Dependent coping relies on external support systems for emotional relief, while independent coping emphasizes personal resilience and self-management. Explore this article to understand which coping style better supports relationship health and personal well-being.
Table of Comparison
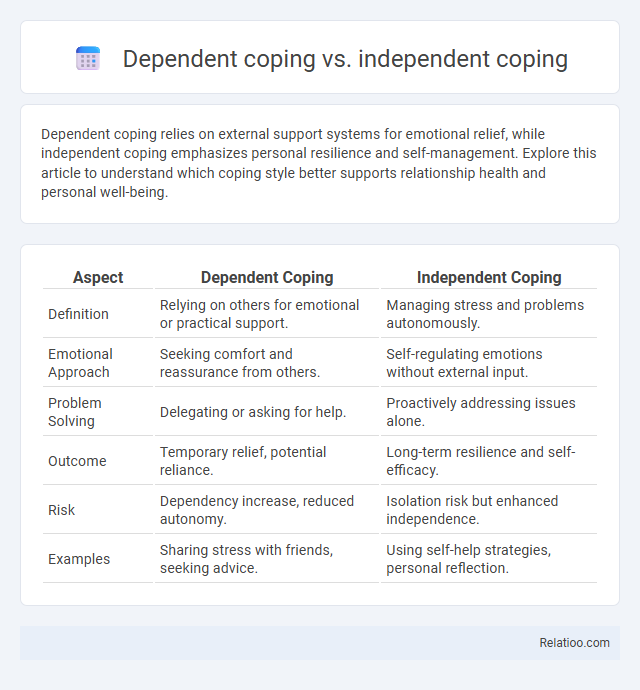
| Aspect | Dependent Coping | Independent Coping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relying on others for emotional or practical support. | Managing stress and problems autonomously. |
| Emotional Approach | Seeking comfort and reassurance from others. | Self-regulating emotions without external input. |
| Problem Solving | Delegating or asking for help. | Proactively addressing issues alone. |
| Outcome | Temporary relief, potential reliance. | Long-term resilience and self-efficacy. |
| Risk | Dependency increase, reduced autonomy. | Isolation risk but enhanced independence. |
| Examples | Sharing stress with friends, seeking advice. | Using self-help strategies, personal reflection. |
Understanding Coping Mechanisms: Dependent vs Independent
Understanding coping mechanisms involves recognizing the differences between dependent and independent coping strategies, where dependent coping relies on external support from others and independent coping emphasizes personal resilience and self-reliance. Your ability to identify which approach suits your situation can significantly enhance stress management effectiveness by tailoring techniques to your emotional and social resources. Skilled stress management involves integrating both coping styles to maintain psychological balance and improve adaptive responses to challenging circumstances.
Defining Dependent Coping: Characteristics and Examples
Dependent coping involves relying on external support systems, such as friends, family, or professionals, to manage stress and emotions. Characteristics include seeking advice, emotional validation, and assistance, often reflecting lower self-reliance in stress situations. Examples of dependent coping are talking to a therapist during anxiety episodes or leaning on close relationships for comfort during crises.
Independent Coping Explained: Key Traits and Strategies
Independent coping involves proactive problem-solving, self-reliance, and emotional regulation to manage stress effectively. Key traits include resilience, autonomy, and a strong sense of control, enabling you to address challenges without relying heavily on external support. Strategies such as mindfulness, goal-setting, and adaptive thinking empower your ability to navigate stress and build long-term psychological well-being.
Psychological Factors Influencing Coping Styles
Psychological factors influencing coping styles include personality traits, self-efficacy, and cognitive appraisal processes, which shape whether individuals adopt dependent or independent coping strategies. Dependent coping often relies on external support and social networks, whereas independent coping emphasizes personal control and problem-solving skills. Effective stress management integrates understanding of these coping styles to tailor interventions that enhance adaptive responses and psychological resilience.
Advantages of Dependent Coping in Stressful Situations
Dependent coping offers the advantage of leveraging social support networks, which can provide emotional comfort and practical assistance during stressful situations. Your ability to share concerns and receive feedback often leads to reduced psychological distress and enhanced resilience. This approach fosters connectedness, making stressful experiences more manageable compared to solely relying on independent coping strategies.
Benefits of Independent Coping for Emotional Wellbeing
Independent coping enhances emotional wellbeing by fostering self-reliance and resilience, allowing you to handle stress more effectively without over-dependence on others. This coping style promotes a stronger sense of control and personal empowerment, which reduces anxiety and improves mood regulation. Developing independent coping skills strengthens your ability to adapt to challenges, leading to sustained mental health and emotional stability.
Risks and Drawbacks of Dependent Coping
Dependent coping, characterized by relying heavily on others for emotional support, poses risks such as reduced self-efficacy and increased vulnerability to stress when social support is unavailable. Independent coping, emphasizing personal resilience and problem-solving, often fosters long-term stress management skills but may lead to isolation if overused. You should balance coping strategies to mitigate the drawbacks of dependency and enhance your overall stress resilience.
Challenges and Limitations of Independent Coping
Independent coping often faces challenges such as limited emotional support and a reduced ability to seek help during high-stress situations, which can lead to ineffective stress management. Individuals relying solely on independent coping may struggle with isolation, making it difficult to gain diverse perspectives or resources to alleviate stress. These limitations highlight the importance of integrating social support mechanisms to enhance overall coping strategies and improve stress resilience.
Choosing the Right Coping Style: Situational Factors
Choosing the right coping style depends heavily on situational factors such as the nature and controllability of the stressor. Dependent coping involves seeking support from others, which is beneficial in situations requiring shared resources or emotional validation, while independent coping relies on self-reliance and problem-solving skills, ideal for challenges you can directly manage. Effective stress management requires assessing your context to determine when to engage social support or employ personal strategies, optimizing your resilience and mental health.
Enhancing Resilience: Balancing Dependent and Independent Coping
Enhancing resilience involves balancing dependent coping, which relies on social support networks, and independent coping, emphasizing personal problem-solving and self-regulation. Effective stress management integrates both strategies, enabling you to draw strength from relationships while cultivating internal resources to navigate adversity. Prioritizing this balance improves psychological flexibility and promotes long-term mental well-being.
Infographic: Dependent coping vs independent coping
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com