A financier provides capital to support business growth, often taking equity or a stake, while a lender offers loans that must be repaid with interest. Discover the key differences and implications of choosing a financier versus a lender in this article.
Table of Comparison
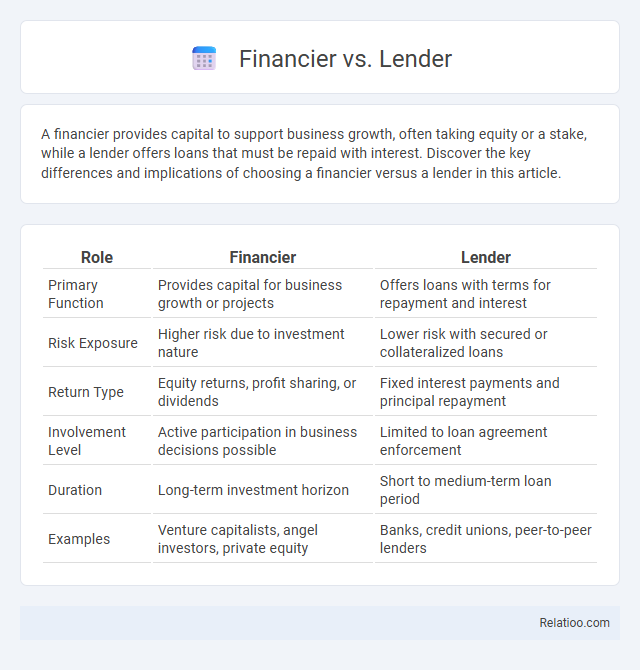
| Role | Financier | Lender |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides capital for business growth or projects | Offers loans with terms for repayment and interest |
| Risk Exposure | Higher risk due to investment nature | Lower risk with secured or collateralized loans |
| Return Type | Equity returns, profit sharing, or dividends | Fixed interest payments and principal repayment |
| Involvement Level | Active participation in business decisions possible | Limited to loan agreement enforcement |
| Duration | Long-term investment horizon | Short to medium-term loan period |
| Examples | Venture capitalists, angel investors, private equity | Banks, credit unions, peer-to-peer lenders |
Understanding the Basics: Financier vs Lender
Understanding the basics of financier vs lender involves recognizing that a financier typically provides large-scale funding tailored to complex financial needs, often with a focus on investment and long-term growth. A lender primarily offers loans with defined repayment terms, such as banks or credit institutions extending credit to individuals or businesses. Your choice between a financier and lender should be guided by the scale and purpose of your financial requirements.
Definition of a Financier
A financier is an individual or entity that provides capital or funding for business ventures, investments, or projects, often specializing in large-scale or complex financial transactions. Unlike lenders who primarily grant loans expecting repayment with interest, financiers may take equity stakes or engage in diverse financing arrangements to support growth. Your understanding of financiers helps distinguish their strategic role in managing risk and capital in financial markets.
Definition of a Lender
A lender is a financial institution or individual that provides funds to a borrower with the expectation of repayment, usually with interest, over a specified period. Unlike financiers, who may invest capital through equity or complex financial instruments, lenders primarily focus on debt-based transactions and formal loan agreements. The role of a lender is fundamental in credit markets, offering structured loans, mortgages, or personal advances that support liquidity and capital access for businesses and consumers.
Key Differences Between Financiers and Lenders
Financiers provide capital through various investment vehicles, including equity and debt, often taking on higher risk for potential returns, while lenders specifically offer loans with fixed terms and interest rates, focusing on debt repayment. Your choice between a financier and lender depends on your need for flexible funding versus structured borrowing with clear repayment schedules. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize financial strategies for business growth or personal funding.
Roles and Responsibilities: Financier vs Lender
A financier provides capital by investing in projects or businesses, often taking on higher risk and sometimes influencing management decisions, while a lender extends credit by offering loans that must be repaid with interest under specific terms and conditions. Financiers typically engage in equity financing or venture capital, focusing on long-term growth and returns, whereas lenders prioritize creditworthiness and repayment schedules to safeguard principal and interest. Both roles involve assessing financial risk, but financiers are more actively involved in business development, whereas lenders maintain a contractual relationship ensuring timely loan servicing.
Types of Financial Products Offered
Financiers offer a broad range of financial products such as investment funds, equity financing, and venture capital tailored to specific industries or growth stages. Lenders primarily provide debt-based products including personal loans, mortgages, credit lines, and business loans with fixed repayment schedules. Your choice between financier and lender depends on whether you seek equity-based investment or debt financing solutions for your financial needs.
Risk and Reward Profiles
Financiers typically assume higher risk by providing capital with diverse investment horizons, seeking substantial returns through equity stakes or profit sharing. Lenders offer fixed returns through interest payments, bearing lower risk due to contractual repayment terms and collateral but achieving more limited rewards. Investors face varying risk-reward profiles depending on their role, with financiers exposed to market fluctuations, lenders protected by debt instruments, and investors balancing these factors to optimize portfolio returns.
How to Choose: Financier or Lender?
Choosing between a financier and a lender depends on Your specific funding needs and repayment flexibility. Financiers often provide tailored investment solutions with equity or profit-sharing options, while lenders offer structured loans with fixed repayments and interest rates. Assess Your business goals, risk tolerance, and cash flow to determine which funding source aligns best with Your financial strategy.
Common Scenarios: When to Use Each
Lenders are typically used for straightforward borrowing needs such as mortgages, personal loans, or business loans where fixed repayment terms are established upfront. Financiers often come into play for complex financial arrangements including venture capital, private equity, or mezzanine financing, where investment strategies and risk-sharing are tailored to the project. Choosing between a lender or financier depends on the borrowing purpose, required flexibility, and the nature of the financial relationship, with financiers suited for innovative or high-growth ventures while lenders serve more conventional credit requirements.
Future Trends in Financing and Lending
Future trends in financing and lending emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology to enhance transaction transparency and efficiency. Financiers are evolving from traditional credit providers to strategic partners offering tailored financial solutions through digital platforms. Lenders are adopting more sophisticated risk assessment models powered by big data analytics, enabling faster loan approvals and personalized interest rates.
Infographic: Financier vs Lender
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com