Accommodation involves altering existing cognitive schemas to incorporate new information, while assimilation integrates new information into pre-existing schemas without changing them. Discover more about how accommodation and assimilation shape relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
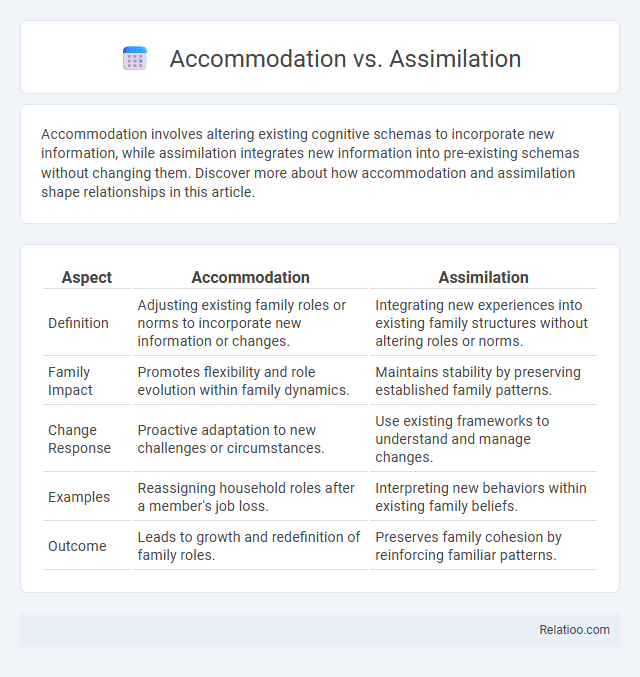
| Aspect | Accommodation | Assimilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusting existing family roles or norms to incorporate new information or changes. | Integrating new experiences into existing family structures without altering roles or norms. |
| Family Impact | Promotes flexibility and role evolution within family dynamics. | Maintains stability by preserving established family patterns. |
| Change Response | Proactive adaptation to new challenges or circumstances. | Use existing frameworks to understand and manage changes. |
| Examples | Reassigning household roles after a member's job loss. | Interpreting new behaviors within existing family beliefs. |
| Outcome | Leads to growth and redefinition of family roles. | Preserves family cohesion by reinforcing familiar patterns. |
Introduction to Accommodation and Assimilation
Accommodation and assimilation are fundamental processes in cognitive development that describe how individuals adapt to new information. Assimilation involves integrating new experiences into existing mental frameworks without changing them, while accommodation requires modifying those frameworks to incorporate new experiences. These complementary mechanisms enable learners to balance understanding and flexibility when encountering unfamiliar concepts.
Defining Key Concepts: Accommodation vs Assimilation
Accommodation involves altering your existing cognitive schemas to incorporate new information, while assimilation refers to integrating new experiences into pre-existing schemas without changing them. These processes are fundamental to understanding cognitive development, as they enable your mind to adapt and organize knowledge effectively. Distinguishing between accommodation and assimilation helps clarify how learning and adaptation occur when encountering novel stimuli.
Historical Background and Theoretical Foundations
Accommodation and assimilation originate from Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development, describing how individuals adapt to new information: assimilation integrates new data into existing schemas, while accommodation modifies schemas to incorporate novel experiences. These processes highlight the dynamic nature of learning and cognitive growth, reflecting Piaget's constructivist approach that knowledge is actively constructed by the learner. Historical foundations trace back to Piaget's early 20th-century work, emphasizing the interplay between mental structures and environmental interactions in shaping human understanding.
Accommodation in Cognitive Development
Accommodation in cognitive development involves modifying existing mental schemas to incorporate new information that does not fit previous understandings, allowing Your brain to adapt and grow more accurately. This process contrasts with assimilation, where new information is integrated into existing schemas without changing them, and equilibrium, which is the balance between assimilation and accommodation ensuring stable cognitive growth. Accommodation is crucial for learning complex concepts and adjusting to novel experiences effectively.
Assimilation in Cognitive Development
Assimilation in cognitive development involves integrating new information into existing mental schemas without changing their structure. This process allows individuals, especially children, to interpret new experiences based on prior knowledge, facilitating learning and adaptation. Compared to accommodation, which modifies schemas to incorporate new data, assimilation emphasizes the use of pre-established cognitive frameworks to understand the environment.
Key Differences Between Accommodation and Assimilation
Accommodation involves modifying your existing cognitive schemas to incorporate new information, while assimilation refers to interpreting new experiences based on pre-existing schemas. The key difference lies in how your mind adapts: accommodation changes the structure of your knowledge, whereas assimilation integrates information without altering the original schemas. Understanding these processes is crucial for grasping human learning and adaptation.
Examples of Accommodation and Assimilation in Real Life
Accommodation occurs when individuals change their existing cognitive schemas to incorporate new information, such as a child learning that a dolphin is not a fish but a mammal after encountering new facts. Assimilation involves integrating new experiences into existing schemas without altering them, like a child calling all four-legged animals "dogs" because they fit their existing concept of a dog. In real life, a student adjusting their understanding of history to include new perspectives demonstrates accommodation, while accepting new vocabulary within known language rules exemplifies assimilation.
Importance in Learning and Education
Accommodation, assimilation, and equilibration are critical cognitive processes in learning, with accommodation involving modifying existing knowledge structures to incorporate new information. Assimilation allows you to integrate new experiences into your current understanding without altering the framework, ensuring information retention and comprehension. Balancing these processes promotes cognitive development, enabling learners to adapt effectively and deepen their understanding in educational settings.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Accommodation faces challenges in maintaining cultural integrity while adapting to new social environments, often criticized for causing identity dilution. Assimilation is criticized for promoting conformity and suppressing minority cultures, leading to loss of cultural diversity and social inequity. Accommodation struggles with practical implementation issues, such as resource allocation and policy enforcement, which can hinder effective integration in multicultural societies.
Conclusion: Balancing Accommodation and Assimilation
Balancing accommodation and assimilation is crucial for effective cognitive development, allowing individuals to adapt to new information while integrating it into existing frameworks. Accommodation involves modifying existing schemas to incorporate novel experiences, enhancing learning flexibility. Assimilation, on the other hand, reinforces current knowledge by fitting new information into preexisting schemas, promoting consistency and stability in understanding.
Infographic: Accommodation vs Assimilation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com