Self-assessment promotes personal growth by encouraging introspection, while peer assessment enhances relationship dynamics through constructive feedback and diverse perspectives. Discover the benefits and challenges of both methods in this article.
Table of Comparison
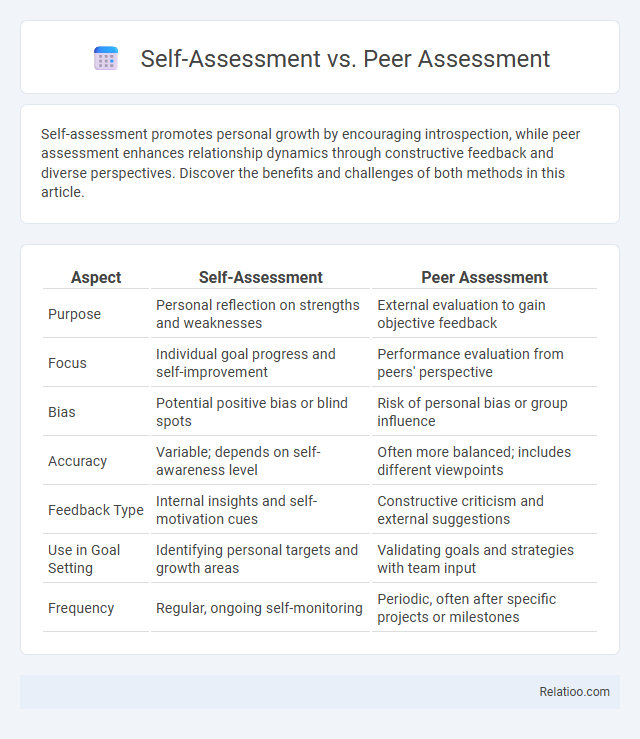
| Aspect | Self-Assessment | Peer Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Personal reflection on strengths and weaknesses | External evaluation to gain objective feedback |
| Focus | Individual goal progress and self-improvement | Performance evaluation from peers' perspective |
| Bias | Potential positive bias or blind spots | Risk of personal bias or group influence |
| Accuracy | Variable; depends on self-awareness level | Often more balanced; includes different viewpoints |
| Feedback Type | Internal insights and self-motivation cues | Constructive criticism and external suggestions |
| Use in Goal Setting | Identifying personal targets and growth areas | Validating goals and strategies with team input |
| Frequency | Regular, ongoing self-monitoring | Periodic, often after specific projects or milestones |
Introduction to Self-Assessment and Peer Assessment
Self-assessment involves individuals evaluating their own performance to identify strengths and areas for improvement, promoting self-awareness and personal growth. Peer assessment entails learners providing constructive feedback to each other, enhancing critical thinking and collaborative skills. Both methods complement traditional assessment by encouraging active participation and deeper engagement in the learning process.
Defining Self-Assessment: Key Features
Self-assessment involves individuals evaluating their own work or performance against predefined criteria, fostering self-awareness and personal accountability. Key features include reflective thinking, goal setting, and critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses, enabling You to take ownership of Your learning or development process. Unlike peer or external assessments, self-assessment emphasizes internal motivation and continuous improvement through honest self-evaluation.
Understanding Peer Assessment: Core Concepts
Peer assessment involves students evaluating each other's work based on set criteria, fostering critical thinking and collaborative learning. Core concepts include anonymity to reduce bias, clear rubrics to ensure objective evaluation, and constructive feedback to promote improvement. This method enhances understanding by enabling learners to engage actively with assessment standards and diverse perspectives.
Benefits of Self-Assessment in Learning
Self-assessment fosters deep learning by encouraging learners to reflect on their understanding, identify gaps, and set personalized improvement goals, enhancing metacognitive skills. It promotes learner autonomy and accountability, which leads to increased motivation and engagement in the educational process. Compared to peer and traditional assessments, self-assessment provides immediate feedback and supports continuous progress by allowing students to monitor and regulate their own learning effectively.
Advantages of Peer Assessment for Collaboration
Peer assessment enhances collaboration by promoting active engagement and deeper understanding through diverse perspectives. It encourages critical thinking and communication skills, fostering a supportive learning environment where students hold each other accountable. This process also builds teamwork and interpersonal skills, essential for collaborative success.
Challenges in Self-Assessment Practices
Challenges in self-assessment practices include difficulties in maintaining objectivity and accurately evaluating one's own performance, often leading to overestimation or underestimation of skills. Lack of clear criteria and insufficient metacognitive skills can cause inconsistencies and reduce the reliability of self-assessment outcomes. These challenges highlight the necessity for structured guidance and training to enhance self-assessment accuracy and effectiveness.
Common Issues in Peer Assessment
Peer assessment often faces challenges such as biased evaluations, lack of objectivity, and inconsistent scoring criteria compared to self-assessment and instructor-led assessment methods. You may encounter difficulties in ensuring fairness and reliability when relying on peers to evaluate performance or contributions. Implementing clear guidelines and training can mitigate common issues like social loafing, favoritism, and inadequate feedback within peer assessment processes.
When to Use Self-Assessment vs Peer Assessment
Self-assessment is ideal when You need to promote reflection and personal responsibility, allowing individuals to evaluate their own strengths and areas for improvement. Peer assessment is best used to encourage collaborative learning and provide diverse feedback from multiple perspectives, enhancing critical thinking skills. Understanding when to use each method depends on the learning objectives, with self-assessment supporting introspection and peer assessment fostering communication and teamwork.
Strategies for Effective Assessment Implementation
Effective assessment implementation requires aligning self-assessment, peer assessment, and traditional assessment with clear objectives and criteria to ensure accuracy and fairness. Incorporating rubrics and continuous feedback fosters student reflection and collaborative learning, enhancing overall performance. Leveraging technology platforms streamlines data collection and analysis, enabling timely adjustments to instructional strategies.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Assessment Method
Choosing the right assessment method depends on your educational goals, the skills being evaluated, and the context of the learning environment. Self-assessment promotes personal reflection and metacognitive skills, while peer assessment encourages collaborative learning and diverse feedback. Traditional assessment remains essential for standardized evaluation, but combining these methods often provides a more comprehensive understanding of student performance.
Infographic: Self-Assessment vs Peer Assessment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com