Texting offers direct, private communication ideal for building deeper personal connections, while social media messaging facilitates broader, casual interactions within larger networks. Discover the key differences and impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
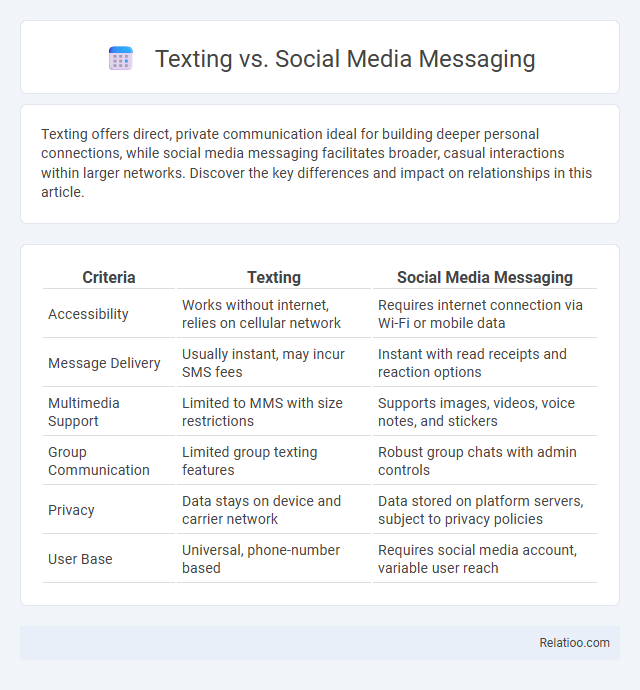
| Criteria | Texting | Social Media Messaging |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Works without internet, relies on cellular network | Requires internet connection via Wi-Fi or mobile data |
| Message Delivery | Usually instant, may incur SMS fees | Instant with read receipts and reaction options |
| Multimedia Support | Limited to MMS with size restrictions | Supports images, videos, voice notes, and stickers |
| Group Communication | Limited group texting features | Robust group chats with admin controls |
| Privacy | Data stays on device and carrier network | Data stored on platform servers, subject to privacy policies |
| User Base | Universal, phone-number based | Requires social media account, variable user reach |
Understanding Texting and Social Media Messaging
Texting primarily involves sending short, direct messages via SMS or MMS protocols, facilitating immediate and personal communication between users. Social media messaging integrates text with multimedia content, enabling interactive conversations within platforms like Facebook Messenger, Instagram, and WhatsApp, often enriched with emojis, stickers, and real-time status updates. Understanding the differences in delivery methods, user engagement, and context is essential for optimizing communication strategies across individual and business interactions.
Historical Evolution of Digital Communication
Texting, originating in the early 1990s with SMS technology, laid the foundation for instant mobile communication by enabling concise, direct messages between users. The rise of social media messaging in the mid-2000s introduced interactive platforms like Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp, integrating multimedia and group conversations to enhance connectivity. Your communication habits have evolved through these stages, reflecting how digital messaging has expanded from simple text exchanges to rich, multimedia social interactions.
User Demographics and Preferences
User demographics for texting show higher adoption among older adults and professionals who prefer direct, reliable communication with minimal distractions. Social media messaging attracts younger audiences, particularly teens and millennials, due to its integration with multimedia, interactive features, and social networking capabilities. Preferences indicate texting is favored for privacy and immediacy, while social media messaging is chosen for social engagement and rich content sharing.
Accessibility and Platform Compatibility
Texting offers universal accessibility and seamless compatibility across all mobile devices without requiring internet access, making it a reliable communication method for Your most essential contacts. Social media messaging depends on platform-specific apps and internet connectivity, limiting accessibility for users without accounts or stable connections but providing richer multimedia options. Messaging apps combine some benefits of texting and social media by supporting various formats while requiring app installation, creating a balance between compatibility and enhanced communication features.
Privacy and Security Considerations
Texting, social media messaging, and instant messaging apps differ significantly in privacy and security features, with traditional SMS lacking end-to-end encryption and being vulnerable to interception. Social media messaging platforms like Facebook Messenger and Instagram offer encryption but often collect extensive user metadata, raising privacy concerns. Encrypted messaging apps such as Signal and WhatsApp provide robust privacy protections, including end-to-end encryption and minimal data retention, making them the preferred choice for secure communication.
Message Delivery Speed and Reliability
SMS texting offers faster and more reliable message delivery compared to social media messaging platforms, which often depend on internet connectivity and can experience delays due to server loads or app performance. Social media messaging allows for multimedia sharing and extended conversations but may sacrifice immediacy and guaranteed delivery, especially in areas with unstable internet access. Traditional texting uses cellular networks, providing consistent delivery even without an internet connection, making it preferable for urgent and critical communications.
Features: Customization and Multimedia Support
Texting offers basic customization with limited font styles and emojis, primarily supporting SMS and MMS for multimedia sharing like photos and videos. Social media messaging platforms provide extensive customization options, including stickers, GIFs, message effects, and themes, alongside advanced multimedia support such as voice notes, video calls, and file sharing. Compared to traditional texting, these platforms enable richer interaction through enhanced multimedia integration and personalized message formats, catering to more dynamic communication needs.
Group Communication Capabilities
Group communication capabilities in texting typically involve basic SMS group chats with limited interactivity and media sharing, while social media messaging platforms like Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp offer more advanced features such as multimedia sharing, reactions, threaded conversations, and real-time typing indicators. Social media messaging supports larger group sizes and integrates seamlessly with other platform functionalities, enhancing collaboration and engagement compared to traditional SMS. Texting lacks the depth of customization and interactive tools found in social media messaging, limiting its effectiveness in dynamic group communication scenarios.
Impact on Mental Health and Social Interaction
Texting, social media messaging, and instant messaging each uniquely affect mental health and social interaction by shaping communication frequency, emotional expression, and perceived social support. Texting enables direct, often private conversations that can enhance intimate connections, reducing feelings of loneliness and anxiety. Social media messaging, while encouraging broader social networks, may contribute to social comparison and increased stress, whereas instant messaging promotes real-time interaction that can both alleviate and amplify social pressure depending on the context.
Choosing the Right Communication Tool
Choosing the right communication tool depends on your message's urgency, context, and audience. Texting offers direct, immediate contact ideal for personal or urgent communication, while social media messaging provides a broader platform for engagement, sharing multimedia, and casual interactions with groups or communities. Evaluate your communication goals, privacy preferences, and the formality required to determine whether texting or social media messaging best suits your needs.
Infographic: Texting vs Social Media Messaging
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com