Social workers provide holistic support by addressing social and environmental factors, while psychologists specialize in diagnosing and treating mental health disorders through therapy. Discover the key differences and how each professional can help you in this article.
Table of Comparison
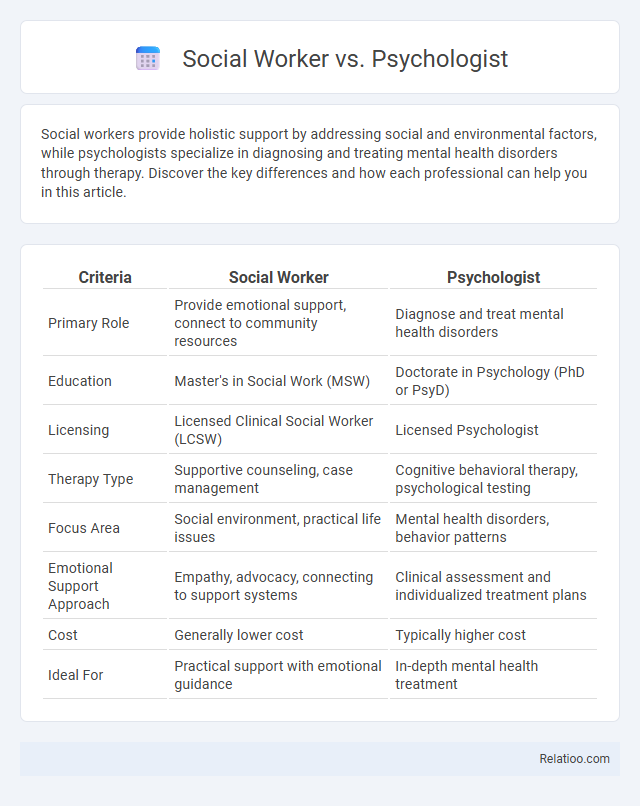
| Criteria | Social Worker | Psychologist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Provide emotional support, connect to community resources | Diagnose and treat mental health disorders |
| Education | Master's in Social Work (MSW) | Doctorate in Psychology (PhD or PsyD) |
| Licensing | Licensed Clinical Social Worker (LCSW) | Licensed Psychologist |
| Therapy Type | Supportive counseling, case management | Cognitive behavioral therapy, psychological testing |
| Focus Area | Social environment, practical life issues | Mental health disorders, behavior patterns |
| Emotional Support Approach | Empathy, advocacy, connecting to support systems | Clinical assessment and individualized treatment plans |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
| Ideal For | Practical support with emotional guidance | In-depth mental health treatment |
Introduction to Social Workers and Psychologists
Social workers focus on connecting individuals with community resources and support systems to improve overall well-being, addressing social and environmental factors impacting mental health. Psychologists specialize in assessing, diagnosing, and treating mental health conditions through evidence-based therapies, providing in-depth psychological evaluations. Understanding the distinct roles of social workers and psychologists helps you choose the right professional for your mental health or social support needs.
Educational Requirements: Social Worker vs Psychologist
Social workers typically require a Bachelor of Social Work (BSW) or Master of Social Work (MSW) degree, with licensure varying by state and often involving supervised clinical hours. Psychologists generally need a Doctorate in Psychology (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) to practice independently, including extensive supervised internships and passing licensing exams. Educational pathways for social workers are more practice-oriented with an emphasis on direct client services, whereas psychologists receive advanced training in psychological assessment, research, and therapy techniques.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Social workers provide community support, connect clients with resources, and advocate for social justice to improve overall well-being. Psychologists assess and diagnose mental health issues, deliver therapy, and conduct research to understand behavior and mental processes. Care professionals focus on daily living assistance, personal support, and ensuring safety for individuals with physical or cognitive challenges, directly impacting Your quality of life.
Work Settings and Environments
Social workers commonly operate in diverse environments such as hospitals, schools, and community organizations, addressing social and emotional challenges through direct client support. Psychologists typically work in clinical settings, private practices, or research institutions, focusing on assessment, diagnosis, and therapeutic interventions for mental health disorders. Care professionals are often found in residential facilities, nursing homes, or home care environments, providing hands-on assistance and support to individuals with physical or cognitive disabilities.
Areas of Specialization
Social workers specialize in community resources, case management, and advocacy for vulnerable populations, often focusing on social justice and client support systems. Psychologists concentrate on mental health assessments, psychotherapy, and behavioral interventions, with expertise in clinical, counseling, or neuropsychology specialties. Care professionals provide direct assistance with daily living activities and medical support, emphasizing practical care in settings like nursing homes, hospitals, or home care services tailored to individual needs.
Therapeutic Approaches and Techniques
Social workers employ a holistic therapeutic approach integrating counseling, case management, and advocacy to address clients' social and environmental factors. Psychologists utilize evidence-based techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychodynamic therapy, and diagnostic assessments to treat mental health disorders through clinical interventions. Your choice between these professionals depends on whether you need comprehensive social support or specialized psychological treatment focusing on mental health.
Licensing and Certification Differences
Social workers must obtain a state license, typically requiring a Master of Social Work (MSW) and passing the Association of Social Work Boards (ASWB) exam, while psychologists need a doctoral degree (PhD or PsyD) and must pass the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology (EPPP) to be licensed. Care providers, often including certified nursing assistants or personal care aides, require certification specific to their role, such as a State Nurse Aide Registry listing or equivalent. Understanding these licensing and certification differences helps ensure you receive qualified support tailored to your mental health or care needs.
Salary and Career Outlook
Social workers earn a median annual salary of approximately $50,000 to $60,000, with job growth projected at 9% due to increased demand for social services. Psychologists typically have higher median salaries around $80,000 to $100,000, driven by specialized skills and clinical roles, and their career outlook is favorable with about 8% growth expected. Careers in care roles, including caregivers and personal care aides, usually offer lower salaries near $25,000 to $30,000, but job opportunities are expanding rapidly at a 17% growth rate due to aging populations and increased need for support services.
How to Choose Between Social Work and Psychology
Choosing between social work and psychology depends on your career goals, preferred work environment, and approach to client support. Social workers often engage in community-based services, advocacy, and case management, focusing on practical assistance and social justice, while psychologists primarily conduct assessments, therapy, and research to address mental health and behavior. Evaluate the required education paths, licensure, and desired client interactions to determine which field aligns best with your professional interests and personal strengths.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Social workers focus on providing support and connecting You with community resources, while psychologists specialize in diagnosing and treating mental health disorders through therapy and assessments. Care providers offer hands-on assistance with daily living activities, emphasizing physical and emotional well-being. Understanding these distinct roles helps in selecting the right professional to meet Your mental health and support needs.
Infographic: Social Worker vs Psychologist
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com