Parentification occurs when children assume adult responsibilities, often leading to emotional neglect where their own needs are unmet. Explore this article to understand the impacts of parentification and emotional neglect on healthy family dynamics.
Table of Comparison
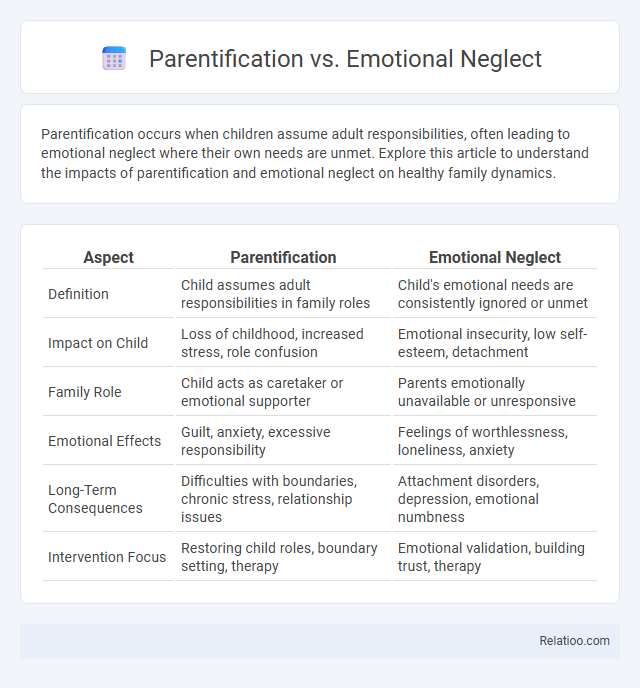
| Aspect | Parentification | Emotional Neglect |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child assumes adult responsibilities in family roles | Child's emotional needs are consistently ignored or unmet |
| Impact on Child | Loss of childhood, increased stress, role confusion | Emotional insecurity, low self-esteem, detachment |
| Family Role | Child acts as caretaker or emotional supporter | Parents emotionally unavailable or unresponsive |
| Emotional Effects | Guilt, anxiety, excessive responsibility | Feelings of worthlessness, loneliness, anxiety |
| Long-Term Consequences | Difficulties with boundaries, chronic stress, relationship issues | Attachment disorders, depression, emotional numbness |
| Intervention Focus | Restoring child roles, boundary setting, therapy | Emotional validation, building trust, therapy |
Understanding Parentification: Definition and Types
Parentification occurs when children assume parental roles, often sacrificing their own emotional needs to support caregivers, which is distinct from emotional neglect where the child's emotional needs are consistently unmet. There are two primary types of parentification: instrumental, involving practical tasks like cooking or caregiving, and emotional, where the child becomes a confidant or emotional support for the parent. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for identifying the impact on child development and addressing the associated psychological challenges effectively.
What Is Emotional Neglect in Childhood?
Emotional neglect in childhood occurs when a child's emotional needs for attention, affection, and support are consistently unmet by caregivers, leading to feelings of invisibility and unworthiness. Unlike parentification, where a child takes on adult responsibilities prematurely, emotional neglect involves the absence of necessary emotional nurturing rather than role reversal. Understanding your experience of emotional neglect is crucial for healing and developing healthy emotional connections.
Key Differences Between Parentification and Emotional Neglect
Parentification involves a child taking on adult responsibilities or emotional support roles within the family, often leading to role reversal and emotional burden. Emotional neglect occurs when a child's emotional needs are consistently ignored or unmet by caregivers, resulting in feelings of abandonment and low self-esteem. The key difference lies in parentification forcing children into caregiving roles, while emotional neglect deprives them of necessary emotional support and validation.
Causes and Risk Factors of Parentification
Parentification occurs when a child is assigned adult responsibilities prematurely, often due to parental emotional unavailability or family dysfunction, leading to role reversal between parent and child. Emotional neglect, a major risk factor for parentification, involves caregivers failing to meet a child's emotional needs, which forces the child to adopt caregiving roles to compensate. Your awareness of these causes helps in identifying unhealthy dynamics and promoting healthier family boundaries.
How Emotional Neglect Develops in Families
Emotional neglect develops in families when parents consistently fail to recognize, validate, or respond to their child's emotional needs, leading to feelings of invisibility and loneliness in the child. This neglect can create an environment where children may adopt parentification, taking on adult responsibilities prematurely to fill emotional gaps left by caregivers. Your understanding of these dynamics is crucial to breaking the cycle and fostering healthier family relationships.
Psychological Effects of Parentification
Parentification often leads to psychological effects such as chronic stress, anxiety, and difficulties in establishing healthy boundaries due to the child assuming adult responsibilities prematurely. Emotional neglect differs by depriving a child of necessary emotional support, causing feelings of worthlessness and attachment struggles, yet it may coexist with parentification where the child is burdened with caretaking roles. Understanding these distinctions highlights how parentification uniquely disrupts emotional development by forcing children into caregiver roles that hinder their own psychological growth.
Long-Term Impact of Emotional Neglect
Emotional neglect in childhood often leads to long-term difficulties such as impaired emotional regulation, low self-esteem, and challenges in forming secure attachments, contrasting with parentification where children assume adult responsibilities prematurely. Unlike parentification, which involves active role reversal, emotional neglect typically manifests through absence or unresponsiveness, resulting in feelings of invisibility and chronic emotional deprivation. The prolonged impact of emotional neglect can contribute to increased risk of mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety, highlighting the critical need for early intervention and therapeutic support.
Signs and Symptoms: Parentification vs Emotional Neglect
Parentification often manifests through signs such as excessive responsibility-taking, role reversal, and a child acting as a caregiver emotionally or physically for their parent. Emotional neglect, in contrast, is characterized by a lack of emotional responsiveness, unmet emotional needs, and feelings of invisibility or abandonment despite physical care. Both conditions may present symptoms like low self-esteem, anxiety, and difficulties in forming healthy relationships, but parentification typically involves over-functioning, whereas emotional neglect involves under-responsiveness to the child's emotional needs.
Healing and Recovery Strategies for Affected Individuals
Healing from parentification requires recognizing the blurred boundaries where children took on adult responsibilities, often leading to emotional neglect and unmet developmental needs. Your recovery strategy should include setting healthy boundaries, seeking therapy focused on trauma and attachment wounds, and developing self-compassion to reclaim your identity beyond imposed roles. Addressing these experiences through support groups and mindfulness practices enhances emotional regulation and fosters long-term resilience.
Supporting Children: Prevention and Intervention Approaches
Supporting children experiencing parentification, emotional neglect, or both requires targeted prevention and intervention approaches that prioritize emotional validation and boundary-setting. You can implement trauma-informed care and family therapy to address role reversals and unmet emotional needs, promoting healthy development. Early identification and training caregivers to recognize signs ensure children receive consistent support and relief from inappropriate caregiving responsibilities.
Infographic: Parentification vs Emotional Neglect
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com