Celibacy is a conscious choice to abstain from sexual activity, often for religious or personal reasons, while virginity refers to the state of never having engaged in sexual intercourse. Explore the nuanced differences and cultural implications of celibacy versus virginity in this article.
Table of Comparison
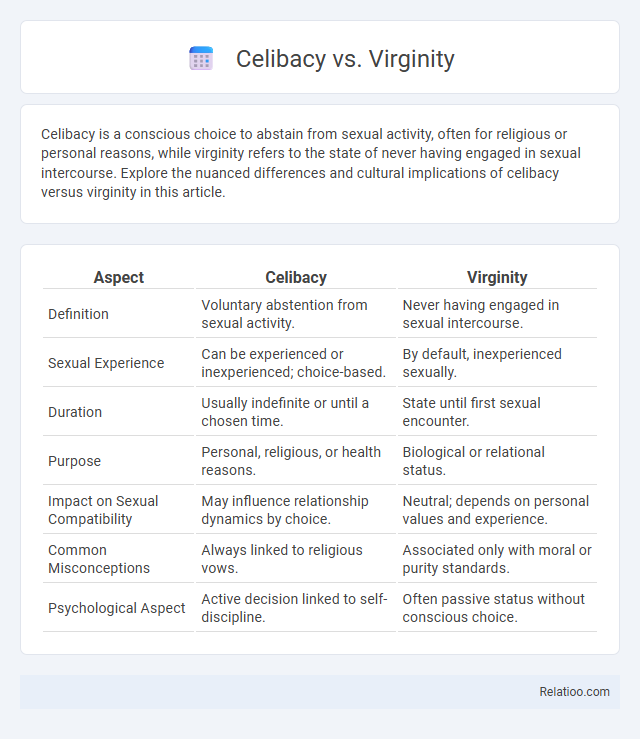
| Aspect | Celibacy | Virginity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary abstention from sexual activity. | Never having engaged in sexual intercourse. |
| Sexual Experience | Can be experienced or inexperienced; choice-based. | By default, inexperienced sexually. |
| Duration | Usually indefinite or until a chosen time. | State until first sexual encounter. |
| Purpose | Personal, religious, or health reasons. | Biological or relational status. |
| Impact on Sexual Compatibility | May influence relationship dynamics by choice. | Neutral; depends on personal values and experience. |
| Common Misconceptions | Always linked to religious vows. | Associated only with moral or purity standards. |
| Psychological Aspect | Active decision linked to self-discipline. | Often passive status without conscious choice. |
Understanding Celibacy: Definition and Origins
Celibacy refers to the voluntary choice to abstain from marriage and sexual relations, often for religious or spiritual reasons, distinguishing it from virginity, which simply denotes someone who has not engaged in sexual intercourse. Historically, celibacy has roots in various religious traditions, such as Catholicism and Buddhism, where it symbolizes devotion, self-discipline, and spiritual purity. Understanding celibacy involves recognizing its role in personal commitment and how it functions beyond the physical state of virginity, emphasizing a lifestyle rather than a momentary condition.
What is Virginity? Key Concepts Explained
Virginity refers to the state of never having engaged in sexual intercourse, often associated with cultural, religious, or personal significance. It is distinct from celibacy, which involves a deliberate choice to abstain from sexual activity regardless of prior experience. Understanding virginity helps clarify personal boundaries and societal expectations surrounding intimacy and sexual health for your well-being.
Historical Contexts: Celibacy and Virginity Across Cultures
Celibacy and virginity have held distinct roles in various historical contexts, with celibacy often linked to religious and spiritual commitments such as those in Catholic monastic traditions and Hindu ascetic practices, emphasizing lifelong abstinence. Virginity, valued across many cultures from ancient Greece to medieval Europe, symbolized purity, social status, and eligibility for marriage, often tied to patriarchal norms and inheritance laws. Unlike celibacy, which is a chosen or imposed lifestyle, virginity primarily denotes a physical state, with its cultural significance evolving through legal, moral, and gendered frameworks over time.
Celibacy in Religious and Spiritual Traditions
Celibacy in religious and spiritual traditions often signifies a deliberate commitment to abstain from marriage and sexual activity to attain spiritual purity and devote oneself entirely to divine service. Unlike virginity, which denotes the state of never having engaged in sexual intercourse, celibacy is a chosen lifelong practice embraced by monks, nuns, priests, and ascetics in traditions such as Catholicism, Buddhism, and Hinduism. This disciplined abstinence is believed to enhance spiritual focus, self-control, and deepen the practitioner's connection with the sacred, transcending physical desires for higher spiritual goals.
Virginity in Social and Moral Perspectives
Virginity often holds significant social and moral weight, symbolizing purity and self-control within various cultures, shaping personal identity and societal expectations. Your adherence to virginity can influence social status, moral judgments, and community acceptance, particularly in traditional or religious contexts where it is linked to virtue and honor. Discussions about virginity intersect with evolving views on sexuality, autonomy, and ethical behavior, reflecting broader societal changes in morality and personal values.
Psychological Aspects of Celibacy vs Virginity
Celibacy involves a conscious decision to abstain from sexual activity, often motivated by psychological factors such as self-discipline, spiritual growth, or emotional healing, whereas virginity typically denotes the state of never having engaged in sexual intercourse without inherently implying a psychological choice. Psychological aspects of celibacy include challenges related to managing sexual desire, identity formation, and coping with societal pressures, which differ from virginity's focus on personal history rather than ongoing relational dynamics. Understanding these distinctions highlights celibacy as an active, psychologically complex process, while virginity remains a static status without intrinsic psychological implications.
Health Implications: Myths and Facts
Celibacy, virginity, and abstinence impact health differently, with various myths surrounding their effects. Celibacy, the deliberate choice to refrain from sexual activity, can promote mental clarity and reduce risks of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), but it does not inherently improve physical health. Virginity, defined as never having engaged in sexual intercourse, carries no direct health benefits or detriments; risks and health implications depend on sexual behavior following loss of virginity, debunking myths that virginity equates to purity or superior health.
Societal Expectations and Stereotypes
Societal expectations often conflate celibacy with virginity, though celibacy refers to the conscious choice to abstain from sexual activity, while virginity denotes the state of never having engaged in sex. Stereotypes around celibacy may depict individuals as morally or spiritually superior, whereas virginity is frequently associated with purity and innocence, especially in cultural and religious contexts. These differing perceptions influence social interactions and personal identity, shaping how individuals experience and express their sexual choices within various communities.
Personal Journeys: Choosing Celibacy or Virginity
Choosing celibacy or virginity reflects distinct personal journeys centered on individual values, beliefs, and goals. Virginity typically refers to the state of never having engaged in sexual intercourse, while celibacy involves a conscious decision to abstain from sexual activity for a specific period or indefinitely. Your choice between these paths can influence emotional growth, spiritual development, and self-discipline, aligning with your unique life priorities and personal empowerment.
Celibacy vs Virginity: Key Differences and Similarities
Celibacy refers to the voluntary choice to abstain from all sexual activity, often for religious or personal reasons, while virginity specifically denotes the state of never having engaged in sexual intercourse. Both concepts involve sexual abstinence but differ in scope; celibacy is an active lifestyle commitment, whereas virginity is a status that may change over time. Similarities include their ethical and cultural significance across societies, with celibacy emphasizing long-term discipline and virginity focusing on the presence or absence of sexual experience.
Infographic: Celibacy vs Virginity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com