Sibling relationships often shape emotional development, yet sibling favoritism can lead to feelings of jealousy and resentment within families. Explore this article to understand the impacts of favoritism on sibling bonds and strategies for fostering fairness.
Table of Comparison
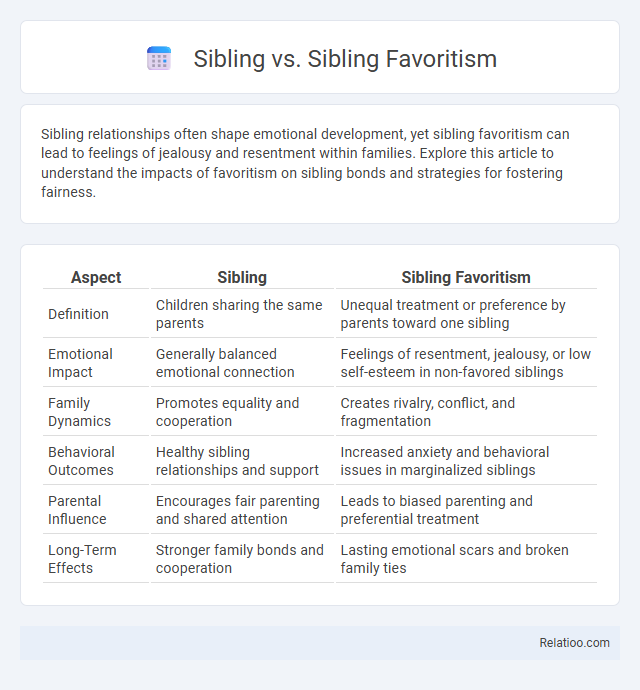
| Aspect | Sibling | Sibling Favoritism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Children sharing the same parents | Unequal treatment or preference by parents toward one sibling |
| Emotional Impact | Generally balanced emotional connection | Feelings of resentment, jealousy, or low self-esteem in non-favored siblings |
| Family Dynamics | Promotes equality and cooperation | Creates rivalry, conflict, and fragmentation |
| Behavioral Outcomes | Healthy sibling relationships and support | Increased anxiety and behavioral issues in marginalized siblings |
| Parental Influence | Encourages fair parenting and shared attention | Leads to biased parenting and preferential treatment |
| Long-Term Effects | Stronger family bonds and cooperation | Lasting emotional scars and broken family ties |
Understanding Sibling Favoritism: Definition and Impact
Sibling favoritism refers to parents or caregivers showing preferential treatment to one child over others, which can lead to feelings of resentment and rivalry among siblings. Understanding sibling favoritism involves recognizing subtle behaviors and patterns that unfairly advantage one sibling, impacting family dynamics and emotional well-being. Your awareness of these dynamics is crucial for promoting fairness and fostering a supportive environment for all children.
Common Signs of Favoritism Among Siblings
Common signs of favoritism among siblings include unequal distribution of parental attention, praise, and privileges, often leading to resentment and rivalry. One sibling may receive more emotional support, resources, or leniency, which negatively impacts family dynamics and individual self-esteem. Identifying patterns of favoritism, such as consistent favoritism in decision-making or disciplinary actions, helps in addressing imbalances and promoting sibling equality.
Psychological Effects on the Favored Child
Sibling favoritism significantly impacts the favored child's psychological well-being, often leading to increased pressure to meet parental expectations and anxiety over maintaining approval. Compared to general favoritism, sibling favoritism can exacerbate feelings of guilt, heightened responsibility, and social isolation within the family dynamic. These psychological effects may contribute to the favored child developing issues such as low self-esteem, perfectionism, or strained sibling relationships.
Consequences for the Less-Favored Sibling
Sibling favoritism often leads to feelings of neglect and lower self-esteem in the less-favored sibling, impacting their emotional well-being and social development. When parents explicitly or implicitly favor one child, the less-favored sibling may experience increased anxiety, depression, and difficulty forming healthy relationships. Your awareness of these dynamics can help in recognizing and addressing the long-term psychological consequences for the less-favored sibling.
Parental Causes of Sibling Favoritism
Parental causes of sibling favoritism often stem from unconscious biases, such as aligning more closely with one child's temperament, interests, or abilities, which can lead to unequal treatment. You may observe favoritism manifest through differential attention, praise, or discipline, impacting sibling relationships and individual self-esteem. Understanding these origins helps address and mitigate the long-term effects of favoritism on family dynamics.
Long-Term Effects on Sibling Relationships
Sibling relationships affected by favoritism often result in long-term emotional distance, decreased trust, and ongoing rivalry. Sibling favoritism can create resentment and insecurity, causing lasting damage to communication and cooperation between brothers and sisters. Understanding these dynamics helps you address and heal strained family bonds over time.
Recognizing Bias in Parenting Styles
Recognizing bias in parenting styles involves understanding the distinctions between sibling relationships, sibling favoritism, and general favoritism. Sibling favoritism occurs when parents consistently show preferential treatment toward one child, impacting your family dynamics and individual self-esteem. Identifying these subtle biases helps create a more balanced and fair environment that fosters healthy sibling relationships and emotional well-being.
Strategies to Prevent Sibling Favoritism
Sibling favoritism involves parents showing preferential treatment toward one child, which can cause rivalry and resentment between siblings. Strategies to prevent sibling favoritism include establishing consistent rules and consequences, recognizing each child's unique strengths, and ensuring equal quality time is spent with each child to foster a balanced family dynamic. By actively addressing these behaviors, you can promote fairness and reduce conflicts within your family.
Healing and Rebuilding Broken Sibling Bonds
Sibling favoritism creates divisions that damage trust and emotional connections, while sibling rivalry stems from natural competition and jealousy. Understanding how favoritism distorts relationships allows you to address pain and foster empathy among siblings. Healing broken sibling bonds involves open communication, validating each other's feelings, and rebuilding trust through consistent support and fairness.
Expert Advice: Creating a Balanced Family Environment
Expert advice on creating a balanced family environment emphasizes understanding the distinctions between sibling relationships, sibling favoritism, and general favoritism. Recognizing that sibling favoritism involves consistently preferring one child over others helps parents address potential emotional harm and promote fairness. Implementing open communication, setting clear expectations, and practicing equal attention foster harmony and reduce resentment among siblings.
Infographic: Sibling vs Sibling Favoritism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com