A proposal is the initial offer of marriage, often a formal or informal ask for consent, while Nikah is the Islamic marriage contract that legally and spiritually binds the couple. Discover the key differences and cultural significance of Proposal vs Nikah in this article.
Table of Comparison
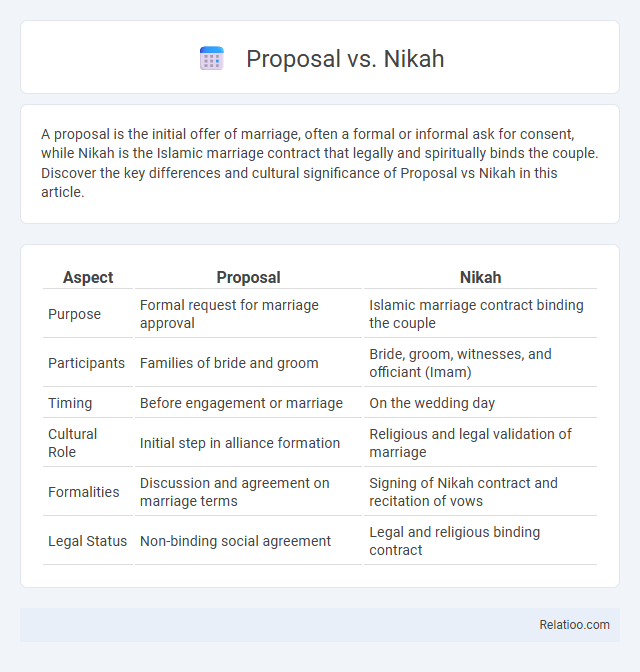
| Aspect | Proposal | Nikah |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Formal request for marriage approval | Islamic marriage contract binding the couple |
| Participants | Families of bride and groom | Bride, groom, witnesses, and officiant (Imam) |
| Timing | Before engagement or marriage | On the wedding day |
| Cultural Role | Initial step in alliance formation | Religious and legal validation of marriage |
| Formalities | Discussion and agreement on marriage terms | Signing of Nikah contract and recitation of vows |
| Legal Status | Non-binding social agreement | Legal and religious binding contract |
Understanding Proposal and Nikah: Key Definitions
A proposal in the context of marriage is an initial offer or request made by one person to another to establish a matrimonial bond, often involving the expression of intention and seeking consent. Nikah is the Islamic legal contract of marriage that outlines the rights and responsibilities of both parties and is recognized by religious and civil authorities. Understanding these concepts is crucial, as a proposal initiates the marriage process, while Nikah formalizes and legitimizes the union according to Islamic law.
Cultural Significance of Proposals in Marriage
The cultural significance of proposals in marriage varies widely, deeply rooted in traditions and societal norms that shape the way relationships are formalized. Your proposal often symbolizes a commitment that extends beyond personal intentions, embodying family values, community recognition, and ritualistic practices unique to each culture. Understanding these nuances in proposals, whether before Nikah or other ceremonies, highlights their role in honoring heritage and solidifying marital bonds.
Nikah: The Islamic Marriage Contract Explained
Nikah is the formal Islamic marriage contract that legally binds a couple in accordance with Sharia law, outlining the rights and responsibilities of both spouses. Unlike a simple marriage proposal, Nikah involves specific rituals such as the offer (Ijab) and acceptance (Qabul), as well as the payment of a mandatory dowry (Mahr) to the bride. This contract ensures mutual consent, legal protection, and religious validation, distinguishing it from informal proposals or engagement discussions.
Differences Between Proposal and Nikah
A proposal is the initial step where one person expresses their intention to marry, often involving family discussions and seeking consent, while Nikah is the formal Islamic marriage contract that legally and religiously binds the couple. The proposal focuses on agreement and readiness, whereas Nikah involves the actual religious ceremony with witnesses, a marriage gift (Mahr), and official registration. Understanding the differences between proposal and Nikah helps you navigate cultural and legal aspects to ensure your marriage process aligns with religious and societal expectations.
The Role of Family in Proposals and Nikah
The role of family in proposals and Nikah is deeply ingrained in many cultures, where families actively participate in arranging and approving matrimonial matches to ensure compatibility and social harmony. During the proposal phase, families often negotiate dowry, cultural customs, and religious considerations, reinforcing their influence on the union's terms and acceptance. In the Nikah ceremony, family presence solidifies the marriage contract, with elders witnessing and blessing the union, thus endorsing the familial and social bonds formed through marriage.
Legal Implications of Proposal vs Nikah
A marriage proposal holds no legal status and serves only as an expression of intent to wed, whereas Nikah is a legally binding contract in Islamic law that formalizes the marriage with specific rights and obligations. Nikah requires witnesses, a marriage guardian, and a defined Mahr (dowry), making it enforceable in religious and civil courts in many Islamic jurisdictions. Failure to comply with Nikah's legal elements can render the marriage invalid and affect spousal rights related to inheritance, custody, and maintenance.
Religious Requirements in Nikah Ceremony
Nikah ceremonies in Islam require strict adherence to religious mandates, including the presence of two adult Muslim witnesses, the offer and acceptance (Ijab and Qabul) by both parties, and the payment of mahr (mandatory dowry) by the groom to the bride. Unlike a casual proposal or engagement, the Nikah is a formal contract that must be conducted in accordance with Sharia law to be considered valid. This religious framework ensures that the union is recognized not only legally but also spiritually within the Muslim community.
Steps Involved from Proposal to Nikah
The process from proposal to Nikah involves several key steps starting with the formal proposal where families discuss compatibility and intentions, followed by the engagement phase often marked by the exchange of rings and setting a wedding date. Pre-Nikah requirements include obtaining a marriage license, completing a Nikah Nama (marriage contract), and arranging witnesses for the ceremony. Your participation in these stages ensures a smooth transition to the Nikah ceremony, where vows are exchanged under Islamic law, formalizing the marriage contract in a spiritual and legal context.
Common Misconceptions about Proposal and Nikah
Common misconceptions about Proposal and Nikah often blur the distinct purposes these events serve in Islamic tradition. A proposal is typically seen as a preliminary step where intentions and compatibility are discussed, while Nikah is the formal, religious marriage contract that legally binds the couple under Islamic law. Understanding these differences clarifies your role and expectations, ensuring respect for both cultural practices and religious obligations.
Proposal and Nikah: Modern Trends and Practices
Proposal and Nikah represent distinct stages in Islamic marriage traditions, with the proposal marking the formal intent to marry and Nikah signifying the legally binding marital contract. Modern trends show an increasing emphasis on mutual consent and compatibility during the proposal phase, often involving personal discussions and premarital counseling. Contemporary Nikah practices integrate traditional rituals with simplified ceremonies, reflecting evolving cultural norms while maintaining religious significance.
Infographic: Proposal vs Nikah
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com