Control often triggers resistance in relationships as individuals seek autonomy and fear losing influence. Explore effective strategies to balance control and resistance to foster healthier connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
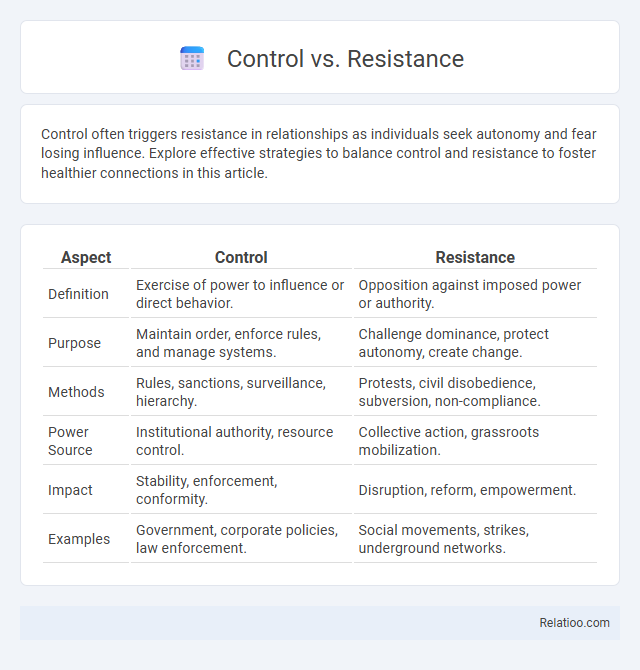
| Aspect | Control | Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exercise of power to influence or direct behavior. | Opposition against imposed power or authority. |
| Purpose | Maintain order, enforce rules, and manage systems. | Challenge dominance, protect autonomy, create change. |
| Methods | Rules, sanctions, surveillance, hierarchy. | Protests, civil disobedience, subversion, non-compliance. |
| Power Source | Institutional authority, resource control. | Collective action, grassroots mobilization. |
| Impact | Stability, enforcement, conformity. | Disruption, reform, empowerment. |
| Examples | Government, corporate policies, law enforcement. | Social movements, strikes, underground networks. |
Understanding Control and Resistance
Control involves asserting influence to direct or manage outcomes within systems or behaviors, often leveraging power, rules, or structures to maintain order and predictability. Resistance refers to actions or attitudes that oppose or challenge control, emerging as a response to perceived constraints or domination, manifesting through dissent, noncompliance, or subversion. Understanding control and resistance requires analyzing their dynamic interplay, where control mechanisms provoke resistance strategies, shaping social, political, or organizational environments.
Origins of Control in Human Behavior
Control in human behavior originates from evolutionary mechanisms designed to maintain order and predictability within social groups, ensuring survival and cooperation. Resistance emerges as a reaction to perceived threats against autonomy, reflecting innate drives for self-preservation and agency. Obliteration represents the extreme rejection or suppression of control structures, often linked to psychological breakdowns or radical shifts in identity and social dynamics.
Psychological Roots of Resistance
Control often stems from the desire to reduce uncertainty and maintain order in one's environment, while resistance arises from psychological roots such as fear of change, loss of autonomy, or deeply ingrained beliefs conflicting with new ideas. Resistance manifests as a defense mechanism protecting Your identity and values, which complicates efforts to influence behavior or implement change. Obliteration, an extreme reaction, indicates a complete rejection or denial, reflecting unresolved emotional or cognitive dissonance within the individual or group.
Control vs Resistance: Core Differences
Control involves exerting authority or influence over a situation or person to direct outcomes, whereas resistance is the act of opposing or standing against that control. Your ability to maintain control relies on managing power dynamics effectively, while resistance thrives on challenging or disrupting these dynamics. Understanding the core difference helps in navigating conflicts where one party aims to dominate and the other seeks to maintain autonomy.
How Control Manifests in Daily Life
Control manifests in daily life through routines, decision-making, and resource management that help you maintain order and predictability. It appears in time management strategies, prioritizing tasks, and setting boundaries to influence outcomes effectively. This balanced exertion of control enhances productivity and reduces stress by creating a structured environment.
Signs and Symptoms of Resistance
Resistance presents with signs such as persistent refusal to comply with directives, increased agitation, and verbal or physical opposition. Symptoms may include avoidance behaviors, slowed task completion, and covert defiance, indicating a mental or emotional struggle against imposed control. Recognizing these signals early allows for targeted interventions to address underlying issues and reduce conflict escalation.
The Impact of Control on Relationships
Control in relationships often undermines trust and mutual respect, leading to increased tension and emotional distance between partners. Resistance to control can trigger defensive behaviors, escalating conflicts and reducing effective communication. Obliteration of autonomy through excessive control can cause long-term psychological harm and may ultimately result in the dissolution of the relationship.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Resistance
Resistance offers significant benefits, including the empowerment to challenge unjust systems and the preservation of individual and collective autonomy, fostering social change and innovation. However, resistance can lead to conflict, instability, and potential backlash, sometimes exacerbating divisions and hindering progress. Balancing resistance with strategic control mechanisms may optimize outcomes, but excessive resistance risks obstructing constructive dialogue and sustainable development.
Strategies to Balance Control and Resistance
Balancing control and resistance involves implementing adaptive leadership approaches that promote flexibility while maintaining clear boundaries, ensuring organizational stability without stifling innovation. Effective strategies include fostering open communication channels to encourage constructive feedback, empowering team members through participative decision-making, and utilizing conflict resolution techniques to address resistance proactively. Integrating these methods helps mitigate the risk of obliteration by ensuring a dynamic equilibrium between authority and employee autonomy, leading to sustainable growth and resilience.
Achieving Harmony: Moving Beyond Control and Resistance
Achieving harmony requires moving beyond control and resistance to embrace acceptance and adaptability, allowing you to flow with challenges rather than fight them. Control imposes rigidity, while resistance breeds conflict, but harmony emerges from a balanced approach that integrates flexibility with intentional action. This shift fosters resilience and peace, creating a sustainable path toward personal and collective well-being.
Infographic: Control vs Resistance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com