A vow is a solemn promise made willingly, often in personal or religious contexts, while an oath is a formal, legally binding declaration typically sworn before witnesses. Discover the key distinctions between vows and oaths in this article.
Table of Comparison
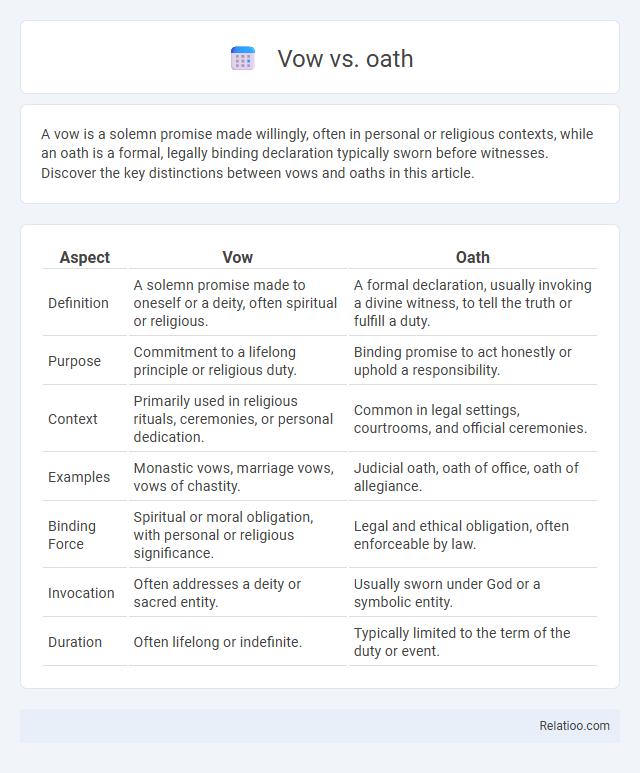
| Aspect | Vow | Oath |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A solemn promise made to oneself or a deity, often spiritual or religious. | A formal declaration, usually invoking a divine witness, to tell the truth or fulfill a duty. |
| Purpose | Commitment to a lifelong principle or religious duty. | Binding promise to act honestly or uphold a responsibility. |
| Context | Primarily used in religious rituals, ceremonies, or personal dedication. | Common in legal settings, courtrooms, and official ceremonies. |
| Examples | Monastic vows, marriage vows, vows of chastity. | Judicial oath, oath of office, oath of allegiance. |
| Binding Force | Spiritual or moral obligation, with personal or religious significance. | Legal and ethical obligation, often enforceable by law. |
| Invocation | Often addresses a deity or sacred entity. | Usually sworn under God or a symbolic entity. |
| Duration | Often lifelong or indefinite. | Typically limited to the term of the duty or event. |
Understanding the Difference: Vow vs Oath
A vow is a solemn promise often made to oneself or a higher power, emphasizing personal commitment, while an oath is a formal pledge typically sworn before an authority, carrying legal or official significance. Understanding the difference between a vow vs oath helps you recognize that vows are deeply personal and spiritual, whereas oaths involve public accountability and enforceable obligations. Both forms of commitment underscore trust and integrity, but your choice depends on the context and level of formality required.
Defining a Vow: Meaning and Contexts
A vow is a solemn promise or commitment made voluntarily, often within religious, legal, or personal contexts, signifying dedication or allegiance to a cause or individual. Unlike an oath, which typically involves invoking a divine witness to guarantee truth or loyalty, a vow centers on a personal pledge that binds the individual morally or spiritually. Vows are integral to ceremonies such as weddings, religious ordinations, and ethical commitments, reflecting deep intention and enduring responsibility.
What is an Oath? Legal and Social Perspectives
An oath is a solemn promise often invoking a divine witness, used to affirm truthfulness or commitment in legal and social contexts. In courts, an oath ensures that testimony is given honestly under penalty of perjury, while socially, it binds individuals to uphold ethical or moral standards. Your understanding of an oath highlights its critical role in establishing trust and accountability across various societal frameworks.
Historical Origins of Vows and Oaths
Vows and oaths both originate from ancient rituals where solemn promises were made to deities or authorities to ensure trustworthiness and accountability. Historically, vows were often linked to religious or spiritual commitments, while oaths served as formal declarations in legal and societal contexts. The use of vows and oaths can be traced back to civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Ancient Greece, and Rome, where they played crucial roles in governance, marriage, and religious ceremonies.
Vows in Religious and Spiritual Traditions
Vows in religious and spiritual traditions serve as solemn promises that bind individuals to specific moral or spiritual commitments, often made before a higher power or community. Your vow may involve lifelong devotion, such as monastic vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience, which are essential for spiritual discipline and religious identity. These sacred promises reinforce faith, guide ethical conduct, and strengthen communal bonds within various spiritual practices worldwide.
Oaths in Legal and Governmental Settings
Oaths in legal and governmental settings serve as formal promises to uphold truth, duties, or allegiance, often required before assuming public office or testifying in court. These oaths carry legal weight and consequences, ensuring accountability and integrity in official actions. Your commitment through an oath legally binds you to honesty and ethical conduct within governmental and judicial processes.
Key Elements: What Sets a Vow Apart from an Oath
A vow is a solemn promise made voluntarily, often with a spiritual or personal commitment, while an oath is a formal declaration typically invoking a higher authority or legal obligation. The key elements that set a vow apart from an oath include the personal and internal nature of vows, which are rooted in individual intent and moral conviction, whereas oaths are externally enforced and often linked to legal or public accountability. Vows emphasize enduring, heartfelt dedication, contrasting with oaths' focus on binding someone to truthfulness or duty under penalty.
Common Examples of Vows and Oaths
Common examples of vows include wedding vows, where individuals promise lifelong commitment and fidelity, and religious vows taken by monks or nuns to live a life of poverty, chastity, and obedience. Oaths often appear in legal or official contexts, such as courtroom testimonies where witnesses swear to tell the truth, or public officials taking an oath of office to uphold the constitution and perform their duties faithfully. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize the solemn commitments involved in both vows and oaths across personal, religious, and legal settings.
Cultural Significance of Vows and Oaths
Vows and oaths hold profound cultural significance, often symbolizing deep personal commitment and social trust across various societies. Vows frequently appear in religious or matrimonial contexts, representing sacred promises that bind individuals spiritually and communally. Oaths, meanwhile, carry a legal or formal weight, used in ceremonies or official settings to uphold truth, loyalty, and ethical duty.
Choosing Between a Vow and an Oath: When and Why
Choosing between a vow and an oath depends on context and intention; a vow is a solemn promise often made to oneself or a higher power, reflecting personal commitment, while an oath is a formal pledge usually taken publicly, asserting truthfulness or duty. In legal or official scenarios, an oath carries binding authority and is enforceable, whereas vows are more common in religious, spiritual, or personal settings emphasizing moral or emotional dedication. Understanding the distinction is crucial for selecting the appropriate form of commitment based on the desired level of formality, accountability, and purpose.
Infographic: Vow vs Oath
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com