Admission involves accepting the truth of a fact, while acknowledgment is the recognition or affirmation of a statement without necessarily agreeing. Explore the detailed differences and impacts of admission versus acknowledgment in relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
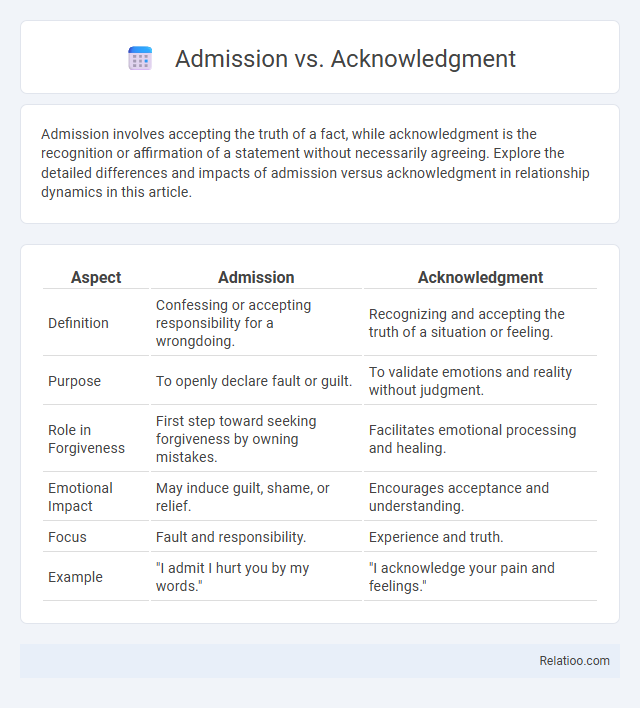
| Aspect | Admission | Acknowledgment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Confessing or accepting responsibility for a wrongdoing. | Recognizing and accepting the truth of a situation or feeling. |
| Purpose | To openly declare fault or guilt. | To validate emotions and reality without judgment. |
| Role in Forgiveness | First step toward seeking forgiveness by owning mistakes. | Facilitates emotional processing and healing. |
| Emotional Impact | May induce guilt, shame, or relief. | Encourages acceptance and understanding. |
| Focus | Fault and responsibility. | Experience and truth. |
| Example | "I admit I hurt you by my words." | "I acknowledge your pain and feelings." |
Understanding Admission and Acknowledgment
Understanding admission involves recognizing a statement's truthfulness or acceptance of responsibility in legal and medical contexts. Acknowledgment refers to the act of confirming receipt or awareness, often used in official communications and document verification. Admission signifies acceptance of facts or guilt, while acknowledgment focuses on verification or recognition without implying guilt.
Definitions: Admission vs Acknowledgment
Admission refers to the act of confessing or accepting the truth of something, often in a legal or formal context where a party concedes a fact. Acknowledgment, on the other hand, involves recognizing or affirming the existence or truth of a fact without necessarily conceding liability or fault. Understanding the distinction between admission and acknowledgment helps you accurately interpret statements or evidence in legal, academic, or professional settings.
Key Differences Between Admission and Acknowledgment
Admission involves formally accepting the truth or existence of a fact, often used in legal or medical contexts to establish liability or condition, while acknowledgment is the act of recognizing or confirming receipt of information or documents without necessarily agreeing with their content. You should note that admissions carry evidentiary weight in court, potentially impacting judgments, whereas acknowledgments primarily serve to validate communication or transaction authenticity. Understanding these distinctions ensures accurate interpretation of responses in official or legal processes.
Legal Implications of Admission
Admission in legal terms refers to a party's voluntary acknowledgment of a fact that can be used as evidence against them in a trial, often implying some degree of liability or guilt. Acknowledgment is a formal declaration or confirmation of a document's authenticity, such as signing a contract or deed, which primarily serves to validate the document but does not necessarily imply any culpability. The legal implications of admission are significant, as it can directly influence the outcome of litigation by providing proof that can establish liability, whereas acknowledgment mainly affects procedural validity and enforceability of documents.
Legal Implications of Acknowledgment
Acknowledgment in legal contexts serves as a formal declaration affirming the authenticity of a document, often required for deeds and contracts to be enforceable against third parties. Unlike admission, which involves conceding facts or liability within litigation, acknowledgment ensures that signatures are genuine, preventing fraud and enhancing evidentiary value. Legal implications of acknowledgment include its necessity for public recordation, affecting property rights and transaction validity under statutes like the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC).
Role in Evidence and Court Proceedings
Admission plays a critical role in court proceedings by serving as a voluntarily acknowledged fact that can be used as evidence against the admitting party, often streamlining the trial process. Acknowledgment, in contrast, typically refers to a formal declaration of a document's authenticity or receipt, which may support the chain of custody but does not directly establish substantive facts. Admission, distinguished from mere acknowledgment, carries probative value by effectively conceding a point relevant to the case, thereby influencing the court's assessment of evidence and credibility.
When to Use Admission or Acknowledgment
You should use admission when formally accepting or confessing to a fact, mistake, or responsibility, typically in legal or personal contexts. Acknowledgment is appropriate when recognizing receipt, understanding, or existence of information, documents, or contributions without implying fault. Admission involves an element of acceptance of truth, whereas acknowledgment signifies awareness or confirmation.
Common Examples in Legal Context
Admission in legal context refers to a party's voluntary acknowledgment of a fact or liability, often used as evidence against them in court. Acknowledgment involves a formal declaration, such as signing a document to confirm authenticity or receipt, commonly seen in contracts and legal notices. Unlike admission and acknowledgment, an admission is specifically a statement that accepts guilt or responsibility, frequently found in criminal cases or civil liability claims.
Impact on Case Outcomes
Admission in legal contexts refers to a party accepting the truth of a fact, which can streamline the case by reducing disputed issues. Acknowledgment involves recognizing a fact without conceding liability, often clarifying evidence without directly affecting outcome responsibility. Distinguishing between admission and acknowledgment significantly impacts case outcomes by determining the strength of evidence and the scope of contested facts.
Best Practices for Handling Admission and Acknowledgment
Effective handling of admission and acknowledgment requires clear protocols that define the distinction between accepting responsibility (admission) and simply acknowledging receipt of information or facts without conceding fault (acknowledgment). Your best practices include documenting statements precisely, avoiding ambiguous language, and training personnel to recognize when an admission could have legal implications versus a neutral acknowledgment. Consistent review and legal oversight ensure that admissions are managed cautiously to protect your organization's interests while acknowledgments maintain transparent communication.
Infographic: Admission vs Acknowledgment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com