Discretion involves the careful judgment to keep sensitive information private, while confidentiality legally binds individuals to protect that information from unauthorized disclosure. Explore this article to understand the critical distinctions and implications of discretion versus confidentiality in building trust.
Table of Comparison
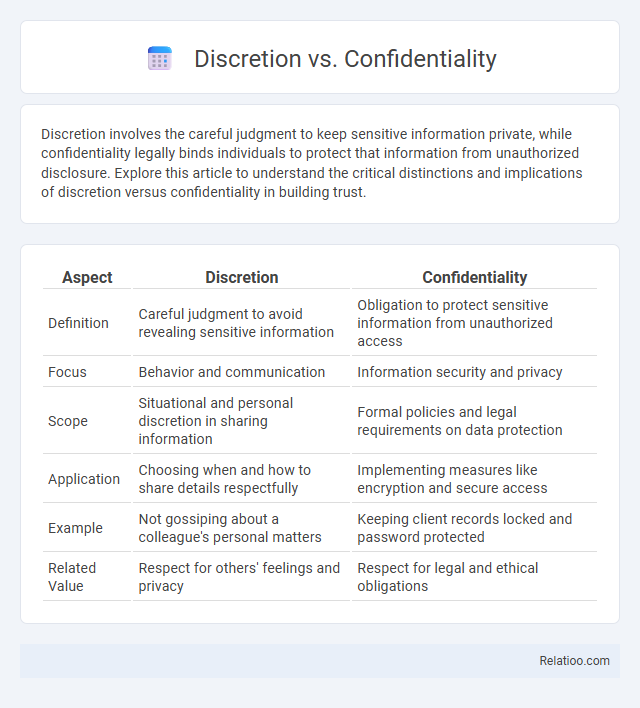
| Aspect | Discretion | Confidentiality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Careful judgment to avoid revealing sensitive information | Obligation to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access |
| Focus | Behavior and communication | Information security and privacy |
| Scope | Situational and personal discretion in sharing information | Formal policies and legal requirements on data protection |
| Application | Choosing when and how to share details respectfully | Implementing measures like encryption and secure access |
| Example | Not gossiping about a colleague's personal matters | Keeping client records locked and password protected |
| Related Value | Respect for others' feelings and privacy | Respect for legal and ethical obligations |
Understanding Discretion and Confidentiality
Discretion involves the careful judgment exercised to avoid causing offense or revealing sensitive information, while confidentiality refers to the ethical and often legal obligation to protect private information from unauthorized disclosure. Both concepts are crucial in professional settings, ensuring trust and integrity by safeguarding information according to established standards and expectations. Understanding discretion and confidentiality helps individuals navigate boundaries between sharing necessary information and maintaining privacy.
Key Differences Between Discretion and Confidentiality
Discretion involves making judicious decisions about sharing information based on context, while confidentiality refers to the obligation to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. Your ability to exercise discretion depends on recognizing what information should remain confidential to maintain trust and privacy. Understanding these key differences ensures you handle information responsibly and ethically in professional and personal settings.
The Importance of Discretion in Professional Settings
Discretion in professional settings ensures sensitive information is handled with the utmost care, preventing unauthorized disclosure and maintaining trust between colleagues and clients. Unlike confidentiality, which legally binds individuals to protect information, discretion involves personal judgment to avoid sharing information that could harm reputations or workplace dynamics. Prioritizing discretion fosters a respectful and secure environment, critical for effective communication and organizational integrity.
The Role of Confidentiality in Building Trust
Confidentiality plays a crucial role in building trust by ensuring that sensitive information shared in professional and personal contexts remains protected from unauthorized disclosure. Maintaining confidentiality fosters a safe environment where individuals feel secure to communicate openly, which strengthens relationships and promotes transparency. Unlike discretion, which involves careful judgment in decision-making and actions, confidentiality specifically emphasizes the ethical duty to safeguard private information.
Real-World Examples of Discretion vs Confidentiality
Discretion involves making judicious decisions about sharing sensitive information based on context, while confidentiality strictly requires withholding information as promised or legally mandated. For example, a manager exercising discretion might choose to withhold details about team restructuring until an official announcement, balancing transparency and employee morale. Conversely, a therapist maintains confidentiality by legally protecting client sessions from disclosure unless consent or danger justifies breaching privacy.
Legal Implications: Discretion vs Confidentiality
Discretion involves the exercise of judgment in handling sensitive information, whereas confidentiality legally binds individuals to protect private data from unauthorized disclosure. Breaches of confidentiality can result in legal penalties, including lawsuits or professional sanctions, emphasizing its critical role in sectors like healthcare and law. Discretion, while ethically important, grants more flexibility without the same strict legal obligations as confidentiality.
Ethical Considerations in Managing Sensitive Information
Ethical considerations in managing sensitive information require distinguishing between discretion, confidentiality, and privacy to ensure appropriate handling. Discretion involves careful judgment in sharing information, confidentiality mandates legally or professionally bound secrecy, and privacy protects individuals' personal data from unauthorized access. Upholding these principles fosters trust, mitigates risks of data breaches, and aligns with ethical standards in information management.
Best Practices for Maintaining Discretion and Confidentiality
Maintaining discretion and confidentiality requires strict adherence to data protection protocols and limited information sharing only with authorized personnel. Best practices include implementing encrypted communication channels, conducting regular staff training on privacy policies, and using access controls to prevent unauthorized data exposure. Consistent monitoring and auditing ensure compliance with legal standards such as GDPR and HIPAA, reinforcing trust and safeguarding sensitive information.
Challenges and Common Pitfalls
Challenges in maintaining discretion, confidentiality, and privacy often stem from overlapping responsibilities and unclear boundaries in handling sensitive information. Common pitfalls include unintentional data breaches due to insufficient training, misinterpretation of confidentiality protocols, and failure to recognize the nuances between discretion and confidentiality in different contexts. Organizations must implement precise guidelines and continuous education to mitigate risks associated with improper information management.
Balancing Discretion and Confidentiality in Decision-Making
Balancing discretion and confidentiality in decision-making involves carefully managing sensitive information to protect privacy while ensuring appropriate transparency. Effective decision-makers apply discretion by selectively sharing information based on context, legal requirements, and ethical considerations, maintaining trust and integrity. Striking this balance helps prevent unauthorized disclosures while enabling informed choices that support organizational goals and stakeholder interests.
Infographic: Discretion vs Confidentiality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com