Hugging symbolizes warmth and emotional connection, while bowing reflects respect and cultural tradition. Explore the deeper meanings and contexts of hugging versus bowing in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
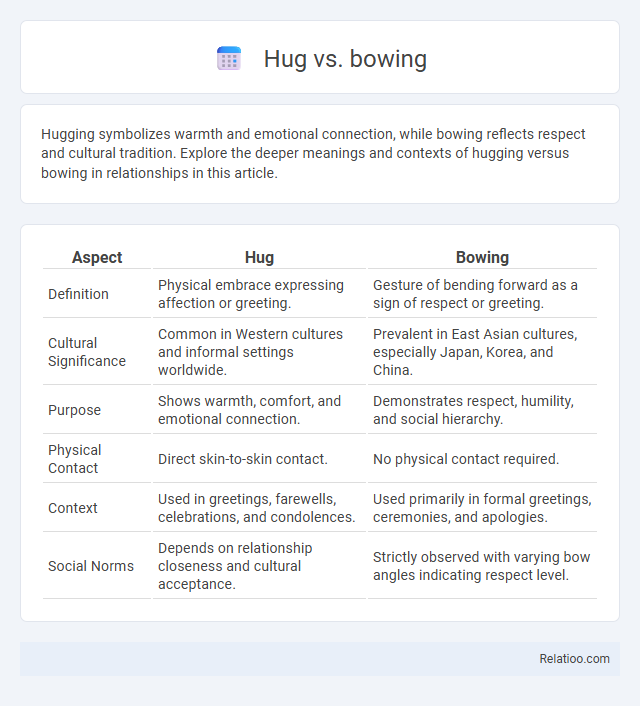
| Aspect | Hug | Bowing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical embrace expressing affection or greeting. | Gesture of bending forward as a sign of respect or greeting. |
| Cultural Significance | Common in Western cultures and informal settings worldwide. | Prevalent in East Asian cultures, especially Japan, Korea, and China. |
| Purpose | Shows warmth, comfort, and emotional connection. | Demonstrates respect, humility, and social hierarchy. |
| Physical Contact | Direct skin-to-skin contact. | No physical contact required. |
| Context | Used in greetings, farewells, celebrations, and condolences. | Used primarily in formal greetings, ceremonies, and apologies. |
| Social Norms | Depends on relationship closeness and cultural acceptance. | Strictly observed with varying bow angles indicating respect level. |
Introduction: Cultural Expressions of Greeting
Hugs, bowing, and handshakes represent distinct cultural expressions of greeting, each carrying unique social meanings and levels of intimacy. In Western societies, a hug signifies warmth and closeness, while bowing in East Asian cultures conveys respect and humility without physical contact. Your understanding of these diverse gestures enhances cross-cultural communication and demonstrates respectful awareness in social interactions.
The History of Hugging
Hugging has evolved as a universal gesture of affection and comfort, with roots dating back to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt where it signified peace and friendship. Unlike bowing, which originated in East Asian cultures as a formal show of respect and social hierarchy, hugging transcends cultural boundaries and fosters emotional connection. Understanding the history of hugging can enhance your appreciation of this intimate form of nonverbal communication and its role in human bonding.
The Origins and Significance of Bowing
Bowing originated in ancient Asian cultures, particularly in Japan, China, and Korea, as a deep-rooted gesture of respect and social hierarchy. Unlike hugging, which is primarily a physical expression of affection, bowing conveys politeness, humility, and acknowledgment without physical contact. This practice remains significant in formal ceremonies, greetings, and cultural rituals, symbolizing honor and deference.
Hug vs Bowing: Symbolism and Meaning
Hugging symbolizes warmth, affection, and emotional connection, often reflecting intimacy and support between individuals, while bowing represents respect, humility, and social hierarchy, commonly observed in East Asian cultures. Hugging involves physical closeness and conveys comfort or celebration, whereas bowing emphasizes formality and acknowledgment without physical contact. The choice between hugging and bowing depends on cultural context, social norms, and the desired expression of interpersonal relationships.
Geographic Variations in Greeting Customs
Hugging, bowing, and waving represent distinct greeting customs shaped by geographic and cultural contexts. In Western countries like the United States and parts of Europe, hugging is a common form of greeting among friends and family, signaling warmth and affection. In East Asian countries such as Japan and South Korea, bowing is a prevalent gesture that conveys respect and social hierarchy, while waving is universally used across various regions as a casual, non-contact greeting.
Social Contexts: When to Hug, When to Bow
Hugging is commonly used in Western cultures as a warm, informal greeting or farewell among friends and family, signaling affection and closeness. Bowing is a prevalent social gesture in East Asian cultures like Japan and Korea, conveying respect, gratitude, or apology, typically in formal or professional settings. Understanding the social context is crucial: hugs are appropriate in casual, personal interactions, while bows suit formal occasions or when showing deference to elders and superiors.
Psychological and Emotional Impacts
Hugging fosters a sense of security and bonding by releasing oxytocin, reducing stress and promoting emotional well-being. Bowing signifies respect and humility, often eliciting feelings of social harmony and cultural connection without physical contact. Your choice between hugging and bowing influences interpersonal dynamics, affecting emotional comfort and perceived social closeness depending on personal and cultural contexts.
Etiquette: Avoiding Greeting Faux Pas
Understanding the etiquette of hugs and bows helps you avoid common greeting faux pas in diverse cultural contexts. A bow is a respectful, non-contact greeting prevalent in East Asian cultures, while a hug is a more intimate, physical gesture suited for close relationships or informal settings. Your awareness of when to hug or bow ensures your greeting is appropriate and respectful, preventing discomfort or unintended offense.
The Influence of Globalization on Traditional Greetings
Globalization has significantly transformed traditional greetings such as hugging and bowing by blending cultural norms and promoting more universal forms of expression. Hugging, once primarily a Western gesture, is increasingly adopted worldwide due to media influence and international interactions, while bowing remains a respected tradition in East Asian cultures, adapting subtly to contemporary contexts. These shifts reflect a dynamic interplay between preserving cultural identity and embracing global social practices in personal interactions.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity in Greetings
Recognizing the cultural significance of hugging, bowing, and handshakes enhances your ability to connect respectfully across diverse societies. Each greeting conveys different levels of intimacy, respect, or formality, reflecting deep-rooted traditions and social norms. Embracing these varied forms of greetings fosters inclusivity and strengthens global relationships through mutual understanding.
Infographic: Hug vs Bowing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com