Passive-aggressiveness involves indirect resistance and hidden hostility in relationships, while manipulation uses calculated tactics to control or influence others for personal gain. Explore effective strategies to recognize and address these behaviors in this article.
Table of Comparison
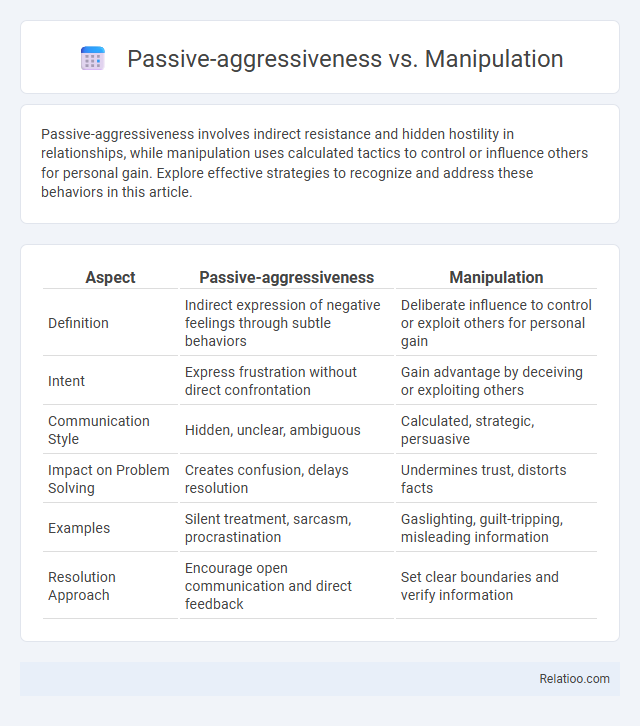
| Aspect | Passive-aggressiveness | Manipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Indirect expression of negative feelings through subtle behaviors | Deliberate influence to control or exploit others for personal gain |
| Intent | Express frustration without direct confrontation | Gain advantage by deceiving or exploiting others |
| Communication Style | Hidden, unclear, ambiguous | Calculated, strategic, persuasive |
| Impact on Problem Solving | Creates confusion, delays resolution | Undermines trust, distorts facts |
| Examples | Silent treatment, sarcasm, procrastination | Gaslighting, guilt-tripping, misleading information |
| Resolution Approach | Encourage open communication and direct feedback | Set clear boundaries and verify information |
Understanding Passive-Aggressiveness: Key Characteristics
Passive-aggressiveness is characterized by indirect resistance to demands or expectations, often expressed through procrastination, stubbornness, or subtle insults, distinguishing it from overt manipulation which involves deliberate control or influence over others. Key traits include withholding communication, expressing sarcasm, and feigning compliance while harboring resentment, making it less transparent than direct aggression or manipulation. Understanding passive-aggressiveness requires recognizing these covert behaviors as attempts to express unmet needs or frustrations without open confrontation.
What is Manipulation? Core Traits and Behaviors
Manipulation involves controlling or influencing others in a deceptive or indirect manner to achieve personal gain, often at the expense of honesty and transparency. Core traits of manipulators include charm, cunning, exploitation of others' weaknesses, and consistent dishonesty, coupled with behaviors such as guilt-tripping, gaslighting, and withholding information. Understanding these traits helps you recognize manipulation early and set boundaries to protect your well-being.
Comparing Passive-Aggressiveness and Manipulation
Passive-aggressiveness involves indirect resistance and subtle hostility such as procrastination or sarcasm to express negative feelings without open confrontation. Manipulation, however, entails deliberate and strategic influence or control over others through deceit, exploitation, or misdirection to achieve personal gain. While both behaviors undermine relationships, passive-aggressiveness is more about covert expression of anger, whereas manipulation is a conscious effort to dominate or exploit.
Psychological Roots of Passive-Aggressive Behavior
Passive-aggressive behavior often stems from unresolved anger, low self-esteem, and fear of direct confrontation, leading individuals to express hostility indirectly. In contrast, manipulation involves deliberate control over others for personal gain, rooted in a desire for power and control. Understanding these psychological roots is crucial for distinguishing passive-aggressiveness from manipulation and fostering healthier communication patterns.
The Motivations Behind Manipulative Actions
The motivations behind manipulative actions often stem from a desire for control, power, or personal gain, making manipulation a deliberate and strategic behavior. Passive-aggressiveness, conversely, is typically driven by underlying feelings of frustration, resentment, or fear of confrontation, resulting in indirect expressions of hostility. Understanding these distinct motivations clarifies the differences between manipulation's calculated intent and passive-aggressive behavior's emotional underpinnings.
Common Signs: How to Spot Passive-Aggressive Behavior
Passive-aggressive behavior often presents through indirect resistance, frequent sarcasm, and subtle sabotage, contrasting with manipulation, which typically involves more overt control and deceit to influence others. Common signs to spot passive-aggressive behavior include silent treatment, procrastination, and backhanded compliments, all designed to express hidden hostility without direct confrontation. Recognizing these patterns helps you address conflicts effectively and avoid misinterpreting passive-aggressive actions as manipulation or other behaviors.
Identifying Manipulation in Relationships
Identifying manipulation in relationships involves recognizing behaviors designed to control or exploit others, often through deceit, guilt-tripping, or emotional exploitation, which differ from passive-aggressiveness characterized by indirect resistance or stubbornness. Passive-aggressiveness manifests as subtle sabotage or avoidance rather than overt deceit, making manipulation more strategic and harmful by intent. Understanding these distinctions helps in setting boundaries and fostering healthier communication dynamics.
Effects on Mental Health: Passive-Aggressiveness vs Manipulation
Passive-aggressiveness often leads to confusion and unresolved tension, negatively impacting your mental health by fostering chronic stress and anxiety. Manipulation can cause significant emotional harm by eroding trust and self-esteem, resulting in feelings of helplessness and depression. Understanding the distinct effects of both behaviors helps in recognizing toxic interactions and protecting your psychological well-being.
Strategies for Dealing with Passive-Aggressive Individuals
Dealing with passive-aggressive individuals requires clear communication and setting firm boundaries to reduce misunderstandings and emotional depletion. Strategies include calmly addressing behaviors without accusatory language and encouraging direct expression of feelings to dismantle manipulative tactics. Your ability to recognize these dynamics fosters healthier interactions and minimizes the impact of subtle hostility.
Healthy Communication Alternatives and Conflict Resolution
Passive-aggressiveness involves indirect resistance and hidden hostility, while manipulation seeks to control others covertly for personal gain, both undermining trust and healthy communication. Adopting assertiveness techniques and open dialogue fosters transparency and mutual respect, which are essential for effective conflict resolution. Emphasizing empathy, active listening, and clear boundary-setting creates a constructive environment, reducing reliance on passive-aggressive or manipulative behaviors.
Infographic: Passive-aggressiveness vs Manipulation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com