Low self-esteem often leads to relationship insecurities and difficulties in communication, while high perfectionism can create unrealistic expectations and persistent dissatisfaction with a partner. Discover how these traits impact your connections and ways to foster healthier relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
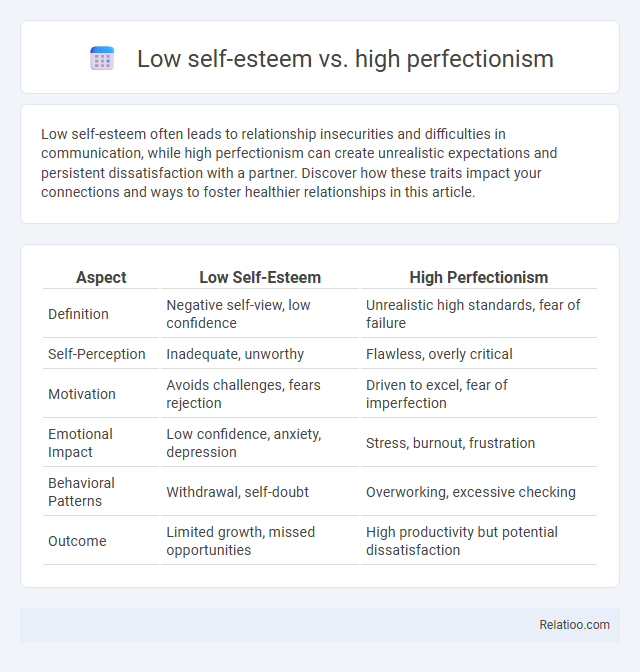
| Aspect | Low Self-Esteem | High Perfectionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Negative self-view, low confidence | Unrealistic high standards, fear of failure |
| Self-Perception | Inadequate, unworthy | Flawless, overly critical |
| Motivation | Avoids challenges, fears rejection | Driven to excel, fear of imperfection |
| Emotional Impact | Low confidence, anxiety, depression | Stress, burnout, frustration |
| Behavioral Patterns | Withdrawal, self-doubt | Overworking, excessive checking |
| Outcome | Limited growth, missed opportunities | High productivity but potential dissatisfaction |
Understanding Low Self-Esteem: Core Traits
Low self-esteem is characterized by feelings of inadequacy, self-doubt, and a pervasive sense of unworthiness that can hinder your confidence and decision-making. High perfectionism involves setting unrealistically high standards and excessive self-criticism, often leading to stress and burnout. Understanding the core traits of low self-esteem helps differentiate it from perfectionism, as the former centers on negative self-perception, whereas perfectionism emphasizes performance and achievement standards.
What is High Perfectionism? Key Characteristics
High perfectionism is characterized by an intense and often unrealistic desire to achieve flawlessness, accompanied by critical self-evaluations and fear of making mistakes. Individuals exhibiting high perfectionism set excessively high standards, experience chronic dissatisfaction with their performance, and are prone to procrastination due to fear of failure. Unlike low self-esteem, which involves negative self-worth, high perfectionism revolves around rigid standards and overemphasis on success and control.
Comparing Low Self-Esteem and High Perfectionism
Low self-esteem stems from a negative self-view and persistent feelings of inadequacy, while high perfectionism drives individuals to set unrealistic standards and exhibit excessive self-criticism. High perfectionists often link their self-worth directly to their achievements, contrasting with those suffering from low self-esteem who may struggle with confidence regardless of success. Understanding the interplay between low self-esteem and high perfectionism highlights the necessity of targeted psychological interventions to break cycles of failure and self-doubt.
Root Causes: Where Do They Begin?
Low self-esteem often stems from early negative experiences, such as criticism or neglect, leading to a diminished sense of self-worth. High perfectionism typically originates from internalized societal or parental expectations, driving individuals to set unrealistically high standards to gain approval or avoid failure. Perfectionism itself begins as a coping mechanism to control uncertainty and anxiety, but when excessive, it can reinforce feelings of inadequacy and deepen low self-esteem.
Signs You Have Low Self-Esteem vs High Perfectionism
Low self-esteem manifests through persistent self-doubt, fear of failure, and feelings of inadequacy, often resulting in avoidance of challenges and social withdrawal. High perfectionism is characterized by an intense need to meet excessively high standards, fear of making mistakes, and relentless self-criticism, leading to stress and procrastination despite competence. Unlike general perfectionism, high perfectionism specifically combines rigid rule-following with harsh self-evaluation, whereas low self-esteem primarily involves negative self-perception without the driving pursuit of flawlessness.
Emotional and Mental Health Impacts
Low self-esteem often leads to feelings of inadequacy and chronic self-doubt, which can increase vulnerability to anxiety and depression. High perfectionism intensifies emotional distress through relentless pressure for flawlessness, fostering burnout and heightened stress levels. Your emotional and mental health may suffer when perfectionism becomes rigid, impairing self-worth and hindering resilience against setbacks.
Effects on Relationships and Social Life
Low self-esteem often leads to social withdrawal and difficulty trusting others, causing strain in Your relationships due to insecurity and fear of rejection. High perfectionism can create unrealistic expectations, resulting in conflicts and dissatisfaction as individuals impose strict standards on themselves and others. Perfectionism overall may hinder social interactions by fostering anxiety and fear of failure, ultimately diminishing the quality of connection and emotional intimacy in relationships.
Performance: Does Either Motivate or Hinder Success?
Low self-esteem often hinders success by fostering fear of failure and reducing confidence, which limits motivation to take on challenges. High perfectionism can both motivate success through setting rigorous standards and hinder it by causing procrastination, excessive self-criticism, and stress. Balancing healthy perfectionism with realistic goals enhances performance, while unchecked perfectionism and low self-esteem typically impair achievement and growth.
Coping Strategies and Interventions
Low self-esteem often leads to self-critical thoughts that can hinder progress, while high perfectionism drives unrealistic standards and fear of failure. Coping strategies for low self-esteem include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to reframe negative beliefs and build self-worth, whereas interventions for perfectionism focus on setting realistic goals and practicing self-compassion. Your recovery benefits from mindfulness techniques, stress management, and gradual exposure to imperfection to balance these traits effectively.
Finding a Healthy Balance for Self-Growth
Low self-esteem often leads to self-doubt and fear of failure, hindering personal growth, while high perfectionism can cause excessive self-criticism and burnout. Perfectionism itself varies from adaptive, which motivates improvement, to maladaptive, which imposes unrealistic standards. Finding a healthy balance involves setting achievable goals, embracing mistakes as learning opportunities, and fostering self-compassion to support sustainable self-growth.
Infographic: Low self-esteem vs High perfectionism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com