Self-compassion involves treating yourself with kindness during personal struggles, while self-forgiveness specifically addresses letting go of guilt for past mistakes to heal emotional pain. Explore the differences and benefits of self-compassion and self-forgiveness in this article.
Table of Comparison
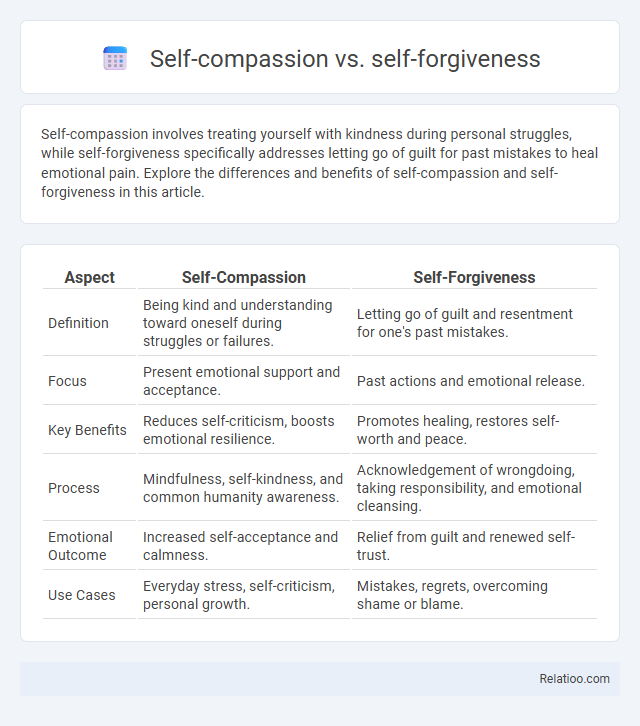
| Aspect | Self-Compassion | Self-Forgiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Being kind and understanding toward oneself during struggles or failures. | Letting go of guilt and resentment for one's past mistakes. |
| Focus | Present emotional support and acceptance. | Past actions and emotional release. |
| Key Benefits | Reduces self-criticism, boosts emotional resilience. | Promotes healing, restores self-worth and peace. |
| Process | Mindfulness, self-kindness, and common humanity awareness. | Acknowledgement of wrongdoing, taking responsibility, and emotional cleansing. |
| Emotional Outcome | Increased self-acceptance and calmness. | Relief from guilt and renewed self-trust. |
| Use Cases | Everyday stress, self-criticism, personal growth. | Mistakes, regrets, overcoming shame or blame. |
Understanding Self-Compassion: A Brief Overview
Understanding self-compassion involves recognizing your own suffering with kindness, mindfulness, and a sense of shared humanity, which fosters emotional resilience and well-being. Unlike self-forgiveness, which focuses on releasing guilt for past mistakes, self-compassion emphasizes treating yourself with the same care you would offer a friend during difficult times. Cultivating self-compassion enables you to navigate challenges without harsh self-criticism, promoting healing and personal growth.
What is Self-Forgiveness? Key Concepts Explained
Self-forgiveness involves acknowledging your mistakes, releasing self-judgment, and accepting your imperfections to foster emotional healing. It differs from self-compassion, which emphasizes kindness and understanding towards yourself during difficult times, and self-esteem, which reflects your overall sense of self-worth. Understanding self-forgiveness enables you to let go of guilt and move forward with greater resilience and inner peace.
Core Differences Between Self-Compassion and Self-Forgiveness
Self-compassion involves treating yourself with kindness and understanding during times of failure or suffering, focusing on emotional support and acceptance without harsh self-judgment. Self-forgiveness specifically addresses releasing guilt and resentment tied to past mistakes, enabling personal growth and healing by acknowledging responsibility without self-condemnation. Your journey towards emotional well-being benefits from recognizing that self-compassion nurtures ongoing kindness, while self-forgiveness facilitates letting go of blame for past actions.
The Role of Self-Blame in Both Practices
Self-blame plays a crucial role in differentiating self-compassion and self-forgiveness, as self-compassion encourages you to treat yourself with kindness despite perceived flaws or mistakes, reducing harsh judgment. In contrast, self-forgiveness specifically addresses overcoming guilt and self-blame from past actions to restore inner peace and personal growth. Understanding these distinctions helps you develop healthier emotional responses by balancing acceptance and accountability in your mental wellness journey.
Psychological Benefits of Self-Compassion
Self-compassion involves treating yourself with kindness and understanding during moments of failure or pain, promoting emotional resilience and reducing anxiety. Unlike self-forgiveness, which centers on releasing guilt for specific wrongdoings, self-compassion provides a broader psychological foundation that nurtures overall mental well-being by encouraging acceptance and mindfulness. You can experience lowered stress levels, greater emotional stability, and enhanced motivation by consistently practicing self-compassion in your daily life.
Emotional Healing Through Self-Forgiveness
Emotional healing through self-forgiveness involves acknowledging personal mistakes and releasing guilt, which fosters a deeper sense of inner peace compared to self-compassion or self-esteem alone. Self-forgiveness focuses specifically on overcoming regret by embracing acceptance and responsibility, whereas self-compassion emphasizes kindness towards oneself in moments of suffering. Integrating self-forgiveness into emotional healing accelerates recovery from psychological wounds by allowing individuals to move beyond past errors without self-condemnation.
Cultivating Self-Compassion: Practical Strategies
Cultivating self-compassion involves recognizing personal suffering and responding with kindness rather than judgment, which differs from self-forgiveness that centers on releasing guilt for past mistakes. Practical strategies for enhancing self-compassion include mindfulness practices, such as meditation and journaling, that promote awareness and acceptance of emotions. Research indicates that consistent self-compassion exercises improve emotional resilience, reduce anxiety, and foster psychological well-being.
Steps to Practice Genuine Self-Forgiveness
Practicing genuine self-forgiveness involves acknowledging your mistakes without judgment, accepting responsibility while understanding your human imperfections, and committing to personal growth to prevent repeated errors. You cultivate self-compassion by treating yourself with kindness and patience during this process, which differs from mere self-pity or avoidance of accountability. Steps to enhance self-forgiveness include reflective journaling, mindfulness meditation to process emotions, and affirmations that reinforce your inherent worth beyond past actions.
Integrating Self-Compassion and Self-Forgiveness for Personal Growth
Integrating self-compassion and self-forgiveness creates a powerful framework for personal growth by promoting emotional resilience and reducing self-criticism. Self-compassion involves treating oneself with kindness during struggles, while self-forgiveness focuses on releasing guilt and accepting past mistakes without judgment. Combining these practices enhances psychological well-being by fostering self-acceptance and encouraging constructive behavioral change.
Overcoming Barriers: Common Challenges and Solutions
Overcoming barriers in self-compassion, self-forgiveness, and self-acceptance involves recognizing common challenges such as harsh self-criticism, guilt, and unrealistic expectations. You can tackle these obstacles by practicing mindful awareness, reframing negative thoughts, and setting realistic goals to foster emotional resilience. Emphasizing consistent self-care routines and seeking supportive environments enhances your ability to cultivate a balanced and compassionate relationship with yourself.
Infographic: Self-compassion vs Self-forgiveness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com