Hyper-independence often results in emotional isolation and challenges in building trust within relationships, while interdependence fosters mutual support and balanced connection. Explore the benefits and drawbacks of each dynamic to understand how they impact relationship health in this article.
Table of Comparison
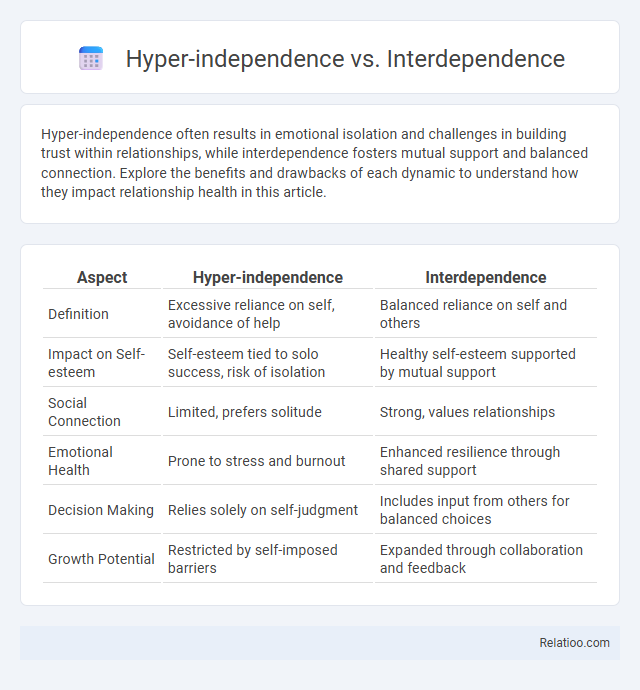
| Aspect | Hyper-independence | Interdependence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive reliance on self, avoidance of help | Balanced reliance on self and others |
| Impact on Self-esteem | Self-esteem tied to solo success, risk of isolation | Healthy self-esteem supported by mutual support |
| Social Connection | Limited, prefers solitude | Strong, values relationships |
| Emotional Health | Prone to stress and burnout | Enhanced resilience through shared support |
| Decision Making | Relies solely on self-judgment | Includes input from others for balanced choices |
| Growth Potential | Restricted by self-imposed barriers | Expanded through collaboration and feedback |
Understanding Hyper-Independence: Definition and Origins
Hyper-independence is characterized by excessive self-reliance and a reluctance to seek help, often stemming from early life experiences of neglect or trauma that foster a deep sense of vulnerability. This coping mechanism, rooted in psychological defense, contrasts with healthy interdependence, where individuals balance autonomy with mutual support and collaboration. Understanding the origins of hyper-independence is crucial for addressing the underlying emotional needs and promoting more adaptive relational patterns.
Defining Interdependence: A Collaborative Approach
Interdependence emphasizes a collaborative approach where individuals rely on each other's strengths to achieve common goals, fostering mutual support and shared responsibility. Unlike hyper-independence, which prioritizes extreme self-reliance, and dependence, where one may overly rely on others, interdependence balances autonomy with connection, promoting effective teamwork and personal growth. Your ability to embrace interdependence enhances communication and synergy, leading to more sustainable and successful outcomes.
Psychological Drivers Behind Hyper-Independence
Psychological drivers behind hyper-independence often stem from deep-seated fears of vulnerability, past trauma, or a strong desire for control, prompting individuals to avoid reliance on others at all costs. This extreme self-reliance contrasts with interdependence, where mutual support and collaboration foster balanced relationships and personal growth. Understanding the roots of hyper-independence aids in addressing isolation and promoting healthier emotional connections.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Hyper-Independence
Hyper-independence offers benefits such as increased self-reliance, enhanced problem-solving skills, and a strong sense of personal control, allowing you to navigate challenges autonomously. However, it can lead to drawbacks including social isolation, difficulty accepting help, and increased stress from handling all responsibilities alone. Balancing hyper-independence with interdependence fosters healthy connections and shared support, optimizing overall well-being and productivity.
The Strengths and Limitations of Interdependence
Interdependence fosters collaboration and promotes diverse perspectives, enhancing problem-solving and innovation within teams. Your ability to rely on others builds trust and shared accountability, which can lead to more sustainable outcomes in complex environments. However, interdependence may sometimes slow decision-making and reduce individual autonomy, highlighting the need to balance cooperative efforts with personal initiative.
Social and Cultural Influences on Independence Styles
Social and cultural influences shape your independence style by determining whether you lean toward hyper-independence, interdependence, or balanced independence. Collectivist cultures often emphasize interdependence, encouraging cooperation and social harmony, while individualist cultures tend to promote hyper-independence, valuing self-reliance and autonomy. Understanding these cultural frameworks helps recognize how social norms and upbringing impact your approach to relationships and personal responsibility.
Hyper-Independence in Relationships: Challenges and Solutions
Hyper-independence in relationships often leads to emotional distance and a lack of vulnerability, making it difficult for partners to build trust and intimacy. This mindset prioritizes self-reliance at the expense of mutual support, which can create barriers to effective communication and conflict resolution. To overcome hyper-independence, you can cultivate interdependence by fostering open dialogue, setting healthy boundaries, and embracing collaboration to strengthen connection and balance autonomy with shared responsibility.
Interdependence and Healthy Boundaries
Interdependence fosters mutual support and collaboration, allowing you to maintain healthy boundaries while relying on others without losing your sense of autonomy. Unlike hyper-independence, which often leads to isolation and burnout, interdependence balances self-sufficiency with meaningful connections. Embracing interdependence enhances emotional resilience and promotes well-being through respectful boundaries that protect your individuality and relationships.
Finding Balance: Moving from Hyper-Independence to Interdependence
Finding balance between hyper-independence and interdependence requires recognizing the drawbacks of extreme self-reliance, such as isolation and burnout, while embracing the strengths of collaborative support networks that enhance problem-solving and emotional resilience. Transitioning involves developing trust, open communication, and mutual accountability, enabling individuals to maintain autonomy yet rely on others for complementary skills and perspectives. Sustainable success and well-being emerge from cultivating interdependent relationships that respect personal boundaries and foster collective growth.
Strategies for Cultivating Healthy Interdependence
Cultivating healthy interdependence involves balancing autonomy and collaboration, fostering open communication, and setting clear boundaries to respect individual needs while encouraging mutual support. Strategies include practicing active listening, building trust through consistent reliability, and encouraging shared decision-making to enhance cooperation and collective problem-solving. Emphasizing empathy and recognizing the value of diverse perspectives strengthens relationships and promotes a sustainable dynamic that avoids the extremes of hyper-independence or overdependence.
Infographic: Hyper-independence vs Interdependence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com