Healthy relationships thrive on genuine care, prioritizing empathy and support instead of control or dominance. Explore the key differences between care and control to build stronger, more trusting connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
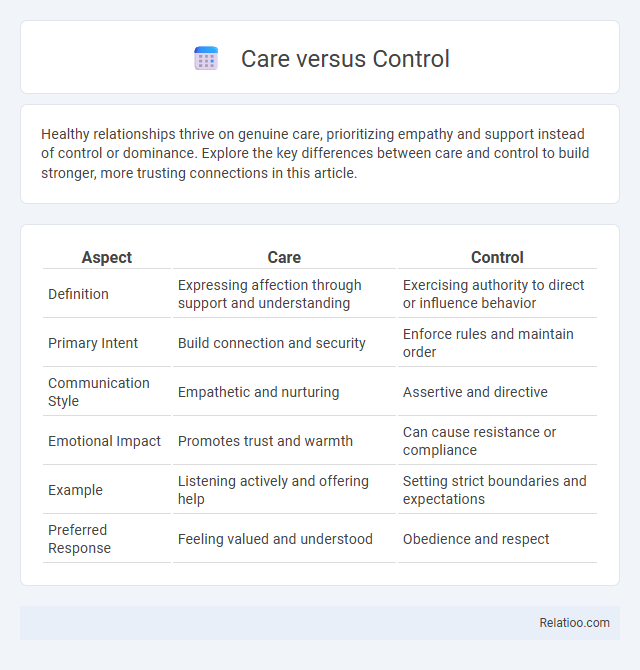
| Aspect | Care | Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expressing affection through support and understanding | Exercising authority to direct or influence behavior |
| Primary Intent | Build connection and security | Enforce rules and maintain order |
| Communication Style | Empathetic and nurturing | Assertive and directive |
| Emotional Impact | Promotes trust and warmth | Can cause resistance or compliance |
| Example | Listening actively and offering help | Setting strict boundaries and expectations |
| Preferred Response | Feeling valued and understood | Obedience and respect |
Understanding the Concepts of Care and Control
Understanding the concepts of care and control involves recognizing care as the expression of empathy, concern, and nurturing aimed at supporting others, while control refers to the regulation or restriction of behaviors to maintain order or achieve specific outcomes. Care fosters positive relationships through emotional connection and trust, whereas control often relies on authority and enforcement to guide actions. Your ability to balance these dynamics influences interpersonal effectiveness and organizational success.
Historical Perspectives on Care vs Control
Historical perspectives on care vs control reveal how societies have oscillated between nurturing support and authoritative regulation in managing populations and social order. The evolution from feudal systems to modern governance shows shifting priorities where care frameworks gradually incorporated institutional controls to enforce public health, education, and welfare. Understanding these dynamics helps you critically assess how contemporary social policies balance empathy and authority in fostering community well-being.
The Psychology of Caring: Motivations and Impacts
The psychology of caring explores how intrinsic motives, such as empathy and altruism, drive individuals to provide support and maintain relationships, distinguishing genuine care from control-based behaviors. Care is characterized by the desire to nurture and benefit others, promoting positive social bonds, whereas control involves exerting influence often motivated by self-interest or power. Understanding the differences in these psychological motivations reveals the profound impact care has on emotional well-being, trust development, and prosocial behaviors in interpersonal dynamics.
Control Mechanisms: Types and Effects
Control mechanisms in organizations include bureaucratic controls, which rely on rules and procedures to regulate behavior; market controls, using pricing and competition as regulators; and clan controls, which depend on shared values and norms to influence members. Each type affects organizational effectiveness by shaping decision-making, employee motivation, and operational efficiency, with bureaucratic controls providing clear structure but risking rigidity, market controls fostering flexibility through competition, and clan controls enhancing commitment via trust and culture. Understanding these control mechanisms helps optimize performance by aligning control methods with organizational goals and environmental conditions.
Comparing Outcomes: Care-Based vs Control-Based Approaches
Care-based approaches prioritize empathy and relationship-building, resulting in stronger social bonds and enhanced psychological well-being. Control-based strategies emphasize rules and enforcement, often producing compliance but risking resistance and diminished trust. Comparing outcomes reveals care-driven models foster cooperative environments, while control-oriented methods may yield short-term order at the cost of long-term engagement.
Ethical Considerations in Balancing Care and Control
Balancing care and control in ethical decision-making requires a nuanced approach that respects individual autonomy while ensuring safety and well-being. Your actions should prioritize empathy and respect for others' dignity, avoiding excessive control that undermines trust. Ethical considerations demand transparency, accountability, and a clear motive rooted in genuine concern rather than self-interest.
Care and Control in Parenting and Education
Care in parenting and education emphasizes nurturing emotional and physical well-being, fostering secure attachments and supportive environments that promote a child's development and self-esteem. Control focuses on setting boundaries, enforcing rules, and maintaining discipline to guide behavior and ensure safety, often implementing structured routines and consequences. Effective parenting and educational strategies balance care and control to cultivate independence, responsibility, and emotional resilience in children.
Workplace Dynamics: Nurturing vs Regulating
Care in workplace dynamics fosters trust and motivation by nurturing employees' well-being and professional growth, enhancing collaboration and innovation. Control emphasizes regulation through policies and supervision, ensuring consistency and accountability but potentially stifling creativity. Understanding your team's motives helps balance care and control, creating an environment that supports both autonomy and organizational goals for optimal performance.
Societal Implications of Care vs Control
Care emphasizes empathy and support, fostering collaborative societies where individuals feel valued and understood. Control relies on authority and regulation, often limiting personal freedoms and potentially breeding resistance or compliance out of fear. Your engagement in a society that balances care with appropriate control can enhance social cohesion and promote ethical governance.
Finding the Balance: Strategies for Harmonizing Care and Control
Finding the balance between care and control requires implementing clear communication strategies that respect emotional needs while establishing firm boundaries. Your ability to harmonize these aspects enhances team dynamics, promotes trust, and prevents micromanagement. Prioritizing empathy alongside accountability creates an environment where motivation and productivity thrive.
Infographic: Care vs Control
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com