Status expectations refer to the anticipated social value or prestige assigned to an individual within a relationship, while role expectations pertain to the specific behaviors and responsibilities assumed by that individual. Explore the distinctions and impacts of status versus role expectations on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
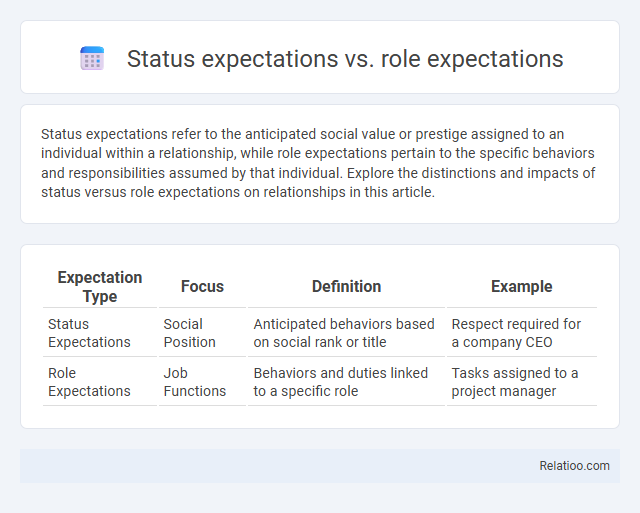
| Expectation Type | Focus | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Status Expectations | Social Position | Anticipated behaviors based on social rank or title | Respect required for a company CEO |
| Role Expectations | Job Functions | Behaviors and duties linked to a specific role | Tasks assigned to a project manager |
Introduction to Status Expectations and Role Expectations
Status expectations refer to the societal assumptions and behaviors anticipated from an individual based on their social position, while role expectations involve the specific duties and norms linked to a particular position or function within a group. Understanding the distinction between status expectations and role expectations is crucial for analyzing social interactions and organizational behavior. Status itself denotes the recognized social standing or rank held by an individual, which shapes both the expectations placed upon them and their interactions within a community.
Defining Status Expectations
Status expectations refer to the anticipated behaviors and privileges associated with a person's hierarchical position within a social structure, influencing how others perceive and interact with them. These expectations shape social interactions by establishing normative patterns tied to status symbols, income levels, or professional titles. Defining status expectations involves understanding the implicit social rules and cultural norms that govern deference, authority, and access to resources based on perceived social rank.
Defining Role Expectations
Role expectations define the specific behaviors, responsibilities, and duties associated with a particular position within an organization or social structure. These expectations guide individuals on how to perform their roles effectively, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and social norms. Clear role expectations reduce ambiguity, enhance accountability, and improve overall group functioning by establishing predictable patterns of conduct.
Key Differences between Status and Role Expectations
Status expectations refer to the anticipated behaviors and privileges associated with a person's social position, while role expectations involve the specific duties and responsibilities tied to a particular function within a group or organization. Key differences between status and role expectations include the fact that status is linked to social hierarchy and prestige, influencing how individuals are perceived and treated, whereas role expectations are task-oriented and define what actions are appropriate for a given position. Status expectations tend to be more subjective and socially constructed, whereas role expectations are often clearly outlined and formalized within institutional settings.
Theoretical Foundations of Expectations in Sociology
Status expectations refer to the anticipated behaviors and attitudes associated with a person's social position, while role expectations pertain to the duties and norms linked to their specific social role within a group or organization. Status in sociology represents a socially defined position or rank that confers a set of expectations, influencing how individuals interact and are perceived in society. Theoretical foundations by scholars like Ralph Linton and Robert K. Merton emphasize that the interplay between status and role expectations structures social order and guides individual behavior within social systems.
Status Expectations in Social Hierarchies
Status expectations in social hierarchies define the anticipated behaviors and privileges associated with a person's perceived social rank. These expectations influence how others interact with you and shape your opportunities for influence and respect within various social settings. Understanding status expectations helps clarify the complex dynamics between one's role expectations and actual status in group interactions.
Role Expectations within Organizations and Groups
Role expectations within organizations and groups define the specific behaviors, responsibilities, and norms associated with a given position or function, guiding individuals on how to perform their duties effectively. These expectations influence group dynamics by establishing clear boundaries and accountability, which enhances coordination and goal achievement. Unlike status expectations, which relate to perceived social prestige or rank, role expectations focus on the functional aspects tied to organizational goals and workflow.
Impact of Conflicting Expectations on Behavior
Conflicting expectations between status and role can cause significant stress and confusion in your social or professional behavior, often leading to decreased performance and strained relationships. When status expectations demand authority or prestige while role expectations require cooperation and humility, individuals may struggle to align their actions, resulting in inconsistent or unpredictable behavior. Understanding and managing these tensions is crucial for maintaining effective communication and achieving desired outcomes in group dynamics.
Real-World Examples: Reconciling Status and Role Demands
Status expectations often shape how individuals are perceived within social hierarchies, influencing behaviors aligned with prestige or authority, while role expectations emphasize the duties and responsibilities associated with a specific position. In real-world contexts, a high-status executive may face conflicting demands between embodying leadership charisma (status expectations) and adhering to strict corporate protocols (role expectations). Reconciling these tensions requires balancing social influence with task performance to maintain legitimacy and effectiveness in professional environments.
Conclusion: Navigating Status and Role Expectations
Navigating status and role expectations requires understanding that status reflects an individual's social standing or prestige, while roles denote the expected behaviors tied to specific positions within a group. Discrepancies between status and role expectations can create tension, making it essential to align perceived status with role responsibilities to foster social harmony and effective interaction. Mastery of this alignment enhances both individual satisfaction and group cohesion by clarifying expectations and reducing conflicts.
Infographic: Status expectations vs Role expectations
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com