Triggers are sensory stimuli or situations that remind individuals of past trauma, often causing immediate distress. Flashbacks are intense, vivid re-experiencing of traumatic events that can disrupt current relationships; learn how to identify and manage these in this article.
Table of Comparison
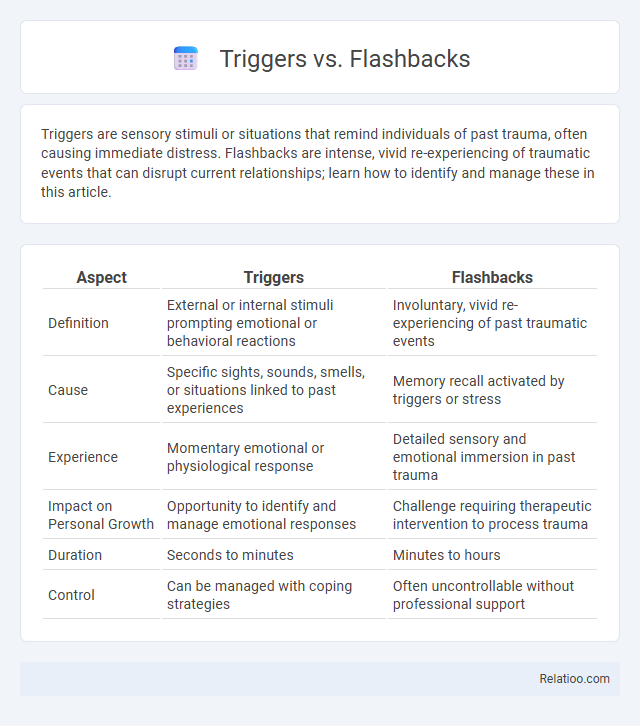
| Aspect | Triggers | Flashbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | External or internal stimuli prompting emotional or behavioral reactions | Involuntary, vivid re-experiencing of past traumatic events |
| Cause | Specific sights, sounds, smells, or situations linked to past experiences | Memory recall activated by triggers or stress |
| Experience | Momentary emotional or physiological response | Detailed sensory and emotional immersion in past trauma |
| Impact on Personal Growth | Opportunity to identify and manage emotional responses | Challenge requiring therapeutic intervention to process trauma |
| Duration | Seconds to minutes | Minutes to hours |
| Control | Can be managed with coping strategies | Often uncontrollable without professional support |
Understanding Triggers: What They Are
Triggers are specific stimuli--such as sights, sounds, or smells--that activate intense emotional or physiological reactions linked to past trauma. Unlike flashbacks, which are vivid, involuntary re-experiences of traumatic events, triggers primarily elicit feelings of distress without fully immersive recall. Understanding triggers helps You recognize and manage emotional responses, promoting healthier coping mechanisms and overall mental well-being.
Defining Flashbacks: A Deeper Look
Flashbacks are vivid, intrusive re-experiences of traumatic events that can overwhelm Your sense of time and reality, often triggered by sensory or emotional cues. Unlike triggers, which act as reminders causing distress, flashbacks thrust You directly back into the trauma, blurring the line between past and present. Understanding the neurological and psychological mechanisms behind flashbacks is essential for effective trauma-informed treatment and recovery.
Key Differences Between Triggers and Flashbacks
Triggers are external stimuli or events that evoke memories or reactions associated with traumatic experiences, often causing intense emotional or physiological responses. Flashbacks involve reliving traumatic events as if they are occurring in the present moment, often with vivid sensory details and loss of awareness of current surroundings. The key difference lies in triggers prompting a reaction without necessarily reliving the trauma, whereas flashbacks immerse the individual in the past experience itself.
How Triggers Manifest in Daily Life
Triggers often manifest as sudden sensory overloads or emotional responses tied to past traumatic events, causing unexpected stress or anxiety in daily life. You may experience physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, or trembling when confronted with reminders of trauma, which can disrupt your concentration and well-being. Recognizing these triggers is essential to managing flashbacks and mitigating their impact on your mental health and daily functioning.
The Experience of Flashbacks Explained
Flashbacks are intense, involuntary re-experiences of traumatic events, often triggered by sensory stimuli that resemble aspects of the original trauma. Unlike general triggers that cause emotional or physiological distress, flashbacks vividly transport individuals back in time, making the traumatic memory feel present and overwhelming. Understanding the neurological basis involving the amygdala and hippocampus helps explain why flashbacks disrupt normal memory processing and create such immersive and distressing experiences.
Psychological Causes of Triggers and Flashbacks
Triggers and flashbacks arise from complex psychological causes rooted in trauma, where your brain associates specific stimuli with past distressing events, sparking intense emotional or sensory responses. Triggers often emerge from sensory inputs, such as sights, sounds, or smells, that subconsciously reconnect you to unresolved traumatic memories, disrupting your present moment awareness. Flashbacks represent acute, vivid re-experiencing of the trauma, driven by the brain's failure to process and integrate traumatic memories properly, often leading to overwhelming feelings resembling the original event.
Common Examples of Triggers and Flashbacks
Triggers such as specific smells, sounds, or places can cause intense emotional reactions linked to past trauma, often leading to flashbacks where you vividly re-experience the traumatic event. Common examples of triggers include loud noises, crowded spaces, or anniversaries of the trauma, while flashbacks may involve seeing images, hearing voices, or feeling physical sensations from the original experience. Understanding these elements helps in identifying and managing trauma responses effectively.
The Impact on Mental Health
Triggers, flashbacks, and trauma distinctly influence mental health by reactivating distressing memories and emotional responses related to past traumatic events. Your encounters with triggers can elicit sudden flashbacks, which may cause overwhelming fear, anxiety, and emotional dysregulation, impairing daily functioning. Understanding these elements aids in developing effective coping strategies to mitigate their detrimental impact on psychological well-being.
Effective Coping Strategies for Triggers and Flashbacks
Triggers and flashbacks often stem from trauma and can evoke intense emotional and physical reactions, disrupting your daily life. Effective coping strategies include grounding techniques such as deep breathing, sensory focus (noticing colors, textures, or sounds), and mindfulness exercises to anchor your awareness in the present moment. Establishing a safe routine and seeking professional support like therapy can also help manage symptoms and promote healing.
Seeking Professional Help: When and Why
Recognizing when triggers or flashbacks severely impact daily functioning signals the need for professional help to address underlying trauma. Persistent symptoms such as intense distress, avoidance behaviors, or intrusive memories often require therapeutic interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR). Early consultation with mental health specialists improves outcomes by developing coping strategies and promoting trauma recovery.
Infographic: Triggers vs Flashbacks
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com