Myths often explain the origins and fundamental truths of relationships, while legends center on heroic figures and historical events that shape relationship ideals. Discover the key differences between myths and legends and their impact on modern relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
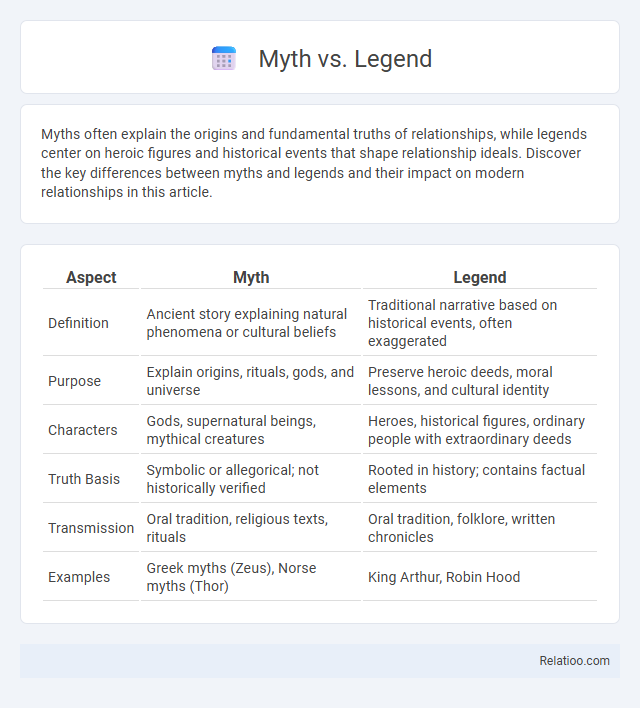
| Aspect | Myth | Legend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ancient story explaining natural phenomena or cultural beliefs | Traditional narrative based on historical events, often exaggerated |
| Purpose | Explain origins, rituals, gods, and universe | Preserve heroic deeds, moral lessons, and cultural identity |
| Characters | Gods, supernatural beings, mythical creatures | Heroes, historical figures, ordinary people with extraordinary deeds |
| Truth Basis | Symbolic or allegorical; not historically verified | Rooted in history; contains factual elements |
| Transmission | Oral tradition, religious texts, rituals | Oral tradition, folklore, written chronicles |
| Examples | Greek myths (Zeus), Norse myths (Thor) | King Arthur, Robin Hood |
Defining Myth and Legend
Myths are traditional narratives rooted in ancient cultures that explain natural phenomena, deities, and cosmic origins, often serving religious or moral purposes. Legends, by contrast, are semi-historical tales centered on human heroes or significant events, blending fact with imaginative embellishments to convey cultural values. Both myths and legends contribute to storytelling by providing frameworks that preserve heritage and shape communal identity through narrative forms.
Historical Origins of Myths and Legends
Myths and legends originate from ancient civilizations as a means to explain natural phenomena, cultural beliefs, and historical events through oral tradition and symbolic narratives. Myths often involve gods and supernatural beings, reflecting early human attempts to understand the universe, while legends typically emphasize heroic human figures grounded in historical facts enhanced by imaginative detail. Storytelling acted as a vital cultural tool in societies such as Mesopotamia, Greece, and Norse regions, preserving collective memory and shaping identity across generations.
Key Differences Between Myths and Legends
Myths are traditional narratives that explain natural phenomena, origins, or deities, often involving supernatural beings and sacred truths, while legends are rooted in historical events or figures but embellished over time to emphasize moral lessons or cultural values. Your understanding of storytelling improves by recognizing myths as symbolic tales with universal themes, whereas legends are more grounded in specific times and places, blending fact with fiction. These key differences highlight how myths convey collective beliefs and legends preserve cultural heritage through memorable characters and episodes.
Common Themes Across Myths and Legends
Common themes across myths and legends often include heroism, moral lessons, creation, and the battle between good and evil. These narratives reflect cultural values and address existential questions, shaping your understanding of human experience and societal norms. Symbolism and archetypes like the hero's journey persist throughout, connecting stories across time and cultures.
Cultural Significance and Functions
Myths embody foundational cultural beliefs and explain natural phenomena or origins, serving as sacred narratives that reinforce societal values and collective identity. Legends often blend historical facts with embellishments, preserving cultural heritage and inspiring communal pride through heroic or moral tales. Storytelling functions as the dynamic medium through which myths and legends are transmitted, fostering social cohesion, education, and the perpetuation of cultural traditions across generations.
Famous Myths Around the World
Famous myths around the world, such as Greece's Odyssey, Norse Thor's hammer tales, and Egypt's Osiris resurrection story, shape cultural identities and convey universal truths through symbolic narratives. Myths differ from legends by intertwining gods and supernatural beings, whereas legends are grounded in historical figures or events embellished over time. Your understanding of storytelling deepens by exploring how these myths inspire literature, art, and modern media, connecting past beliefs to contemporary culture.
Notable Legends from Different Cultures
Notable legends from different cultures reveal unique values, histories, and beliefs through captivating narratives that blend historical facts with imaginative elements. Examples include King Arthur from British folklore, whose tales emphasize chivalry and heroism, and the Japanese legend of Momotaro, symbolizing bravery and camaraderie. These legends endure as cultural touchstones, offering insight into the societies that cherish them and enriching global storytelling traditions.
The Role of Heroes and Deities
Heroes in myths embody divine qualities and moral archetypes that shape cultural values, while legends often elevate historical figures through embellished narratives reflecting communal identity. Deities in mythology function as powerful agents influencing human fate and natural phenomena, reinforcing spiritual beliefs and societal norms. Storytelling weaves these elements together to transmit collective wisdom, preserve traditions, and inspire heroism across generations.
Myths and Legends in Modern Storytelling
Myths and legends form the backbone of modern storytelling, providing rich cultural narratives that shape characters and themes in contemporary media. Your understanding of these ancient tales enhances the depth and resonance of stories by connecting timeless archetypes with modern issues. The fusion of mythic symbolism and legendary heroism continues to inspire writers, filmmakers, and game designers in crafting compelling, immersive experiences.
Why Myths and Legends Endure
Myths and legends endure because they provide timeless truths and cultural values that resonate across generations, offering explanations for natural phenomena and human experiences. Your connection to these narratives taps into a collective identity, preserving heritage through memorable characters and symbolic themes. Storytelling reinforces this bond by adapting myths and legends to contemporary contexts, ensuring their relevance and emotional impact persist.
Infographic: Myth vs Legend
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com