Active listeners engage fully by providing feedback and clarifying, enhancing mutual understanding and trust in relationships. Passive listeners may miss emotional cues and hinder effective communication. Discover deeper insights about improving your connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
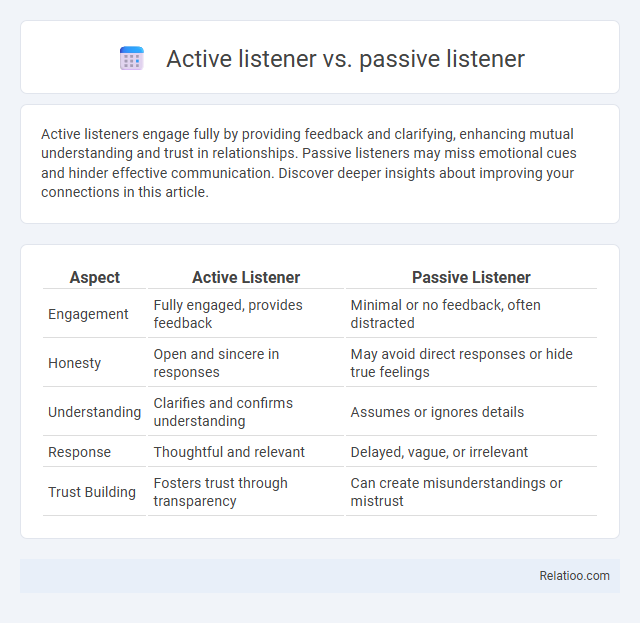
| Aspect | Active Listener | Passive Listener |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | Fully engaged, provides feedback | Minimal or no feedback, often distracted |
| Honesty | Open and sincere in responses | May avoid direct responses or hide true feelings |
| Understanding | Clarifies and confirms understanding | Assumes or ignores details |
| Response | Thoughtful and relevant | Delayed, vague, or irrelevant |
| Trust Building | Fosters trust through transparency | Can create misunderstandings or mistrust |
Introduction to Active and Passive Listening
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker by responding thoughtfully and clarifying meanings, enhancing comprehension and communication effectiveness. Passive listening, meanwhile, means hearing the speaker without providing feedback or verifying understanding, which can lead to misunderstandings and missed information. Your ability to distinguish between these listening styles directly impacts how well you process and retain information during conversations.
Defining Active Listening
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding thoughtfully to a speaker, making it a dynamic and engaged form of communication. Passive listening refers to hearing the words without actively processing or responding to the message, often resulting in minimal retention and comprehension. A listener can adopt either active or passive roles, but active listening is essential for effective interpersonal communication, conflict resolution, and building trust.
Understanding Passive Listening
Passive listening occurs when your attention drifts and you hear words without fully processing their meaning, unlike active listening where you engage and respond thoughtfully. A passive listener might miss key information or emotional undertones, leading to misunderstandings or lack of connection. Understanding passive listening helps you recognize the importance of transitioning to active listening for clearer communication and stronger relationships.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Listening
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker by providing feedback, asking questions, and showing empathy, whereas passive listening means hearing the words without processing or responding thoughtfully. Your ability to retain information and build meaningful connections improves significantly with active listening, contrasting the minimal involvement of passive listeners. The key difference lies in active listening requiring conscious effort and interaction, while passive listening is largely inattentive and non-responsive.
Benefits of Being an Active Listener
Active listening enhances your communication by fully engaging with the speaker, improving understanding and reducing misunderstandings. Unlike passive listeners who hear but do not process information deeply, active listeners retain key details and respond thoughtfully. Being an active listener fosters trust, strengthens relationships, and increases the effectiveness of conversations.
Drawbacks of Passive Listening
Passive listening involves receiving information without actively engaging or providing feedback, which can lead to misunderstandings and missed details. Unlike active listeners who process and respond thoughtfully, passive listeners often fail to retain important information, reducing communication effectiveness. Your ability to contribute meaningfully in conversations diminishes when you rely on passive listening, as it hinders comprehension and connection.
Impact on Communication and Relationships
Active listeners enhance communication by fully engaging with the speaker, leading to stronger relationships and greater trust. Passive listeners often miss crucial information and emotional cues, which can cause misunderstandings and weaken connections. Effective listeners balance attentiveness and responsiveness, fostering clearer dialogue and deeper interpersonal bonds.
Techniques to Enhance Active Listening Skills
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, responding, and remembering what is being said, whereas passive listening means hearing without engaging or providing feedback. Techniques to enhance your active listening skills include maintaining eye contact, nodding to show understanding, summarizing key points, and asking clarifying questions to ensure accurate comprehension. Practicing these methods helps transform a passive listener into an attentive listener, improving communication and mutual understanding.
Common Barriers to Effective Listening
Active listeners engage fully by focusing on the speaker, interpreting both verbal and non-verbal cues, whereas passive listeners hear without processing meaning or responding thoughtfully. Common barriers to effective listening include distractions, preconceived notions, emotional biases, and environmental noise, which impair comprehension and retention. Overcoming these obstacles requires conscious effort to maintain attention, empathy, and an open mind during communication.
Choosing the Right Listening Approach
Choosing the right listening approach depends on the context and desired outcomes, where an active listener engages fully by providing feedback, asking clarifying questions, and demonstrating empathy to enhance understanding and connection. A passive listener hears the message without offering responses or confirming comprehension, suitable for situations requiring minimal interaction or when absorbing information without immediate reaction. Balancing these styles allows effective communication, with active listening fostering collaboration and passive listening supporting observation or information intake.
Infographic: Active listener vs passive listener
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com