Oral tradition preserves cultural heritage through spoken stories passed down generations, while written tradition secures knowledge in texts for broader and longer-lasting access. Explore this article to understand how these two modes shape human relationships and cultural continuity.
Table of Comparison
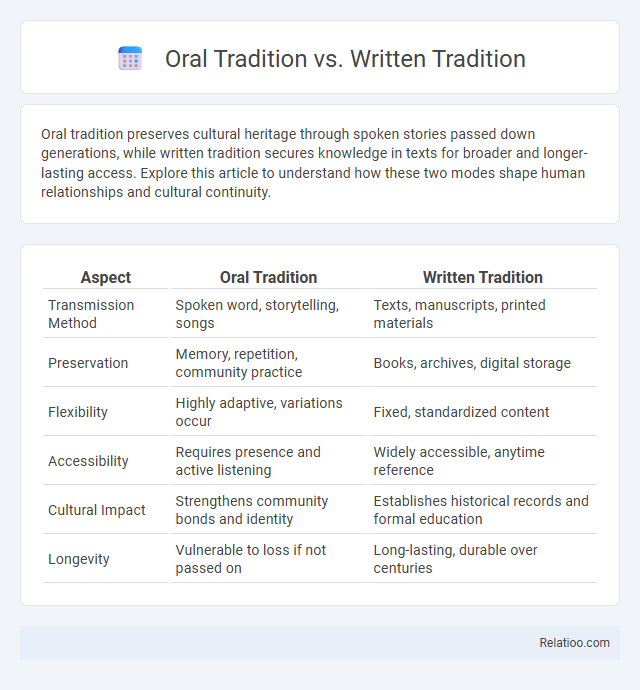
| Aspect | Oral Tradition | Written Tradition |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Method | Spoken word, storytelling, songs | Texts, manuscripts, printed materials |
| Preservation | Memory, repetition, community practice | Books, archives, digital storage |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptive, variations occur | Fixed, standardized content |
| Accessibility | Requires presence and active listening | Widely accessible, anytime reference |
| Cultural Impact | Strengthens community bonds and identity | Establishes historical records and formal education |
| Longevity | Vulnerable to loss if not passed on | Long-lasting, durable over centuries |
Introduction to Oral and Written Traditions
Oral tradition preserves cultural knowledge, history, and values through spoken word, relying on memory and communal participation. Written tradition involves recording information in texts, allowing for accurate preservation, widespread dissemination, and independent access to knowledge. Your understanding of these traditions highlights how societies transmit wisdom, with oral methods fostering communal bonds and written records ensuring longevity.
Historical Origins of Oral Tradition
Oral tradition originated as the primary method of preserving and transmitting cultural knowledge before the advent of writing systems, relying on memory, repetition, and communal participation. This mode of communication allowed ancient societies to pass down myths, laws, and historical events across generations without written records. The historical origins of oral tradition are rooted in prehistoric times, serving as a foundational framework for cultural identity and social cohesion long before written tradition emerged.
Emergence and Evolution of Written Tradition
The emergence of written tradition marked a significant evolution from oral tradition by providing a stable and permanent medium for preserving knowledge, culture, and history across generations. Unlike oral storytelling, which relies on memory and verbal transmission susceptible to variations, written traditions enable precise documentation and widespread dissemination of information. This shift facilitated the development of complex societies by supporting legal systems, literature, and educational frameworks, ultimately transforming human communication and cultural continuity.
Key Characteristics of Oral Traditions
Oral traditions rely on verbal communication to preserve and transmit cultural knowledge, emphasizing memory, repetition, and performance to engage listeners. Key characteristics include fluidity and adaptability, allowing stories to evolve with each retelling, ensuring your cultural heritage remains relevant across generations. Unlike written traditions, oral narratives often use rhyme, rhythm, and mnemonic devices to aid memorization and enhance storytelling impact.
Defining Features of Written Traditions
Written traditions are characterized by the tangible preservation of knowledge through scripts and texts, allowing for precise record-keeping and wide dissemination across time and space. Unlike oral traditions that rely on memory and verbal transmission, written traditions provide a stable, unchanging reference that can be revisited and analyzed. This form of communication facilitates complex legal systems, historical chronicles, and literary works that contribute to cultural continuity and intellectual development.
Transmission and Preservation Methods
Oral tradition relies on memory and verbal communication to transmit cultural knowledge and stories across generations, preserving the nuances of language and community values through repeated retelling. Written tradition captures information in permanent, physical forms such as manuscripts and books, ensuring long-term preservation but often losing the dynamic and performative aspects of oral narratives. Storytelling blends elements of both, using performance and creativity to engage audiences while maintaining the core content, allowing your cultural heritage to be preserved through both live interaction and recorded forms.
Accuracy and Transformation of Stories
Oral tradition relies on memorization and performance, often resulting in variations and transformations of stories over time due to human memory limitations and cultural influences. Written tradition preserves narratives with greater accuracy, providing a fixed reference that resists change but may lack the dynamic adaptability of oral accounts. Storytelling blends both methods by allowing creative interpretation during oral transmission while sometimes being documented in writing, balancing accuracy with the evolution of story elements.
Social and Cultural Impacts
Oral tradition preserves cultural identity and communal memory through spoken narratives, fostering social cohesion and intergenerational knowledge transfer. Written tradition enables the documentation and standardization of cultural values, supporting educational systems and historical record-keeping that influence societal norms. Storytelling, blending elements of both oral and written forms, acts as a dynamic medium for cultural expression and social connection, promoting empathy and shared understanding within communities.
Modern Relevance of Both Traditions
Oral tradition remains vital in preserving cultural identities and community histories, especially among indigenous and marginalized groups where literacy rates may be lower. Written tradition offers permanence and wider dissemination, enabling the archiving of knowledge, legal systems, and scientific advancements critical to modern education and governance. Storytelling bridges both forms, using digital media platforms to engage diverse audiences, enhance memory retention, and foster empathy across global communities.
Oral vs. Written Tradition: A Comparative Analysis
Oral tradition preserves cultural heritage through spoken word, emphasizing memory, performance, and community engagement, while written tradition relies on documentation, permanence, and individual interpretation. Your understanding of history and culture is shaped differently by oral narratives that evolve over time and written records that provide fixed accounts. Both forms serve crucial roles in knowledge transmission, with oral tradition fostering adaptability and written tradition ensuring accuracy and longevity.
Infographic: Oral Tradition vs Written Tradition
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com