Hajj is an obligatory Islamic pilgrimage performed annually during specific dates in Dhu al-Hijjah, while Umrah is a voluntary pilgrimage that can be undertaken at any time of the year, involving fewer rituals. Discover the key differences and spiritual significance of Hajj and Umrah in this article.
Table of Comparison
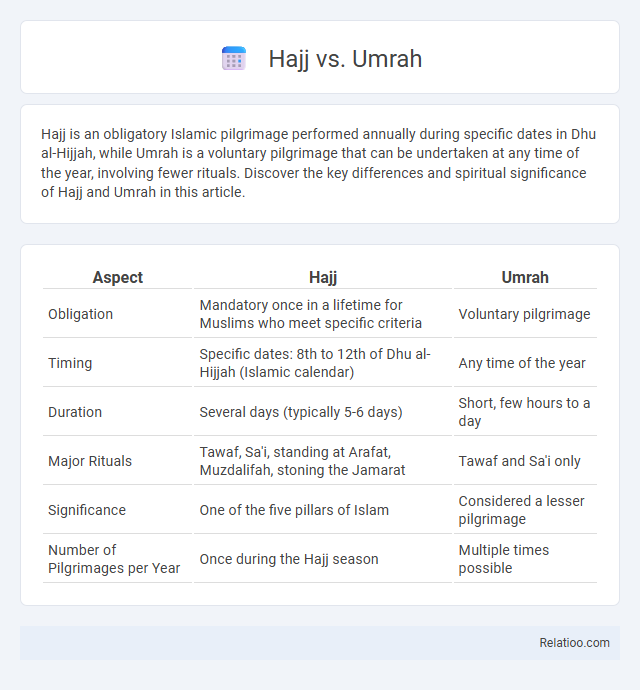
| Aspect | Hajj | Umrah |
|---|---|---|
| Obligation | Mandatory once in a lifetime for Muslims who meet specific criteria | Voluntary pilgrimage |
| Timing | Specific dates: 8th to 12th of Dhu al-Hijjah (Islamic calendar) | Any time of the year |
| Duration | Several days (typically 5-6 days) | Short, few hours to a day |
| Major Rituals | Tawaf, Sa'i, standing at Arafat, Muzdalifah, stoning the Jamarat | Tawaf and Sa'i only |
| Significance | One of the five pillars of Islam | Considered a lesser pilgrimage |
| Number of Pilgrimages per Year | Once during the Hajj season | Multiple times possible |
Introduction to Hajj and Umrah
Hajj and Umrah are two significant Islamic pilgrimages to the holy city of Mecca, each with distinct religious importance and rituals. Hajj, obligatory once in a lifetime for physically and financially able Muslims, occurs annually during the lunar month of Dhu al-Hijjah, involving specific rites such as Tawaf and Sa'i performed over several days. Umrah, considered a lesser pilgrimage, can be undertaken at any time of the year, allowing you to experience spiritual cleansing through shorter, flexible rituals similar to those in Hajj but without the same obligatory status.
Key Differences Between Hajj and Umrah
Hajj, an obligatory Islamic pilgrimage performed annually during specific dates in the month of Dhu al-Hijjah, consists of a series of prescribed rituals including Tawaf, Sa'i, and standing at Arafat, making it a mandatory act of worship for all able Muslims once in their lifetime. Umrah, often called the "lesser pilgrimage," can be undertaken at any time of the year and involves fewer rites--primarily Tawaf and Sa'i--without the standing at Arafat or the requirement to perform it once in a lifetime. In contrast, pilgrimage is a broader term that can refer to any journey to a sacred place, but within Islamic context, Hajj and Umrah are distinct forms with differing religious obligations, timing, and rituals.
Religious Significance of Hajj
Hajj, one of the Five Pillars of Islam, holds profound religious significance as it is an obligatory pilgrimage for Muslims to perform once in their lifetime if physically and financially able, representing unity, submission, and purification. Unlike Umrah, which is a voluntary act of worship without specific timing, Hajj occurs annually during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah and includes prescribed rituals such as Tawaf, Sa'i, and standing at Arafat. Your participation in Hajj symbolizes spiritual renewal and a deep connection to Islamic history, distinguishing it from other forms of pilgrimage by its mandatory nature and comprehensive rites.
Religious Importance of Umrah
Umrah holds profound religious significance as a pilgrimage performed at any time of the year, symbolizing devotion and spiritual renewal for Muslims. Unlike Hajj, which is obligatory and performed during specific Islamic months, Umrah offers a flexible opportunity for You to seek forgiveness and strengthen Your faith. Its rituals, including Tawaf and Sa'i, represent key elements of Islamic worship that enhance spiritual connection and religious commitment.
Rituals of Hajj Explained
Hajj, Umrah, and Pilgrimage each hold unique significance in Islamic tradition, with Hajj being a mandatory annual pilgrimage involving specific rituals such as Ihram, Tawaf around the Kaaba, Sa'i between Safa and Marwah, standing at Arafat, and symbolic stoning of the devil in Mina. Unlike Umrah, which is a non-mandatory, shorter pilgrimage without the Arafat standing or stoning rituals, Hajj is performed during a fixed Islamic month, Dhu al-Hijjah. The completion of Hajj signifies spiritual purification and fulfillment of one of the Five Pillars of Islam, distinguishing it from other types of pilgrimages that may not include these compulsory rites.
Step-by-Step Guide to Umrah Rituals
The Step-by-Step Guide to Umrah Rituals includes Ihram preparation, Tawaf around the Kaaba, Sa'i between Safa and Marwah, and shaving or trimming hair to complete the spiritual journey. Unlike Hajj, Umrah is a shorter pilgrimage performed anytime, whereas Hajj has specific dates and is an obligatory act for Muslims who meet certain conditions. Pilgrimage, in general, encompasses both Hajj and Umrah, with Hajj being the major pilgrimage and Umrah considered the minor pilgrimage.
Timing: When to Perform Hajj or Umrah
Hajj is performed annually during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah, specifically between the 8th and 13th days, making its timing fixed and mandatory for eligible Muslims. Umrah can be undertaken at any time throughout the year, offering greater flexibility for Your spiritual journey. While pilgrimage encompasses both Hajj and Umrah, understanding the distinct timing requirements ensures proper planning and fulfillment of these sacred rites.
Eligibility and Requirements
Hajj requires Muslim adults who are physically and financially capable, with specific timings from the 8th to 12th of Dhu al-Hijjah, and completion is mandatory once in a lifetime. Umrah is a non-mandatory pilgrimage that can be performed any time of the year by Muslims with the financial means and physical ability, involving fewer rituals. Pilgrimage in general signifies a spiritual journey with varying requirements based on religious context, where eligibility often depends on faith adherence, physical health, and sometimes financial capability.
Cost and Logistics: Hajj vs Umrah
The cost of Hajj significantly exceeds that of Umrah due to its compulsory rituals, limited quotas, and peak travel season, often ranging from $5,000 to $15,000 per pilgrim versus Umrah's $1,000 to $3,000. Logistics for Hajj involve extensive planning, including securing permits, accommodation in Mecca during overcrowded periods, and transportation coordination amid millions of pilgrims, whereas Umrah permits are easier to obtain year-round with more flexible scheduling and less congested facilities. Travel packages for Hajj typically include mandatory vaccinations, group travel arrangements, and guided services, contrasting with the more flexible, individually tailored Umrah trips.
Spiritual Rewards and Benefits
Hajj, performed annually during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah, offers immense spiritual rewards, including the forgiveness of all past sins and a profound renewal of faith due to its status as one of the Five Pillars of Islam. Umrah, a non-mandatory pilgrimage that can be undertaken at any time of the year, provides believers with spiritual benefits such as increased devotion, purification of the heart, and closeness to Allah, though its rewards are considered less comprehensive than those of Hajj. The broader concept of pilgrimage in Islam encompasses both Hajj and Umrah, emphasizing spiritual growth, personal transformation, and a deepened connection to Islamic traditions.
Infographic: Hajj vs Umrah
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com