Impulse control plays a critical role in maintaining healthy relationships by preventing emotional outbursts that can damage trust and communication. Discover effective strategies to balance impulse control and emotional expression in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
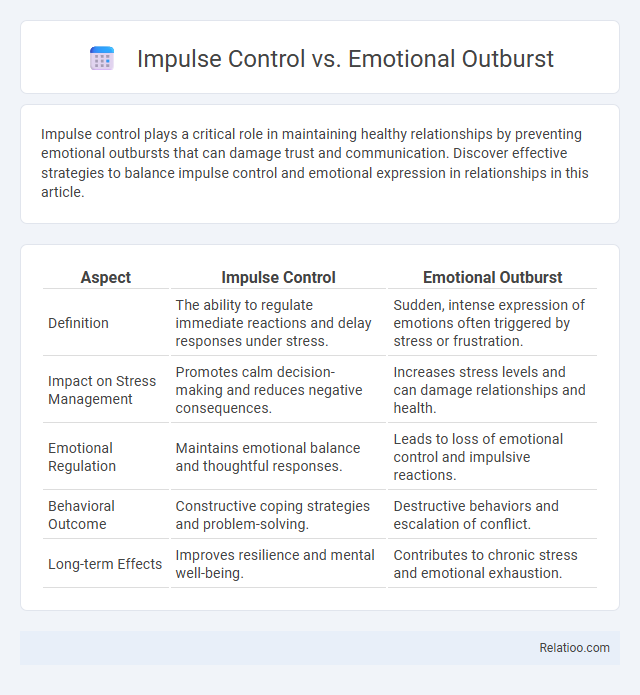
| Aspect | Impulse Control | Emotional Outburst |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to regulate immediate reactions and delay responses under stress. | Sudden, intense expression of emotions often triggered by stress or frustration. |
| Impact on Stress Management | Promotes calm decision-making and reduces negative consequences. | Increases stress levels and can damage relationships and health. |
| Emotional Regulation | Maintains emotional balance and thoughtful responses. | Leads to loss of emotional control and impulsive reactions. |
| Behavioral Outcome | Constructive coping strategies and problem-solving. | Destructive behaviors and escalation of conflict. |
| Long-term Effects | Improves resilience and mental well-being. | Contributes to chronic stress and emotional exhaustion. |
Understanding Impulse Control
Impulse control is the ability to resist immediate temptations or urges, enabling thoughtful decision-making rather than rapid, emotion-driven responses. Emotional outbursts occur when these impulses overwhelm your capacity to pause, leading to reactive behaviors that may be disproportionate to the triggering event. Understanding impulse control empowers you to manage your reactions more effectively, promoting emotional regulation and healthier interpersonal interactions.
Defining Emotional Outbursts
Emotional outbursts are intense, uncontrolled expressions of feelings triggered by overwhelming stimuli that surpass your impulse control capacity. Unlike reactivity, which involves immediate, often automatic responses to situations, emotional outbursts are characterized by a loss of regulation that causes disproportionate reactions. Understanding the difference between impulse control and emotional outbursts is essential for managing your emotional responses effectively.
Key Differences Between Impulse Control and Emotional Outbursts
Impulse control involves the ability to pause and regulate responses before acting, while emotional outbursts are sudden, intense expressions of emotions without restraint. Key differences include impulse control being a deliberate, cognitive process that helps manage behavior, whereas emotional outbursts often bypass rational thought and result in spontaneous reactions. Understanding these distinctions aids in developing strategies for emotional regulation and improved interpersonal communication.
Psychological Factors Influencing Impulse Control
Psychological factors influencing impulse control include executive function deficits, emotional regulation capacity, and stress response mechanisms. Impaired prefrontal cortex activity reduces the ability to inhibit immediate reactions, increasing susceptibility to emotional outbursts and reactivity. Neurotransmitter imbalances, such as dopamine and serotonin dysregulation, further affect impulse control by altering mood stability and decision-making processes.
Common Triggers for Emotional Outbursts
Common triggers for emotional outbursts include stress, feeling overwhelmed, and unmet expectations, which can compromise impulse control and lead to heightened reactivity. Your ability to manage these triggers through mindful awareness and coping strategies plays a crucial role in preventing impulsive reactions and maintaining emotional balance. Recognizing patterns such as fatigue, criticism, or perceived threats helps reduce the frequency and intensity of emotional reactivity.
The Role of Brain Chemistry in Impulse Regulation
Impulse control, emotional outbursts, and reactivity are primarily influenced by the brain's neurotransmitter balance, particularly involving serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Serotonin regulates mood stability and inhibitory control, while dopamine modulates reward processing and impulsivity, and GABA supports neural inhibition reducing overreactivity. Dysregulation in these neurochemical pathways can impair impulse regulation, triggering heightened emotional responses and rapid, unfiltered reactions.
Long-term Effects of Poor Impulse Control
Poor impulse control often leads to chronic emotional outbursts and heightened reactivity, impairing social relationships and professional stability over time. Long-term effects include increased risk of mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, and substance abuse, as well as persistent stress-related physical conditions like hypertension. Developing effective self-regulation strategies is crucial to mitigate these consequences and promote emotional resilience.
Strategies to Manage Emotional Outbursts
Effective strategies to manage emotional outbursts include practicing deep breathing techniques, engaging in mindfulness meditation, and developing emotional awareness through journaling or therapy. Cognitive-behavioral approaches help individuals recognize triggers that lead to impulsive reactions and develop healthier responses through self-regulation skills. Creating a coping plan that involves removing oneself from triggering situations and employing grounding exercises can significantly reduce the intensity and frequency of emotional outbursts.
Building Better Impulse Control Skills
Building better impulse control skills helps you manage emotional outbursts and reduce reactivity, promoting healthier responses in stressful situations. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, and cognitive restructuring enable the brain's prefrontal cortex to regulate impulses more effectively. Consistent practice of these strategies strengthens neural pathways that support self-regulation and emotional resilience.
When to Seek Professional Help for Emotional Dysregulation
Persistent difficulties with impulse control, frequent emotional outbursts, and heightened reactivity that disrupt daily functioning may indicate emotional dysregulation requiring professional evaluation. Seek help if these responses lead to impaired relationships, work challenges, or escalating distress despite self-management efforts. Mental health professionals can provide targeted interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or medication to improve emotional regulation and overall well-being.
Infographic: Impulse Control vs Emotional Outburst
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com