Fostering growth in relationships requires continuous communication, mutual support, and adaptability to overcome challenges. Discover effective strategies to nurture connection and avoid stagnation in this article.
Table of Comparison
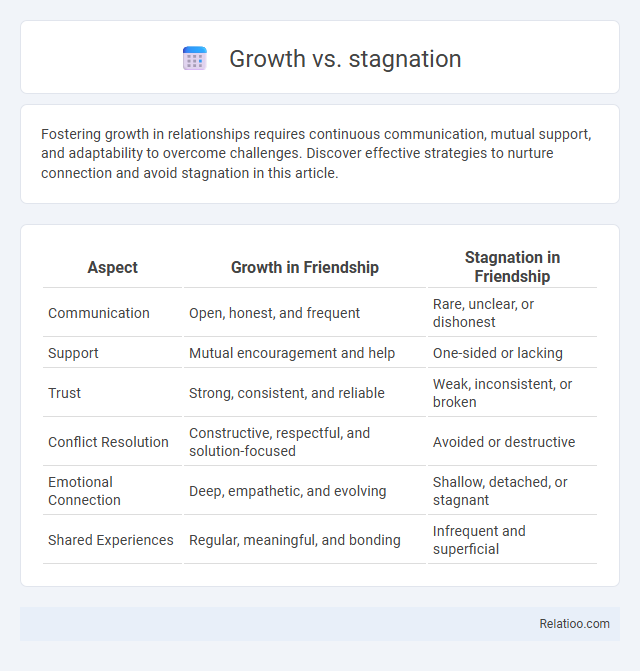
| Aspect | Growth in Friendship | Stagnation in Friendship |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Open, honest, and frequent | Rare, unclear, or dishonest |
| Support | Mutual encouragement and help | One-sided or lacking |
| Trust | Strong, consistent, and reliable | Weak, inconsistent, or broken |
| Conflict Resolution | Constructive, respectful, and solution-focused | Avoided or destructive |
| Emotional Connection | Deep, empathetic, and evolving | Shallow, detached, or stagnant |
| Shared Experiences | Regular, meaningful, and bonding | Infrequent and superficial |
Understanding Growth and Stagnation
Growth involves continuous progress and expansion in skills, knowledge, or business metrics, fostering innovation and resilience. Stagnation occurs when progress halts, leading to missed opportunities and potential decline in competitive edge. Understanding your position between growth and stagnation allows you to implement strategies that encourage development and avoid complacency.
Key Indicators of Personal Growth
Key indicators of personal growth include increased self-awareness, enhanced emotional intelligence, and the consistent achievement of meaningful goals. Measuring progress through reflection on behavior changes and resilience in facing challenges reveals growth compared to stagnation. Transformation is often marked by profound shifts in values or identity, signaling deeper, fundamental personal evolution.
Signs You May Be Stagnating
Signs you may be stagnating include a persistent lack of motivation, feeling stuck in repetitive routines, and minimal progress toward personal or professional goals. Your skills and knowledge may plateau, leading to frustration and decreased satisfaction in daily activities. Recognizing these indicators early allows you to shift focus toward growth and transformative change.
Psychological Impacts of Stagnation
Stagnation in psychological terms manifests as feelings of frustration, low motivation, and a diminished sense of purpose, impairing your overall well-being and mental health. Unlike growth, which fosters resilience and adaptability, stagnation often leads to increased anxiety, depression, and a decline in self-esteem. Recognizing these impacts is crucial for initiating transformation, which promotes psychological renewal and sustainable personal development.
The Role of Mindset in Driving Growth
Mindset plays a crucial role in driving growth by shaping how you perceive challenges and opportunities. A growth mindset encourages embracing learning, adapting to change, and pushing beyond comfort zones, which contrasts with stagnation driven by fixed mindset limitations. Transformation occurs when your mindset actively fosters continuous self-improvement and resilience, leading to profound personal and professional evolution.
Strategies to Overcome Stagnation
Implementing continuous innovation and agile methodologies drives growth by adapting to market changes and customer needs. Investing in employee development and fostering a culture of experimentation encourages transformation and breaks cycles of stagnation. Leveraging data analytics and customer feedback helps identify pain points and optimize business processes, accelerating progress beyond plateaus.
Growth vs Stagnation in the Workplace
Workplace growth is characterized by continuous skill development, increased productivity, and adaptation to new challenges, leading to enhanced employee engagement and organizational success. Stagnation occurs when employees encounter repetitive tasks, lack opportunities for advancement, and experience limited professional development, resulting in decreased motivation and higher turnover rates. Prioritizing growth strategies such as training programs, career pathing, and innovation fosters a dynamic work environment that mitigates stagnation and drives sustained performance.
Embracing Change for Sustainable Growth
Embracing change is essential for sustainable growth as it enables organizations to move beyond stagnation and foster continuous innovation. Transformation involves adopting new strategies, technologies, and mindsets that align with evolving market demands and customer needs. Prioritizing adaptability facilitates resilient growth trajectories and long-term competitive advantage.
Measuring Your Progress: Tools and Metrics
Tracking your progress in growth, stagnation, or transformation relies on precise tools and metrics such as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), Balanced Scorecards, and OKRs (Objectives and Key Results). Analytics platforms like Google Analytics and business intelligence tools like Tableau provide real-time data visualization and performance tracking. Regular assessment through customer feedback, employee engagement scores, and financial ratios ensures accurate measurement of development phases and strategic adjustments.
Cultivating a Growth-Oriented Lifestyle
Cultivating a growth-oriented lifestyle involves embracing challenges as opportunities to learn and improve, rather than settling into stagnation where comfort zones limit progress. Transformation occurs when consistent growth habits rewire your mindset, enabling continuous personal and professional development. Your commitment to adopting a growth mindset empowers resilience, adaptability, and sustained success in dynamic environments.
Infographic: Growth vs Stagnation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com