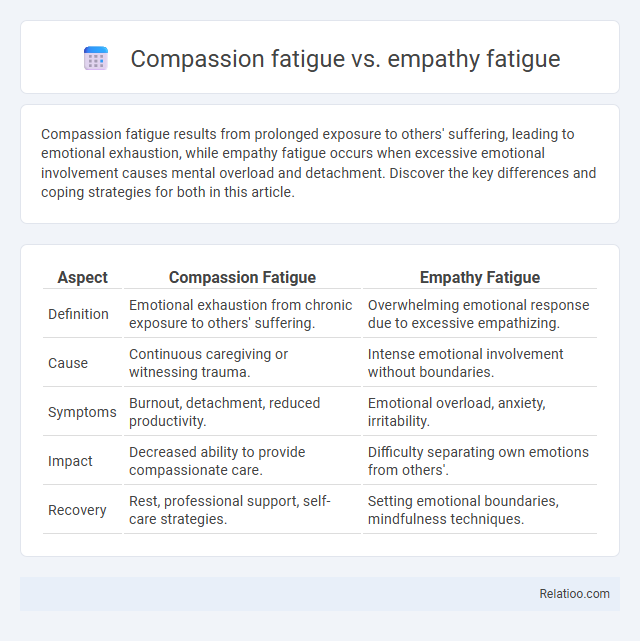
Compassion fatigue results from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, leading to emotional exhaustion, while empathy fatigue occurs when excessive emotional involvement causes mental overload and detachment. Discover the key differences and coping strategies for both in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Compassion Fatigue | Empathy Fatigue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional exhaustion from chronic exposure to others' suffering. | Overwhelming emotional response due to excessive empathizing. |
| Cause | Continuous caregiving or witnessing trauma. | Intense emotional involvement without boundaries. |
| Symptoms | Burnout, detachment, reduced productivity. | Emotional overload, anxiety, irritability. |
| Impact | Decreased ability to provide compassionate care. | Difficulty separating own emotions from others'. |
| Recovery | Rest, professional support, self-care strategies. | Setting emotional boundaries, mindfulness techniques. |
Understanding Compassion Fatigue: Definition and Signs
Compassion fatigue refers to the emotional and physical exhaustion that caregivers experience from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, manifesting as decreased empathy, detachment, and burnout. Unlike empathy fatigue, which specifically relates to the distress caused by absorbing others' feelings, compassion fatigue encompasses a broader depletion of emotional resources and a reduced capacity to provide care. Recognizing signs such as irritability, chronic fatigue, and a diminished sense of accomplishment can help you address compassion fatigue before it impacts your well-being and caregiving effectiveness.
Defining Empathy Fatigue: Key Differences
Empathy fatigue occurs when continuous emotional involvement in others' suffering leads to exhaustion, differing from compassion fatigue which centers on the deep emotional impact of caregiving stress. Empathy fatigue primarily reflects a depletion of the capacity to understand and share others' feelings, whereas compassion fatigue involves a more profound sense of helplessness and emotional distress. Recognizing these distinctions is essential for mental health professionals to implement targeted strategies that restore emotional resilience and prevent burnout.
The Overlap: Compassion Fatigue vs Empathy Fatigue
Compassion fatigue and empathy fatigue share significant overlap as both involve emotional exhaustion from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, yet compassion fatigue specifically refers to the diminished capacity to feel compassion after constant caregiving. Your emotional resilience can erode when empathy fatigue causes overwhelming emotional responses to others' distress, leading to burnout and reduced professional effectiveness. Understanding these distinctions helps in developing targeted self-care strategies to maintain emotional balance and sustain compassionate engagement.
Causes and Risk Factors for Each Type
Compassion fatigue arises primarily from prolonged exposure to others' trauma and suffering, often affecting healthcare professionals, emergency responders, and caregivers due to high emotional demands and insufficient recovery time. Empathy fatigue results from the cognitive strain of deeply understanding and sharing others' emotions, frequently impacting individuals in counseling, social work, and customer service roles where constant emotional attunement is required. While compassion fatigue stems from emotional exhaustion linked to caregiving roles, empathy fatigue is caused by mental overload from empathic engagement, with risk factors including lack of support systems, burnout, and personal trauma history increasing vulnerability for both conditions.
Emotional and Physical Symptoms to Recognize
Compassion fatigue presents emotional symptoms like persistent sadness, irritability, and feelings of helplessness, while physical signs include chronic exhaustion and headaches. Empathy fatigue often manifests as emotional numbness, detachment, and decreased ability to connect with others, accompanied by physical tension and disrupted sleep patterns. Your ability to recognize these emotional and physical symptoms is crucial for addressing compassion fatigue, empathy fatigue, and protecting your mental and physical health effectively.
Impacts on Caregivers and Helping Professionals
Compassion fatigue, empathy fatigue, and secondary traumatic stress significantly impact caregivers and helping professionals by causing emotional exhaustion, decreased job satisfaction, and impaired decision-making. Compassion fatigue results from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, leading to a loss of the ability to empathize, while empathy fatigue arises from over-identifying with clients' emotions, causing emotional depletion. Your ability to provide effective support diminishes as these conditions compromise mental health, increase burnout risk, and reduce overall caregiving quality.
Prevention Strategies for Compassion and Empathy Fatigue
Prevention strategies for compassion fatigue and empathy fatigue emphasize self-care, setting emotional boundaries, and regular mental health check-ins to maintain emotional resilience. Implementing mindfulness practices, peer support groups, and professional counseling can effectively reduce the risk of emotional exhaustion in caregivers and healthcare professionals. Prioritizing workload management and promoting work-life balance further strengthens prevention efforts for sustained compassion and empathy in caregiving roles.
Approaches to Treatment and Recovery
Compassion fatigue, empathy fatigue, and secondary traumatic stress require targeted treatment approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness-based stress reduction, and structured self-care routines to restore emotional resilience. Your recovery plan should include professional counseling, peer support groups, and regular boundaries setting to prevent burnout and maintain healthy empathy levels. Effective intervention focuses on recognizing symptoms early, promoting emotional detachment when needed, and fostering a sustainable balance between compassion and personal well-being.
Building Healthy Emotional Boundaries
Compassion fatigue, empathy fatigue, and secondary traumatic stress all stem from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, but compassion fatigue specifically impacts caregivers who consistently provide emotional support. Building healthy emotional boundaries is essential for You to protect your mental health by distinguishing between empathizing with others and absorbing their pain. Techniques like mindfulness, self-care routines, and professional supervision can prevent emotional exhaustion and promote resilience in caregiving roles.
Fostering Sustainable Compassion and Empathy
Compassion fatigue, empathy fatigue, and secondary traumatic stress represent different aspects of emotional exhaustion experienced by caregivers and professionals. Understanding the nuances between these conditions is essential for fostering sustainable compassion and empathy, which involve setting boundaries, practicing self-care, and engaging in regular emotional resilience training. Your ability to maintain a healthy balance between compassionate engagement and personal well-being ensures long-term effectiveness in caregiving roles.
Infographic: Compassion fatigue vs empathy fatigue
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com