Baby Boomers prioritize long-term commitment and traditional values in relationships, while Generation X tends to value independence and flexibility. Discover more insights on how these generational differences shape modern relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
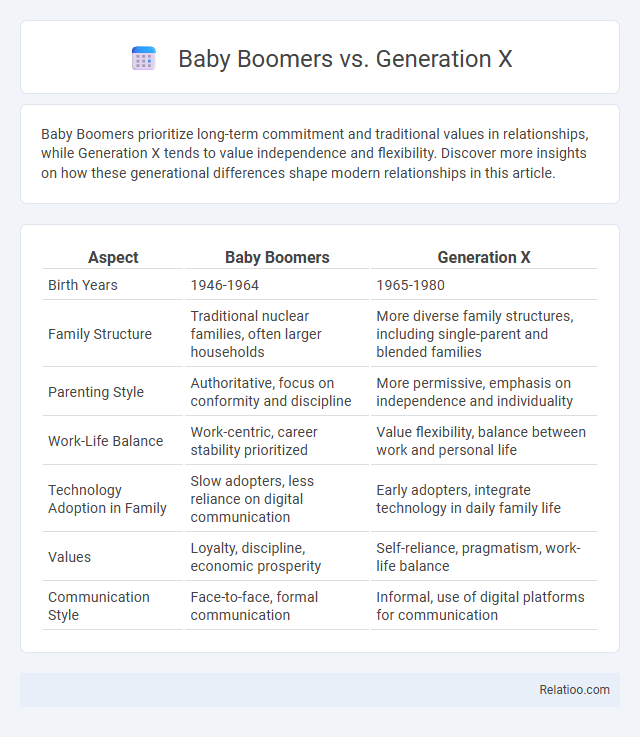
| Aspect | Baby Boomers | Generation X |
|---|---|---|
| Birth Years | 1946-1964 | 1965-1980 |
| Family Structure | Traditional nuclear families, often larger households | More diverse family structures, including single-parent and blended families |
| Parenting Style | Authoritative, focus on conformity and discipline | More permissive, emphasis on independence and individuality |
| Work-Life Balance | Work-centric, career stability prioritized | Value flexibility, balance between work and personal life |
| Technology Adoption in Family | Slow adopters, less reliance on digital communication | Early adopters, integrate technology in daily family life |
| Values | Loyalty, discipline, economic prosperity | Self-reliance, pragmatism, work-life balance |
| Communication Style | Face-to-face, formal communication | Informal, use of digital platforms for communication |
Defining Baby Boomers and Generation X
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, are characterized by their post-World War II upbringing, strong work ethic, and significant influence on economic growth and cultural shifts. Generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, is known for its adaptability, independence, and being the first generation to grow up with personal computers and the internet. The generational gap between Baby Boomers and Generation X often reflects differences in values, technology use, and communication styles shaped by distinct historical and social experiences.
Historical Context and Key Events
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, experienced post-World War II economic growth, the civil rights movement, and the Vietnam War, shaping their values around stability and social change. Generation X, born from 1965 to 1980, grew up during the Cold War, the rise of personal computing, and economic recessions, fostering a mindset of independence and adaptability. The generational gap between Baby Boomers and Generation X reflects differing responses to technology, work ethics, and cultural shifts influenced by these distinct historical contexts and key events.
Core Values and Beliefs
Baby Boomers prioritize loyalty, hard work, and a strong sense of community, while Generation X values independence, self-reliance, and work-life balance. The generational gap between these groups is often defined by differences in technology adoption, communication styles, and attitudes toward authority and career. Understanding these core values and beliefs can help you bridge gaps in the workplace and foster better intergenerational collaboration.
Work Ethic and Career Attitudes
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, are characterized by a strong work ethic and loyalty to long-term career goals, often valuing job stability and hierarchical advancement. Generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, tends to prioritize work-life balance, adaptability, and skepticism toward corporate loyalty, favoring skill development and career flexibility. The generational gap between Boomers and Gen X manifests in differing views on career commitment and authority, influencing workplace dynamics and management styles.
Technology Adoption and Digital Skills
Baby Boomers typically adopt technology at a slower pace compared to Generation X, who display higher proficiency in digital skills due to exposure during their formative years. Generation X bridges the generational gap by integrating traditional work ethics with modern technological tools, enhancing productivity and communication. This contrast in technology adoption highlights the importance of tailored digital literacy programs to address varying skill levels across generations.
Family Dynamics and Parenting Styles
Baby Boomers tend to value traditional family roles and authoritative parenting, emphasizing stability and discipline, while Generation X favors more flexible family dynamics with an emphasis on independence and open communication. The generational gap reflects differing attitudes toward work-life balance, technology use, and child-rearing philosophies, often leading to varied expectations within multigenerational households. Understanding these contrasts helps you navigate and appreciate the evolving nature of family relationships across generations.
Financial Habits and Retirement Planning
Baby Boomers prioritize traditional savings and pension plans, often leveraging home equity to secure retirement, while Generation X tends to adopt a mix of 401(k) contributions and diversified investments reflecting a cautious yet proactive approach to financial planning. The generational gap influences risk tolerance and spending habits, with Generation X typically exhibiting more financial skepticism due to economic downturn experiences, contrasting with Baby Boomers' stronger reliance on employer-sponsored retirement benefits. Understanding these differences helps tailor retirement planning strategies to align with each generation's unique financial behavior and long-term goals.
Social Views and Political Leanings
Baby Boomers generally exhibit more traditional social views and historically leaned towards conservative politics, though many shifted progressive in recent decades. Generation X tends to hold more moderate and pragmatic social perspectives, showing greater acceptance of diversity and often favoring centrist or independent political stances. The generational gap reflects these divergent social attitudes and political leanings, influencing public policy debates and electoral outcomes across the United States.
Communication Preferences
Baby Boomers prefer face-to-face communication and phone calls, valuing formality and direct interaction, while Generation X favors emails and text messages for efficiency and flexibility. The generational gap reflects contrasting communication styles, where Baby Boomers prioritize personal connection and Generation X embraces digital channels for quick, concise exchanges. Understanding these preferences enhances intergenerational collaboration and reduces misunderstandings in workplaces and social environments.
Intergenerational Collaboration and Challenges
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, often prioritize loyalty and experience in the workplace, while Generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, values independence and technological adaptability. The generational gap between these groups presents challenges such as differing communication styles and work expectations, yet fostering intergenerational collaboration can leverage Baby Boomers' institutional knowledge alongside Generation X's digital proficiency. Organizations that implement cross-generational mentorship and inclusive practices benefit from enhanced innovation, employee engagement, and a more cohesive work environment.
Infographic: Baby Boomers vs Generation X
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com