Voyeurism involves deriving pleasure from observing others without their knowledge, while fetish focuses on sexual arousal from specific objects or body parts. Discover the key differences and psychological aspects of Voyeurism vs Fetish in this article.
Table of Comparison
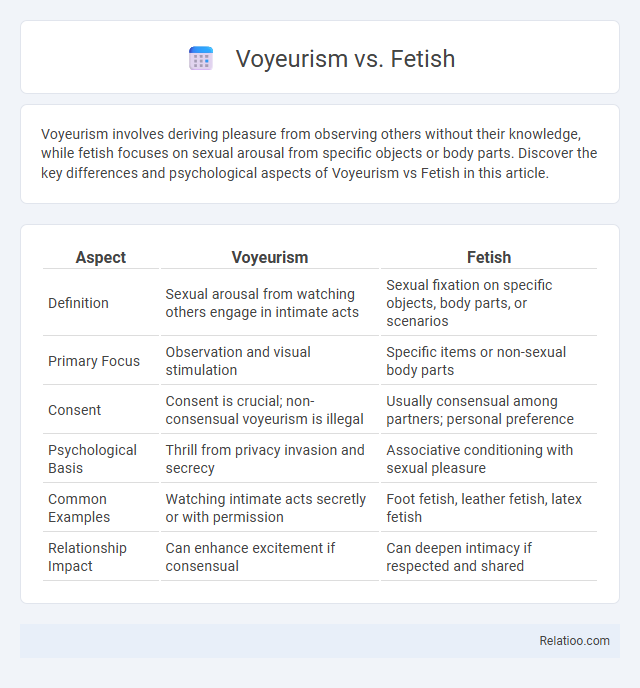
| Aspect | Voyeurism | Fetish |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sexual arousal from watching others engage in intimate acts | Sexual fixation on specific objects, body parts, or scenarios |
| Primary Focus | Observation and visual stimulation | Specific items or non-sexual body parts |
| Consent | Consent is crucial; non-consensual voyeurism is illegal | Usually consensual among partners; personal preference |
| Psychological Basis | Thrill from privacy invasion and secrecy | Associative conditioning with sexual pleasure |
| Common Examples | Watching intimate acts secretly or with permission | Foot fetish, leather fetish, latex fetish |
| Relationship Impact | Can enhance excitement if consensual | Can deepen intimacy if respected and shared |
Understanding Voyeurism: Definition and Key Features
Voyeurism is characterized by the intense desire to observe others engaging in intimate activities without their consent, often deriving sexual gratification from this act. It differs from fetishism, which involves sexual arousal linked to specific objects, body parts, or situations rather than the act of watching others. Key features of voyeurism include covert observation, an emphasis on consent violation, and the psychological drive behind the thrill of witnessing private moments.
What is a Fetish? Exploring the Essentials
A fetish is a sexual fixation on a specific object, body part, or scenario that is essential for sexual arousal or satisfaction, distinguishing it from broader sexual interests. Unlike voyeurism, which involves deriving pleasure from watching others without their knowledge, fetishism centers on particular stimuli that hold unique erotic significance. Understanding the psychological and physiological aspects of fetishes helps clarify how they differ fundamentally from voyeuristic behaviors.
Voyeurism vs Fetish: Core Differences Explained
Voyeurism involves deriving sexual pleasure from observing others without their knowledge, emphasizing non-consensual visual stimulation, while fetish centers on sexual arousal linked to specific objects, body parts, or scenarios, often consensual and personalized. The core difference lies in consent and focus: voyeurism is about illicit observation, whereas fetishism is about specific stimuli that trigger sexual desire. Understanding this distinction clarifies legal and psychological perspectives, as voyeurism can be criminal, but fetishism is typically considered a benign variation of human sexuality.
Psychological Roots: Why Do These Behaviors Occur?
Voyeurism, fetishism, and exhibitionism each stem from distinct psychological roots tied to desire, arousal patterns, and past experiences. Voyeurism involves deriving pleasure from observing others without their knowledge, often linked to feelings of power or control and early exposure to taboo scenarios. Fetishism focuses on intense sexual fixation on specific objects or body parts, originating from associative conditioning or trauma, while exhibitionism is characterized by exposing oneself to others to gain validation or excitement, often rooted in needs for attention or overcoming social inhibitions.
Common Misconceptions About Voyeurism and Fetishes
Voyeurism is often misunderstood as simply a harmless curiosity, but it involves deriving sexual pleasure from secretly watching others, which can breach consent and privacy, unlike consensual fetishes that focus on specific objects or scenarios. Fetishes encompass a wide range of objects or body parts that are essential for sexual arousal, whereas voyeurism centers on the act of observing others without their knowledge, causing ethical and legal issues. Your understanding of these concepts is crucial to distinguish between consensual sexual expression and behaviors that may infringe on others' rights.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Voyeurism involves observing individuals without their consent, often breaching privacy laws and resulting in criminal charges in many jurisdictions. Fetishism, centered on consensual sexual preferences, is legal as long as all parties involved agree and no harm occurs. Legal and ethical considerations distinguish these behaviors by consent and privacy, with voyeurism commonly condemned due to its intrusive and non-consensual nature, while fetishism is recognized as a legitimate sexual expression within consensual relationships.
Signs and Symptoms: When to Seek Help
Experiencing persistent, intense sexual arousal from observing others without consent (voyeurism) or fixation on specific objects or body parts (fetish) can interfere with daily life and relationships. Signs warranting professional help include distress, repetitive compulsive behavior, or legal issues stemming from these urges. Early intervention through therapy can address underlying causes and promote healthier coping mechanisms.
Cultural Perspectives on Voyeurism and Fetishes
Cultural perspectives on voyeurism often vary widely, with some societies viewing voyeuristic behavior as taboo or criminal, while others may tolerate it within consensual contexts. Fetishes, by contrast, are frequently interpreted through the lens of cultural norms and psychological frameworks, where acceptance depends on societal openness to diverse sexual expressions. Your understanding of voyeurism and fetishes can deepen by recognizing these cultural differences, which shape attitudes, legal boundaries, and personal experiences worldwide.
Consent and Boundaries in Sexual Expression
Consent and boundaries are crucial in distinguishing voyeurism, fetishism, and exhibitionism within sexual expression. Voyeurism involves gaining sexual pleasure from observing others without their consent, violating personal boundaries and legal ethics. Fetishism respects consent by focusing on specific objects or body parts, emphasizing mutual agreement, while exhibitionism requires consensual exposure to others, balancing desire with respect for personal and social limits.
Treatment and Support Options for Healthy Sexuality
Treatment for voyeurism and fetishism involves tailored therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychodynamic therapy to address underlying psychological factors and promote healthy sexual expression. Support options include specialized counseling, group therapy, and possibly medication management for compulsive behaviors, aiming to reduce distress and prevent harmful actions. Emphasizing education on consent, boundaries, and sexual health is crucial in fostering healthy sexuality and ensuring respectful relationships.
Infographic: Voyeurism vs Fetish
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com