Compassion fatigue and burnout both affect caregivers but compassion fatigue arises from emotional exhaustion due to prolonged exposure to others' trauma, while burnout stems from chronic workplace stress and overload. Discover how to identify, prevent, and manage these conditions in this article.
Table of Comparison
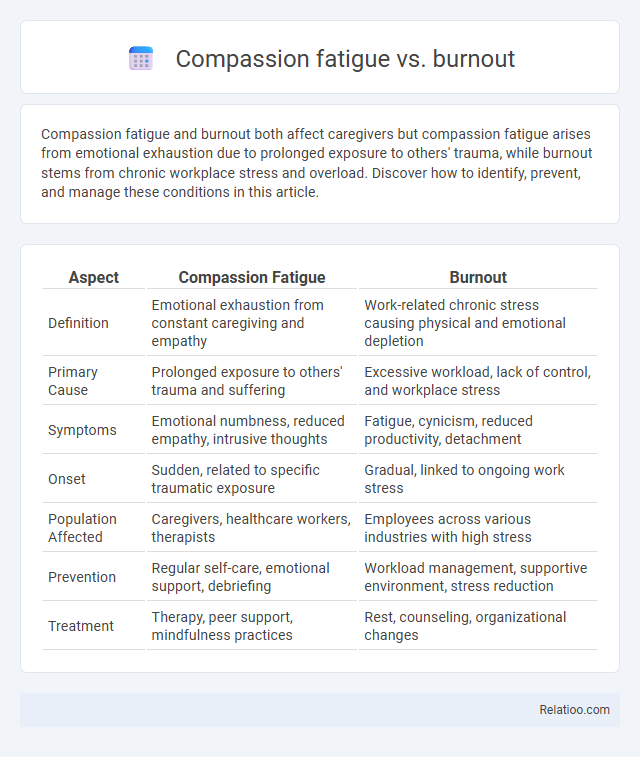
| Aspect | Compassion Fatigue | Burnout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional exhaustion from constant caregiving and empathy | Work-related chronic stress causing physical and emotional depletion |
| Primary Cause | Prolonged exposure to others' trauma and suffering | Excessive workload, lack of control, and workplace stress |
| Symptoms | Emotional numbness, reduced empathy, intrusive thoughts | Fatigue, cynicism, reduced productivity, detachment |
| Onset | Sudden, related to specific traumatic exposure | Gradual, linked to ongoing work stress |
| Population Affected | Caregivers, healthcare workers, therapists | Employees across various industries with high stress |
| Prevention | Regular self-care, emotional support, debriefing | Workload management, supportive environment, stress reduction |
| Treatment | Therapy, peer support, mindfulness practices | Rest, counseling, organizational changes |
Understanding Compassion Fatigue and Burnout
Compassion fatigue is a state of physical and emotional exhaustion resulting from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, often experienced by caregivers and healthcare professionals. Burnout involves chronic workplace stress characterized by feelings of energy depletion, reduced professional efficacy, and detachment, which can overlap with compassion fatigue but stems more from systemic job pressures. Understanding these conditions helps you recognize the signs early and implement self-care strategies to maintain mental health and professional engagement.
Key Differences Between Compassion Fatigue and Burnout
Compassion fatigue primarily arises from prolonged exposure to others' trauma, leading to emotional numbness and decreased empathy, whereas burnout results from chronic workplace stress and feelings of inefficacy. Key differences include compassion fatigue's rapid onset linked to secondary traumatic stress compared to burnout's gradual development due to overwhelming job demands. Recovery from compassion fatigue often requires trauma-focused interventions, while burnout necessitates organizational changes and stress management strategies.
Causes of Compassion Fatigue
Compassion fatigue arises primarily from prolonged exposure to others' trauma and emotional suffering, commonly affecting healthcare workers, first responders, and caregivers. It is caused by continuous empathetic engagement without adequate recovery, leading to emotional exhaustion, reduced empathy, and feelings of helplessness. Unlike burnout, which stems from workplace stress and overload, compassion fatigue specifically results from secondary traumatic stress linked to caring for traumatized individuals.
Common Triggers of Burnout
Burnout commonly stems from prolonged exposure to high job demands, lack of control, insufficient rewards, and workplace conflicts. Factors such as heavy workloads, unclear job roles, and poor support systems significantly increase burnout risk. Identifying these triggers is essential for implementing effective interventions to maintain employee well-being and productivity.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Signs and symptoms of compassion fatigue include emotional exhaustion, reduced empathy, and intrusive thoughts related to others' suffering, while burnout typically manifests as chronic physical and mental fatigue, cynicism, and decreased job performance. Compassion fatigue often involves feelings of helplessness and frustration, whereas burnout is characterized by a pervasive sense of inefficacy and detachment from work. Recognizing these distinctions helps you identify when to seek support and prevent long-term emotional and professional decline.
Risk Factors: Who Is Most Vulnerable?
Risk factors for compassion fatigue include prolonged exposure to trauma and high-empathy professions such as healthcare, social work, and emergency services, making individuals in these roles most vulnerable. Burnout risk escalates with chronic workplace stress, excessive workloads, lack of control, and insufficient support, affecting a broader range of professions beyond emotional caregiving. You are most susceptible to compassion fatigue or burnout if you experience continuous emotional strain without adequate recovery or resources.
Impact on Personal and Professional Life
Compassion fatigue significantly diminishes empathy and emotional reserves, leading to emotional exhaustion that affects both personal relationships and workplace performance. Burnout causes chronic physical and mental fatigue, reducing productivity, increasing absenteeism, and straining social connections outside of work. While both conditions impair well-being, compassion fatigue uniquely disrupts caregivers' ability to connect, whereas burnout broadly undermines overall motivation and job satisfaction.
Prevention Strategies for Compassion Fatigue
Compassion fatigue differs from burnout in that it specifically arises from prolonged exposure to others' trauma, whereas burnout results from chronic workplace stress affecting overall well-being. Prevention strategies for compassion fatigue emphasize regular self-care practices, establishing emotional boundaries, and seeking professional support or peer supervision to process secondary traumatic stress. Incorporating resilience-building techniques such as mindfulness, stress management, and adequate rest can significantly reduce the risk of compassion fatigue among healthcare and caregiving professionals.
Effective Approaches to Managing Burnout
Understanding the differences between compassion fatigue, burnout, and their overlapping symptoms is essential for effective stress management. Compassion fatigue primarily stems from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, while burnout results from chronic workplace stress and emotional exhaustion. Your best approach to managing burnout includes setting clear boundaries, prioritizing self-care routines, and seeking professional support to restore resilience and maintain long-term wellbeing.
Building Long-Term Resilience and Wellbeing
Compassion fatigue and burnout both result from chronic workplace stress, with compassion fatigue arising specifically from exposure to others' trauma, while burnout stems from prolonged emotional and physical exhaustion. Building long-term resilience and wellbeing requires adopting self-care strategies such as mindfulness, regular physical activity, and seeking professional support to manage stress effectively. Your ability to recognize early symptoms and implement restorative practices enhances recovery and sustains emotional strength over time.
Infographic: Compassion fatigue vs burnout
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com