Peacemaker personalities prioritize harmony through empathy and emotional connection, while Diplomats emphasize strategic communication and conflict resolution skills. Discover the key distinctions and how each role shapes relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
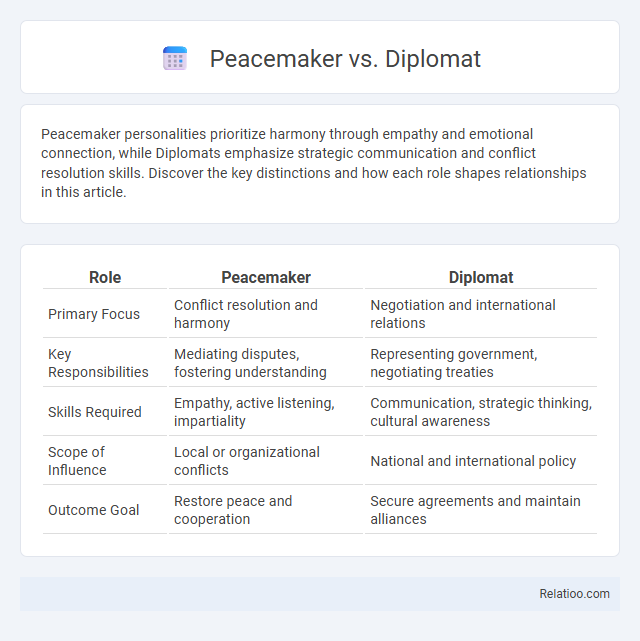
| Role | Peacemaker | Diplomat |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Conflict resolution and harmony | Negotiation and international relations |
| Key Responsibilities | Mediating disputes, fostering understanding | Representing government, negotiating treaties |
| Skills Required | Empathy, active listening, impartiality | Communication, strategic thinking, cultural awareness |
| Scope of Influence | Local or organizational conflicts | National and international policy |
| Outcome Goal | Restore peace and cooperation | Secure agreements and maintain alliances |
Peacemaker vs Diplomat: Key Definitions
A Peacemaker is defined by their ability to mediate conflicts and foster harmony through empathy and compromise, prioritizing emotional balance in relationships. A Diplomat, on the other hand, specializes in strategic negotiation and communication to resolve disputes, often representing organizational or political interests with tact and professionalism. Understanding Peacemaker vs Diplomat highlights contrasting approaches: emotional reconciliation versus strategic negotiation, each essential in conflict resolution dynamics.
Core Qualities of a Peacemaker
Peacemakers excel in creating harmony by actively listening and mediating conflicts with empathy and patience, fostering mutual understanding. Their core qualities include a deep commitment to unity, calmness in tense situations, and an ability to remain impartial while encouraging collaboration. By embodying these traits, your interactions can become more peaceful and constructive, promoting lasting reconciliation in personal and professional environments.
Essential Traits of a Diplomat
A diplomat exhibits essential traits such as exceptional communication skills, cultural sensitivity, and the ability to negotiate effectively under pressure. Unlike the peacemaker, who primarily focuses on resolving conflicts through harmony and compromise, the diplomat strategically balances multiple interests while maintaining international relations. Mastery in tact, discretion, and adaptability defines the diplomat's role in achieving long-term cooperation and peace.
Historical Roles: Peacemakers and Diplomats in Action
Peacemakers and diplomats have historically shaped conflict resolution through distinct but complementary roles; peacemakers often engage directly in mediating armed conflicts or brokering peace treaties, while diplomats focus on maintaining ongoing state relations and negotiating agreements to prevent escalation. Key historical examples include the Congress of Vienna, where diplomats established a balance of power after the Napoleonic Wars, and the Camp David Accords, where peacemakers facilitated direct negotiation between conflicting leaders. Their combined efforts have proven essential in transforming hostilities into sustained peace.
Tools and Tactics: Methods of Conflict Resolution
Peacemakers use empathy and active listening as core tools, fostering understanding by addressing emotional undercurrents to defuse tensions. Diplomats employ negotiation, strategic compromises, and formal dialogue, leveraging institutional frameworks and cultural sensitivity to mediate complex conflicts. Both approaches emphasize communication, but peacemakers prioritize relational harmony, while diplomats focus on policy-driven solutions and maintaining long-term alliances.
Communication Styles: Peacemakers vs Diplomats
Peacemakers communicate with warmth and empathy, prioritizing harmony and avoiding conflict to maintain peaceful relationships. Diplomats use tact and persuasion, skillfully navigating differing opinions to reach mutually beneficial agreements while maintaining respect. Both prioritize cooperation, but Peacemakers lean toward emotional connection, whereas Diplomats emphasize strategic dialogue and negotiation.
Decision-Making Approaches Compared
Peacemakers prioritize harmony and avoid conflict by seeking consensus and maintaining emotional balance, which can sometimes delay decision-making. Diplomats emphasize negotiation and compromise, actively gathering diverse perspectives to reach mutually beneficial solutions with strategic communication. Peacemakers rely more on intuition and emotional understanding, diplomats use logical analysis combined with interpersonal skills, and peacemakers focus on patience and empathy to guide effective decision-making processes.
Challenges Faced by Peacemakers and Diplomats
Peacemakers often face challenges including deep-rooted mistrust between conflicting parties and emotional burnout from continuous mediation efforts. Diplomats encounter obstacles such as navigating complex political landscapes, balancing national interests, and managing international protocols. Both roles require exceptional communication skills and resilience to effectively address misunderstandings and foster long-term peace agreements.
Impact on International Relations
The Peacemaker approach prioritizes conflict resolution and fostering trust, significantly reducing tensions between nations and promoting long-term stability. The Diplomat strategy leverages negotiation and strategic communication to build alliances and enhance cooperation, which strengthens international partnerships and economic ties. Your choice between these roles influences global peace dynamics, where Peacemakers emphasize reconciliation and Diplomats focus on pragmatic alliance-building to impact international relations effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach: Peacemaking or Diplomacy?
Choosing the right approach between peacemaking and diplomacy depends on the context and desired outcomes; peacemaking directly addresses conflict resolution by engaging conflicting parties in dialogue and negotiation, aiming to restore peace swiftly. Diplomacy, however, involves a broader strategy of managing international relations and preventing conflicts through dialogue, alliances, and long-term policies. Understanding when to prioritize immediate conflict resolution (peacemaker) or structured negotiation and relationship building (diplomat) is crucial for effective conflict management and sustainable peace.
Infographic: Peacemaker vs Diplomat
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com