Kanban emphasizes continuous workflow by visualizing tasks and limiting work in progress to improve efficiency, while Scrum structures work in fixed sprints with defined roles and ceremonies for iterative progress. Explore this article to understand which methodology better supports your team's workflow continuity.
Table of Comparison
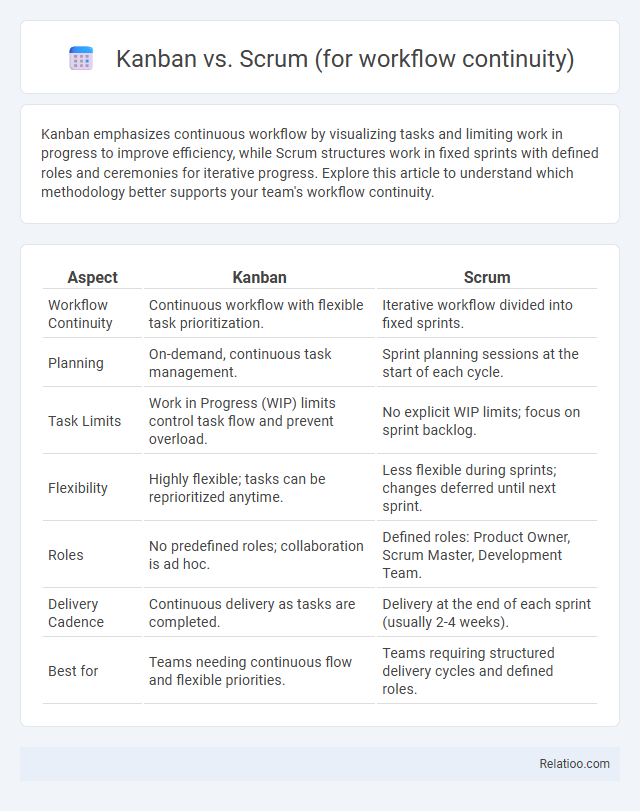
| Aspect | Kanban | Scrum |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Continuity | Continuous workflow with flexible task prioritization. | Iterative workflow divided into fixed sprints. |
| Planning | On-demand, continuous task management. | Sprint planning sessions at the start of each cycle. |
| Task Limits | Work in Progress (WIP) limits control task flow and prevent overload. | No explicit WIP limits; focus on sprint backlog. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; tasks can be reprioritized anytime. | Less flexible during sprints; changes deferred until next sprint. |
| Roles | No predefined roles; collaboration is ad hoc. | Defined roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Development Team. |
| Delivery Cadence | Continuous delivery as tasks are completed. | Delivery at the end of each sprint (usually 2-4 weeks). |
| Best for | Teams needing continuous flow and flexible priorities. | Teams requiring structured delivery cycles and defined roles. |
Introduction to Kanban and Scrum
Kanban and Scrum are two popular frameworks for managing workflow continuity, each offering distinct approaches to work organization and delivery. Kanban emphasizes visualizing work, limiting work in progress, and continuous flow to enhance process efficiency, while Scrum structures work into fixed-length iterations called sprints, promoting regular reviews and adaptive planning. Understanding These methodologies helps you optimize your team's productivity and maintain smooth workflow continuity.
Core Principles of Kanban
Kanban emphasizes visual workflow management, limiting work in progress to enhance efficiency and continuous delivery, ensuring your team maintains a steady pace without overload. Its core principles focus on transparency, flow improvement, and evolutionary change, which support workflow continuity by allowing incremental adjustments based on real-time feedback. Unlike Scrum's fixed iterations, Kanban offers flexibility in task prioritization and delivery timing, making it ideal for ongoing process optimization and smoother task transitions.
Core Principles of Scrum
Scrum emphasizes iterative progress through fixed-length sprints, defined roles like Scrum Master and Product Owner, and regular ceremonies such as daily stand-ups to ensure team alignment and adaptive planning. Kanban focuses on visualizing workflow with a continuous flow model, limiting work in progress to optimize cycle time and reduce bottlenecks. For workflow continuity, Scrum's core principles of transparency, inspection, and adaptation foster incremental delivery and responsiveness, whereas Kanban provides flexible, real-time flow management without prescribed roles or timeboxes.
Workflow Continuity Defined
Workflow continuity ensures consistent and uninterrupted progress in project management, maintaining steady task flow and minimizing bottlenecks. Kanban emphasizes visualizing work, limiting work in progress, and managing flow to sustain continuous delivery, while Scrum uses iterative sprints and structured roles to provide regular progress checkpoints and adaptability. Your choice between Kanban, Scrum, or hybrid approaches should focus on how each method supports seamless workflow continuity tailored to your team's needs and project complexity.
How Kanban Ensures Workflow Continuity
Kanban ensures workflow continuity by visualizing tasks on a board, limiting work in progress (WIP), and enabling teams to identify bottlenecks quickly for continuous delivery. Unlike Scrum's fixed sprints and ceremonies, Kanban offers flexible task prioritization and flow, reducing idle time and enhancing response to changing priorities. This real-time adaptability supports seamless workflow continuity by maintaining a steady pace and improving overall process efficiency.
How Scrum Maintains Workflow Continuity
Scrum maintains workflow continuity through its fixed-length sprints, ensuring consistent delivery cycles and predictable progress tracking. You benefit from daily stand-ups that address blockers promptly, facilitating swift adjustments and uninterrupted task flow. Sprint retrospectives further enhance continuity by promoting continuous process improvements based on team feedback.
Key Differences: Kanban vs Scrum for Workflow Continuity
Kanban emphasizes continuous workflow by visualizing tasks on a board with WIP (work-in-progress) limits to optimize throughput and reduce bottlenecks, ideal for teams needing flexible prioritization. Scrum structures work into fixed-length sprints, promoting iterative progress with defined roles and ceremonies, which may introduce interruptions in workflow continuity due to sprint planning and review cycles. Kanban suits environments requiring ongoing flow and adaptability, while Scrum is better for projects needing regular deliverables and structured cadence.
Advantages of Kanban in Continuous Workflows
Kanban enhances continuous workflows by visualizing tasks on a board, allowing teams to manage work in progress (WIP) limits effectively and reduce bottlenecks, which fosters a smooth and uninterrupted flow of tasks. Unlike Scrum's fixed sprints, Kanban's flexible, pull-based approach supports real-time prioritization and quicker adaptation to changes, ensuring consistent delivery without waiting for iteration cycles to end. Its continuous delivery model improves transparency and workflow efficiency, making it ideal for projects requiring ongoing updates and steady productivity.
When to Choose Scrum for Workflow Continuity
Scrum is ideal for workflow continuity when your project involves complex tasks requiring frequent inspection and adaptation through fixed-length sprints and regular retrospectives. You benefit from Scrum's structured roles, such as Scrum Master and Product Owner, to ensure accountability and continuous improvement within cross-functional teams. Your workflow gains clarity and responsiveness, especially in environments where priorities evolve rapidly and iterative progress is essential.
Deciding the Right Framework for Your Team’s Workflow Continuity
Kanban provides continuous delivery by visualizing work in progress and limiting tasks to enhance flow, while Scrum uses fixed-length sprints to structure work and improve predictability. Choosing the right framework depends on team flexibility, project complexity, and the need for iterative feedback or steady output. Teams prioritizing smooth, uninterrupted workflow may benefit from Kanban's adaptability, whereas those requiring structured planning and regular reviews often find Scrum more effective for maintaining workflow continuity.
Infographic: Kanban vs Scrum (for workflow continuity)
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com