Joint families foster strong multi-generational bonds through shared responsibilities and traditions, while blended families navigate unique dynamics by uniting members from previous relationships. Discover key differences and insights on how each family structure shapes relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
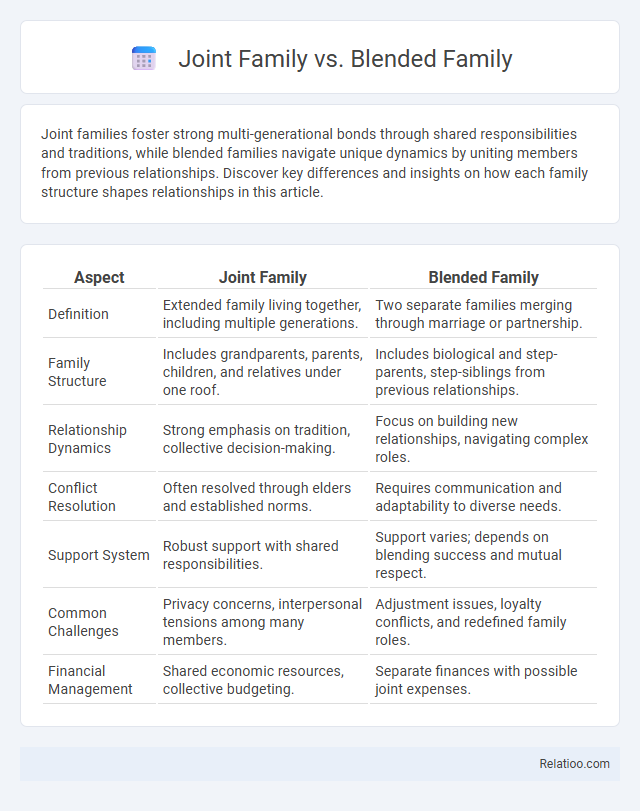
| Aspect | Joint Family | Blended Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extended family living together, including multiple generations. | Two separate families merging through marriage or partnership. |
| Family Structure | Includes grandparents, parents, children, and relatives under one roof. | Includes biological and step-parents, step-siblings from previous relationships. |
| Relationship Dynamics | Strong emphasis on tradition, collective decision-making. | Focus on building new relationships, navigating complex roles. |
| Conflict Resolution | Often resolved through elders and established norms. | Requires communication and adaptability to diverse needs. |
| Support System | Robust support with shared responsibilities. | Support varies; depends on blending success and mutual respect. |
| Common Challenges | Privacy concerns, interpersonal tensions among many members. | Adjustment issues, loyalty conflicts, and redefined family roles. |
| Financial Management | Shared economic resources, collective budgeting. | Separate finances with possible joint expenses. |
Understanding Joint Families: Definition and Structure
Joint families consist of multiple generations living under one roof, sharing resources, responsibilities, and decision-making processes. The structure typically includes grandparents, parents, children, and sometimes extended relatives, emphasizing collective support and strong familial bonds. This arrangement fosters interdependence, cultural continuity, and shared economic stability within the household.
Blended Families Explained: Key Characteristics
Blended families consist of members from two previously separate families, typically formed after remarriage, combining biological children and stepchildren under one household. Key characteristics include navigating complex relationships, establishing new family roles, and adapting to varied parenting styles. Effective communication and flexibility are essential to foster trust and cohesion within blended families.
Origins and Evolution of Joint and Blended Families
Joint families originated primarily in agrarian societies where extended kinship ties supported collective labor and resource sharing, fostering economic stability and social cohesion. Blended families emerged more prominently in modern contexts, often resulting from increased divorce and remarriage rates, reflecting evolving social norms and diverse family structures. Both family types continuously adapt to cultural, economic, and demographic shifts, influencing their internal dynamics and societal roles.
Cultural Perspectives on Family Systems
Cultural perspectives significantly shape the dynamics of joint families and blended families, influencing how roles and responsibilities are distributed among members. Joint families, prevalent in many Asian and African cultures, emphasize collective decision-making and multigenerational living, fostering strong familial bonds and shared resources. Your understanding of these family systems can help navigate cultural expectations and promote harmony within diverse household structures.
Emotional Dynamics in Joint vs Blended Families
Emotional dynamics in joint families often revolve around deep-rooted traditions, shared responsibilities, and collective decision-making, fostering a strong sense of belonging and support among extended relatives. In contrast, blended families face unique emotional challenges like integrating different family cultures, managing loyalty conflicts, and establishing new bonds, which require open communication and adaptability. Your ability to navigate these emotional landscapes significantly impacts family harmony and individual well-being in both family structures.
Parenting Styles and Challenges Compared
Joint families often follow traditional parenting styles with collective decision-making and shared responsibilities, fostering strong intergenerational bonds but facing challenges like limited privacy and conflicting authority. Blended families, composed of step-parents and step-siblings, require adaptive parenting approaches emphasizing flexibility, communication, and conflict resolution to address complex emotional dynamics and loyalty issues. Parenting challenges in both family structures revolve around balancing authority, managing diverse expectations, and nurturing healthy relationships amidst evolving family roles.
Financial Management in Different Family Types
Financial management in joint families involves pooling resources from multiple members, allowing for shared expenses and collective savings, which can lead to greater economic stability but also requires effective communication to avoid conflicts. Blended families often face complexities in budgeting and asset allocation due to varying financial obligations and individual spending habits, necessitating clear agreements and transparency to ensure fairness. Family dynamics significantly influence financial decision-making processes, where trust, role clarity, and conflict resolution abilities are crucial for managing joint finances successfully in any family structure.
Social Support and Conflict Resolution
Joint families provide extensive social support through shared responsibilities and deep-rooted cultural bonds, enhancing collective problem-solving and emotional resilience. Blended families offer diverse perspectives and adaptive conflict resolution strategies, though they may face challenges in establishing trust and unity due to differing backgrounds. Your ability to navigate family dynamics improves by recognizing these unique social frameworks, fostering harmony and effective communication within any family structure.
Impact on Children’s Development and Well-being
Joint families, characterized by multiple generations living together, provide children with a strong support network, fostering emotional security and social skills through constant interaction. Blended families, formed by merging two separate family units, require children to adapt to new relationships, which can enhance resilience but also cause stress if not managed with clear communication. Your child's development and well-being are deeply influenced by the family dynamics present, making it crucial to cultivate a nurturing environment that promotes stability, understanding, and healthy emotional expression.
Choosing the Right Family Structure: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right family structure involves evaluating emotional support, stability, and cultural values present in joint and blended families. Joint families offer shared responsibilities and deep-rooted traditions, while blended families emphasize adaptability and co-parenting dynamics between biological and step-relatives. Factors such as communication patterns, conflict resolution styles, and individual needs significantly influence the optimal family environment.
Infographic: Joint Family vs Blended Family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com