Prayer fosters a personal dialogue with a higher power, while mantra repetition centers the mind through rhythmic sound vibrations. Discover how these spiritual practices uniquely impact mental well-being and emotional balance in this article.
Table of Comparison
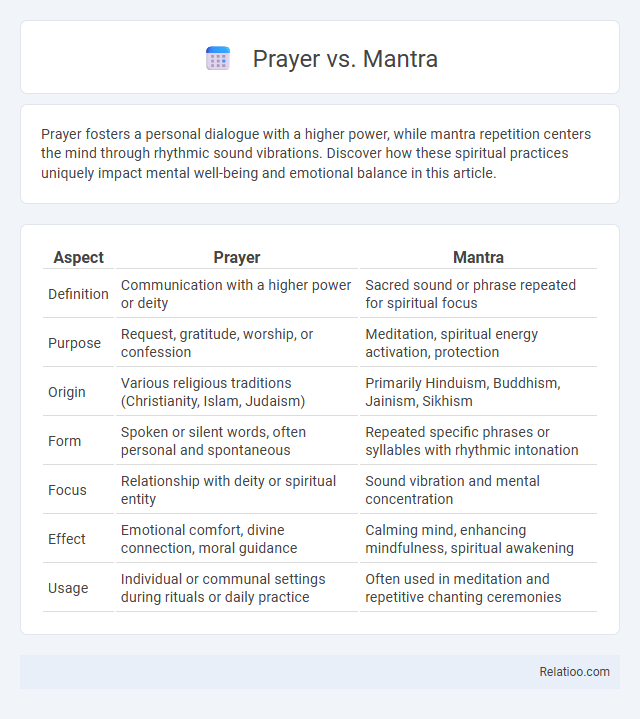
| Aspect | Prayer | Mantra |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication with a higher power or deity | Sacred sound or phrase repeated for spiritual focus |
| Purpose | Request, gratitude, worship, or confession | Meditation, spiritual energy activation, protection |
| Origin | Various religious traditions (Christianity, Islam, Judaism) | Primarily Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism |
| Form | Spoken or silent words, often personal and spontaneous | Repeated specific phrases or syllables with rhythmic intonation |
| Focus | Relationship with deity or spiritual entity | Sound vibration and mental concentration |
| Effect | Emotional comfort, divine connection, moral guidance | Calming mind, enhancing mindfulness, spiritual awakening |
| Usage | Individual or communal settings during rituals or daily practice | Often used in meditation and repetitive chanting ceremonies |
Understanding Prayer: Definitions and Origins
Prayer involves direct communication with a deity or higher power, often expressed through praise, requests, or confession, rooted in religious traditions globally. Mantras are sacred sound vibrations or phrases repeated to focus the mind, originating mainly from Hindu and Buddhist practices. Your understanding deepens by recognizing prayer's diverse forms and historical origins across cultures, highlighting its personal and communal significance.
What is a Mantra? Historical Background
A mantra is a sacred sound, word, or phrase repeated during meditation or spiritual practice to focus the mind and invoke divine energy. Originating in ancient Indian Vedic traditions, mantras were first documented in the Rigveda around 1500 BCE and have been integral to Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism rituals. Unlike general prayer, which involves direct communication with a deity, mantras emphasize vibrational resonance and mental repetition to achieve spiritual awakening and inner peace.
Key Differences Between Prayer and Mantra
Prayer involves communicating directly with a deity or higher power, often expressing gratitude, requests, or devotion, while a mantra consists of repetitive sounds, words, or phrases chanted to aid concentration and spiritual growth. You engage in prayer to foster a personal relationship with the divine, whereas mantras function as tools to focus the mind and invoke spiritual energy without necessarily addressing a deity. Understanding these key differences enhances your spiritual practice by aligning your intentions with the appropriate method for meditation or worship.
Spiritual Purposes: Prayer vs Mantra
Prayer and mantra serve distinct spiritual purposes, with prayer typically involving a direct communication or petition to a deity, fostering a personal relationship and seeking guidance, blessings, or forgiveness. Mantras are sacred sounds or phrases repeated to induce a meditative state, enhance concentration, and connect with universal consciousness, often focusing on inner transformation and spiritual awakening. While prayer emphasizes expression and devotion, mantras prioritize vibrational energy and mental discipline for spiritual growth.
Techniques of Practice: Methods and Rituals
Prayer techniques often involve vocalizing or mentally reciting sacred words or phrases, usually accompanied by specific gestures such as folding hands or bowing, performed in designated sacred spaces. Mantra practice centers on repetitive chanting or silent repetition of particular sounds or phrases, frequently using a mala (prayer beads) to count repetitions and induce meditative focus. Rituals in prayer may include lighting candles, burning incense, or offering symbolic items, while mantra rituals emphasize breath control, rhythmic chanting, and mental visualization to deepen spiritual connection.
Psychological Effects: Prayer and Mantra in Mindfulness
Prayer and mantra both offer significant psychological benefits in mindfulness practice by promoting relaxation and reducing stress, yet they differ in focus; prayer often involves communicating with a higher power, fostering a sense of hope and emotional support, while mantra repetition centers attention and cultivates mental clarity. Your mind experiences enhanced concentration and emotional stability during mantra meditation, as the rhythmic chanting induces calmness and diminishes negative thoughts. Research indicates that both methods can increase positive neuroplasticity, improving overall mental resilience and well-being.
Prayer in Major World Religions
Prayer in major world religions serves as a vital form of communication with the divine, often involving spoken words, silent thoughts, or ritualistic practices tailored to specific beliefs. In Christianity, prayer typically includes praise, confession, thanksgiving, and supplication directed to God, while Islam emphasizes Salah, a structured set of prayers performed five times daily facing Mecca. Your spiritual practice can deepen understanding by distinguishing prayer's personal and communal aspects from the repetitive chants of mantras and affirmations.
The Role of Mantras in Eastern Spirituality
Mantras play a central role in Eastern spirituality by serving as powerful tools for meditation, concentration, and spiritual awakening. Unlike general prayers that often involve requests or expressions of faith, mantras are repetitive sacred sounds or phrases believed to carry vibrational energy that aligns the mind with higher states of consciousness. Their consistent use in traditions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism helps practitioners cultivate inner peace, focus, and connection with the divine through auditory and vibrational resonance.
Scientific Studies on Prayer and Mantra Practices
Scientific studies on prayer and mantra practices reveal distinct neurological and psychological effects, with prayer linked to heightened emotional well-being and reduced stress through activation of brain regions associated with compassion and empathy. Mantra repetition influences brainwave patterns, promoting relaxation and improved focus by stimulating areas involved in attention and self-regulation. Understanding these effects can help you choose a practice that supports mental clarity and emotional balance based on empirical evidence.
Choosing Between Prayer and Mantra: Personal and Cultural Considerations
Choosing between prayer and mantra involves understanding personal beliefs and cultural backgrounds, as prayer typically reflects direct communication with a deity, while mantras focus on repetitive sound or phrase to influence the mind and spirit. Personal considerations include the individual's spiritual goals, whether seeking guidance, connection, or mental clarity, whereas cultural contexts shape the practices' meanings and methods, such as prayer's prominence in Abrahamic religions versus mantra's roots in Hinduism and Buddhism. Selecting the appropriate practice depends on aligning one's faith, intention, and cultural identity to enhance spiritual well-being.
Infographic: Prayer vs Mantra
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com