A godparent provides spiritual guidance and support, while a guardian has legal authority and responsibility for a child's care and well-being. Discover the key differences and roles in this article.
Table of Comparison
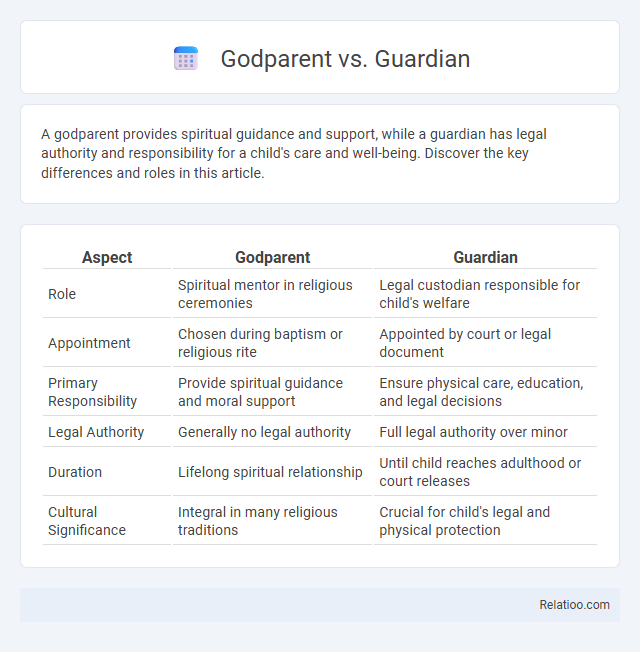
| Aspect | Godparent | Guardian |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Spiritual mentor in religious ceremonies | Legal custodian responsible for child's welfare |
| Appointment | Chosen during baptism or religious rite | Appointed by court or legal document |
| Primary Responsibility | Provide spiritual guidance and moral support | Ensure physical care, education, and legal decisions |
| Legal Authority | Generally no legal authority | Full legal authority over minor |
| Duration | Lifelong spiritual relationship | Until child reaches adulthood or court releases |
| Cultural Significance | Integral in many religious traditions | Crucial for child's legal and physical protection |
Understanding the Roles: Godparent vs Guardian
Godparents serve as spiritual mentors and moral guides without legal authority, whereas guardians have legal responsibility for a child's care and decision-making if parents are unavailable. Parents maintain full legal rights and duties related to upbringing, education, and welfare of their children. Clearly distinguishing these roles helps in planning family support and legal arrangements effectively.
Historical Origins of Godparents and Guardians
The historical origins of godparents trace back to early Christian traditions, where they were chosen to sponsor a child's baptism and ensure their religious upbringing. Guardians, on the other hand, have roots in Roman law, established to manage the affairs of minors and protect their legal rights when parents were absent or unable to care for them. Parents hold the primary legal and biological role, with rights and responsibilities dating back to ancient familial structures and societal norms governing lineage and inheritance.
Legal Responsibilities: Guardian Explained
A legal guardian holds court-appointed authority to make key decisions regarding a child's welfare, education, and healthcare, distinct from the typically honorary role of a godparent. Unlike parents who have inherent legal rights and duties from birth or adoption, guardianship is established through legal processes to protect a child when parents are unable or unavailable. Guardians are legally responsible for the child's daily care, managing their assets, and acting in the best interest of the child's safety and development.
Spiritual Duties: The Role of a Godparent
Godparents hold a unique spiritual duty, guiding Your godchild's faith development and moral growth through prayer, mentorship, and example. Unlike parents or guardians who oversee legal care and daily needs, godparents focus specifically on fostering Christian values and supporting religious milestones such as baptism and confirmation. This sacred role creates a lifelong bond centered on spiritual nurturing rather than custodial responsibility.
Key Differences Between Godparents and Guardians
Godparents serve primarily as spiritual mentors and guides, often selected during religious ceremonies to support Your child's moral and faith development. Guardians hold legal responsibility for a child's care and decision-making in the absence of parents, ensuring the child's welfare and upbringing according to the law. Parents possess full biological or legal rights and duties, including custody, care, and the ability to make major decisions impacting the child's life.
How to Choose a Godparent or Guardian
Choosing a godparent or guardian involves considering trustworthiness, values, and the ability to provide emotional and financial support for Your child. A godparent typically fulfills a spiritual or ceremonial role, while a guardian assumes legal responsibility for the child's care if parents are unable. Evaluate candidates based on their willingness to commit, alignment with Your family's beliefs, and capacity to ensure Your child's well-being in all aspects.
Legal Process of Appointing a Guardian
The legal process of appointing a guardian typically involves a court petition submitted by interested parties, who must demonstrate the guardian's capability to care for the minor or incapacitated individual. Unlike godparents, who usually have ceremonial or religious roles without legal authority, guardians assume full legal responsibility, including decision-making for health, education, and welfare. Parents retain primary legal rights unless a guardian is formally appointed by a judge after assessing the child's best interests and the prospective guardian's suitability.
Religious Traditions and the Godparent’s Role
Godparents play a significant role in religious traditions, serving as spiritual guides and supporters for Your child's faith development, while guardians are legally responsible for the child's care if parents are unable to fulfill their duties. Parents hold primary responsibility for both the child's upbringing and legal guardianship, but godparents often provide moral and religious mentorship rather than day-to-day caregiving. Many Christian denominations formally appoint godparents during baptism ceremonies to symbolize lifelong spiritual guidance and commitment.
When Does a Guardian Take Over Parental Duties?
A guardian takes over parental duties when a court legally appoints them due to the biological parents' inability to care for the child, such as in cases of death, incapacity, or neglect. Unlike godparents, who provide spiritual guidance without legal authority, guardians assume full responsibility for the child's welfare, education, and medical decisions. Parents retain rights until a guardian's appointment is formalized through legal processes in family or probate courts.
Frequently Asked Questions: Godparent vs Guardian
A godparent is a person chosen to take a special spiritual role in your child's life, often participating in religious ceremonies, while a guardian is legally appointed to care for your child if you are unable to do so. Your child's guardian has the authority to make important decisions regarding their welfare, education, and healthcare, which a godparent typically does not possess unless also designated as a guardian. Understanding these distinctions is crucial when deciding who will provide the best support and protection for your child's future.
Infographic: Godparent vs Guardian
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com