Guardians actively protect and nurture relationships by providing emotional support and stability, while Watchers observe interactions to maintain awareness and ensure boundaries are respected. Discover more about the distinct roles of Guardians and Watchers in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
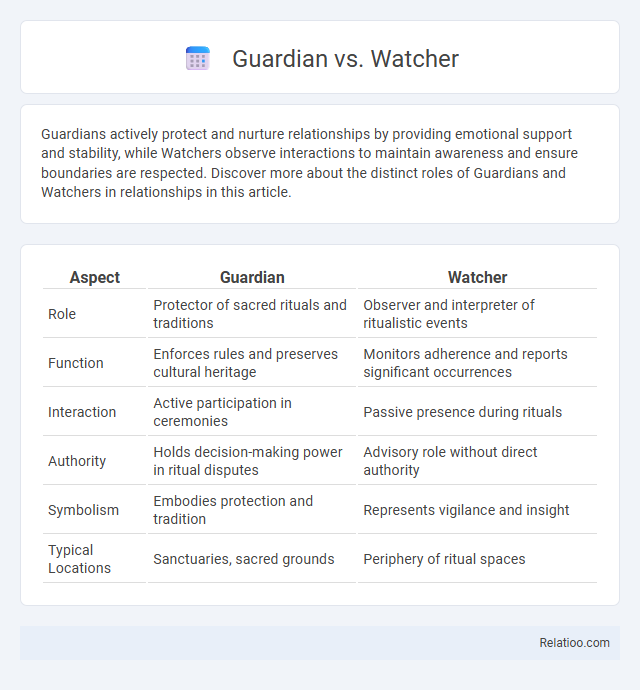
| Aspect | Guardian | Watcher |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Protector of sacred rituals and traditions | Observer and interpreter of ritualistic events |
| Function | Enforces rules and preserves cultural heritage | Monitors adherence and reports significant occurrences |
| Interaction | Active participation in ceremonies | Passive presence during rituals |
| Authority | Holds decision-making power in ritual disputes | Advisory role without direct authority |
| Symbolism | Embodies protection and tradition | Represents vigilance and insight |
| Typical Locations | Sanctuaries, sacred grounds | Periphery of ritual spaces |
Guardian vs Watcher: Key Differences
Guardians specialize in protection and defense, often serving as frontline defenders who safeguard people or places with physical strength and resilience. Watchers focus on observation and vigilance, monitoring environments or situations to detect threats early and provide crucial intelligence. Your understanding of these roles helps clarify that Guardians take direct action to prevent harm, while Watchers act as sentinels gathering information to support timely intervention.
Defining the Roles: What Is a Guardian?
A Guardian is a legal or appointed individual responsible for protecting the rights and well-being of another person, often a minor or someone unable to manage their own affairs. Unlike a Watcher who typically monitors situations without decision-making power, a Guardian holds authority to make critical decisions about healthcare, education, and finances on behalf of the ward. Your role as a Guardian ensures that the protected individual's interests are upheld with legal and ethical responsibility.
What Makes a Watcher Unique?
A Watcher distinguishes itself from a Guardian by its primary role of continuous observation and information gathering to prevent threats before they occur, rather than directly intervening like a Guardian. Watchers utilize advanced surveillance technologies and real-time data analytics to monitor environments with precision and accuracy. Your security strategy benefits from Watchers by enabling proactive risk detection, ensuring timely responses to potential hazards.
Origins and Historical Context
The Guardian concept originated in ancient mythologies as protectors assigned by gods to safeguard humans or sacred places, symbolizing vigilance and divine duty. The Watcher, emerging primarily from apocryphal texts like the Book of Enoch, represents celestial beings tasked with observing humanity, often with ambiguous moral roles reflecting themes of surveillance and judgment. Historically, the term Guardian evolved to encompass both physical and spiritual guardianship roles across cultures, while Watchers maintained a more enigmatic presence tied to cosmic oversight and forbidden knowledge.
Duties and Responsibilities Compared
Guardians are primarily responsible for protecting individuals or property, ensuring safety through active monitoring and intervention as needed. Watchers focus on surveillance and observation, gathering critical information without direct engagement unless an immediate threat arises. Your choice between a Guardian and a Watcher depends on whether you prioritize proactive defense or passive oversight in fulfilling security duties.
Powers and Abilities: Guardian vs Watcher
Guardians possess formidable defensive powers, including enhanced strength, impenetrable shields, and the ability to generate protective barriers that safeguard allies from harm. Watchers exhibit heightened perceptive abilities, such as precognition, telepathy, and the capacity to monitor vast distances or hidden threats, making them exceptional sentinels. Your choice depends on whether you prefer a protector with overwhelming physical power or a vigilant observer with unmatched awareness and strategic insight.
Philosophical and Ethical Perspectives
Philosophical and ethical perspectives on Guardian vs Watcher emphasize different modes of vigilance and responsibility toward humanity. Guardians are often seen as moral agents committed to protection and intervention, embodying duty and care, while Watchers represent impartial observers who prioritize non-interference and ethical restraint. Your understanding of these roles shapes how society balances the tension between safeguarding freedoms and respecting autonomy in ethical decision-making.
Common Misconceptions
Common misconceptions confuse the terms Guardian, Watcher, and Sentinel, often assuming they represent identical security roles, while each has distinct responsibilities and capabilities. Guardians focus on protective intervention and threat prevention, Watchers specialize in real-time monitoring and alert generation, and Sentinels integrate both functions with advanced analytics for proactive defense. Misunderstanding these roles can lead to improper resource allocation and security gaps in organizational risk management.
Guardian or Watcher: Which Suits Your Needs?
Choosing between Guardian and Watcher depends on your specific requirements for security and monitoring features. Guardian excels in robust protection with real-time threat detection and advanced alert systems, making it ideal for comprehensive defense. Watcher offers streamlined surveillance with ease of use and efficient activity tracking, which suits users prioritizing simplicity and continuous monitoring.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Protector
Choosing the right protector depends on your specific needs and the level of vigilance required. Guardians provide comprehensive security with proactive measures, while Watchers offer observational monitoring suited for real-time alerts. Your final decision should balance the intensity of protection and responsiveness needed to safeguard your assets effectively.
Infographic: Guardian vs Watcher
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com