explained: A Deeper Dive
Repentance involves a sincere commitment to change behavior, going beyond mere remorse or contrition, which mainly signifies feeling sorry for wrongdoing. It encompasses a transformative process that includes acknowledging mistakes, seeking forgiveness, and actively making amends to avoid repeating the same errors. This deeper, actionable component distinguishes repentance as a pivotal step in personal growth and spiritual renewal.
Key Differences Between Contrition and Repentance
Contrition involves a deep sense of guilt and sorrow for sins committed, often accompanied by a genuine emotional remorse. Repentance goes beyond contrition by including a firm resolution to change one's behavior and avoid future wrongdoing. While contrition focuses on the internal feeling of remorse, repentance emphasizes actionable steps toward moral improvement and reconciliation.
The Role of Emotion in Contrition
Contrition involves a deep emotional sorrow for wrongdoing, serving as the foundation for genuine repentance and moral transformation. Your experience of heartfelt remorse distinguishes contrition, emphasizing sincere emotional engagement rather than mere external compliance. This emotional depth catalyzes authentic repentance, leading to meaningful changes in behavior and reconciliation.
The Action-Oriented Nature of Repentance
Repentance involves a decisive, action-oriented commitment to change, reflecting genuine remorse through tangible steps toward improvement. Contrition focuses more on the internal feeling of sorrow and regret for wrongdoing without necessarily initiating change. Your transformation is driven by repentance's proactive efforts to amend behavior, distinguishing it from the primarily emotional response of contrition.
Religious Contexts: Contrition vs Repentance
Contrition in religious contexts refers to the sincere remorse and sorrow for sins committed, often accompanied by a heartfelt intention to avoid sin in the future. Repentance involves both contrition and a deliberate commitment to change one's behavior, emphasizing transformation and restitution. Unlike general sorrow, contrition is the internal grief for sin, while repentance manifests outwardly through actions reflecting moral and spiritual renewal.
Contrition and Repentance in Daily Life
Contrition involves a deep, sincere sorrow for wrongdoing, emphasizing an internal emotional response that motivates change, while repentance requires a conscious decision to turn away from sin and actively pursue moral improvement. In daily life, contrition fuels genuine remorse that fosters self-awareness and humility, whereas repentance drives practical actions such as seeking forgiveness and making amends. Together, contrition and repentance form the foundation of ethical living by combining heartfelt regret with committed behavioral transformation.
Psychological Perspectives on Contrition and Repentance
Contrition and repentance are distinct psychological processes; contrition involves deep remorse for wrongdoing that often triggers emotional pain, while repentance includes a commitment to change behavior and make amends. Understanding these differences can help you cultivate genuine emotional healing and moral growth by addressing both the affective regret and the practical steps toward improvement. Psychological studies highlight that true contrition fosters empathy and guilt, whereas repentance motivates actionable reform, essential for long-term personal development.
Why Both Contrition and Repentance Matter
Contrition signifies genuine sorrow for wrongdoing, while repentance involves a committed change of behavior reflecting that sorrow. Both contrition and repentance matter because they demonstrate not only remorse but also a proactive effort to amend one's actions, fostering true moral and spiritual growth. Your sincere contrition without repentance may lead to guilt without change, whereas repentance without contrition risks superficial compliance without heartfelt transformation.
Cultivating True Change: Integrating Contrition and Repentance
Cultivating true change requires integrating contrition and repentance, where contrition reflects genuine remorse for wrongdoing, and repentance involves actionable steps toward behavioral transformation. Your emotional acknowledgment of fault (contrition) must be paired with a committed effort to amend past mistakes (repentance) for authentic personal growth. This combination fosters a profound internal shift that leads to sustained moral and spiritual renewal.
Infographic: Contrition vs Repentance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com