Psychologists specialize in therapy and behavioral interventions for mental health, while psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication and manage psychiatric treatments. Discover the key differences and benefits of each profession in this article.
Table of Comparison
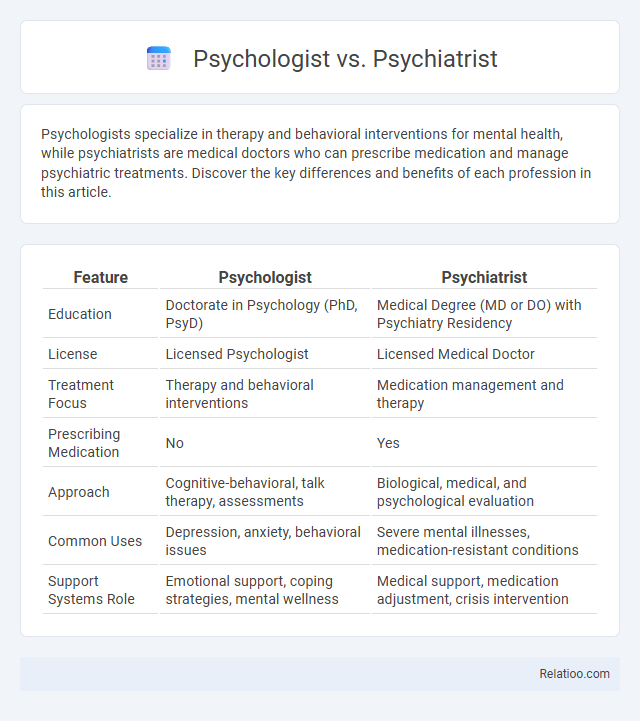
| Feature | Psychologist | Psychiatrist |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Doctorate in Psychology (PhD, PsyD) | Medical Degree (MD or DO) with Psychiatry Residency |
| License | Licensed Psychologist | Licensed Medical Doctor |
| Treatment Focus | Therapy and behavioral interventions | Medication management and therapy |
| Prescribing Medication | No | Yes |
| Approach | Cognitive-behavioral, talk therapy, assessments | Biological, medical, and psychological evaluation |
| Common Uses | Depression, anxiety, behavioral issues | Severe mental illnesses, medication-resistant conditions |
| Support Systems Role | Emotional support, coping strategies, mental wellness | Medical support, medication adjustment, crisis intervention |
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: Key Differences
Psychologists specialize in psychotherapy and behavioral interventions, using psychological assessments to diagnose mental health conditions, while psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication and focus on the biological aspects of mental illness. Your choice between a psychologist and a psychiatrist depends on whether you seek therapy, medication management, or a combination of both. Confidentiality is a crucial aspect in both professions, ensuring your personal information is protected during treatment.
Educational Pathways: Psychologists and Psychiatrists
Psychologists typically pursue a doctoral degree such as a PhD or PsyD, focusing extensively on research, psychological testing, and psychotherapy, while psychiatrists complete medical school and a residency in psychiatry, enabling them to prescribe medications and manage complex mental health disorders. Both professions require supervised clinical training, but psychiatrists' education integrates medical and biological sciences, contrasting with psychologists' emphasis on behavioral science and therapeutic techniques. Confidentiality principles govern both fields, but psychiatrists must also navigate legal and ethical standards related to medical treatment and patient privacy.
Roles and Responsibilities in Patient Care
Psychologists specialize in evaluating and treating mental health disorders through psychotherapy and behavioral interventions, focusing on emotional and cognitive aspects of patient care. Psychiatrists are medical doctors authorized to diagnose, prescribe medications, and manage complex psychiatric conditions, integrating biological and psychological approaches. Both professionals uphold strict confidentiality standards to protect patient privacy, fostering trust and promoting effective therapeutic relationships essential for successful treatment outcomes.
Approaches to Diagnosis and Treatment
Psychologists primarily use psychological assessments and therapeutic techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy to diagnose and treat mental health disorders, focusing on behavior and emotional processes. Psychiatrists, as medical doctors, utilize medical evaluations, prescribe medication, and manage complex psychiatric conditions alongside psychotherapy. Both professions adhere strictly to confidentiality laws and ethical guidelines, ensuring patient information is protected throughout diagnosis and treatment.
Medication Prescription Rights: Who Can Prescribe?
Psychiatrists are medical doctors with the authority to prescribe medication for mental health conditions, while psychologists primarily provide therapy and psychological assessments without prescription rights. Confidentiality laws protect patient information in both professions, but psychiatrists' prescription capabilities often require coordination with primary care providers to manage medication regimens safely. Understanding these distinctions helps patients seek appropriate care based on their need for medication management versus therapeutic support.
Types of Therapy Used by Psychologists and Psychiatrists
Psychologists primarily utilize talk therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychodynamic therapy, and humanistic approaches to address mental health concerns, focusing on behavioral change and emotional insight. Psychiatrists often combine psychotherapy with pharmacological treatments, prescribing medications alongside therapies like cognitive-behavioral or interpersonal therapy to manage psychiatric disorders more comprehensively. When seeking treatment, understanding the differences in therapy types and how confidentiality is maintained can empower Your informed decisions during mental health care.
Work Settings: Where Do They Practice?
Psychologists primarily work in private practices, schools, hospitals, and mental health clinics, providing therapy and psychological assessments. Psychiatrists generally practice in hospitals, private clinics, and psychiatric institutions, focusing on medical treatments and prescribing medications. Both professionals adhere to strict confidentiality protocols governed by legal and ethical standards to protect patient privacy within their respective work environments.
Conditions Treated by Each Profession
Psychologists primarily treat mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and behavioral disorders through therapy and counseling, focusing on emotional and cognitive aspects without prescribing medication. Psychiatrists are medical doctors who diagnose and treat severe mental illnesses like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder, often combining medication management with psychotherapy. Confidentiality is paramount in both professions, regulated by ethical guidelines and laws like HIPAA, ensuring patient information remains private unless safety concerns or legal mandates require disclosure.
How to Choose: Psychologist or Psychiatrist?
Choosing between a psychologist and a psychiatrist depends on your mental health needs and treatment preferences. Psychologists specialize in therapy and behavioral interventions, while psychiatrists can prescribe medication and manage complex psychiatric conditions. Your decision should consider whether you require medication management or primarily counseling to address your concerns effectively.
Collaborative Care: When They Work Together
Psychologists and psychiatrists collaborate within interdisciplinary teams to enhance patient outcomes by integrating psychotherapy with medical treatments. Psychiatrists provide diagnostic expertise and prescribe medications, while psychologists offer evidence-based behavioral interventions, ensuring a comprehensive approach that respects patient confidentiality and ethical standards. This collaborative model promotes seamless communication and coordinated care, optimizing mental health treatment effectiveness.
Infographic: Psychologist vs Psychiatrist
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com