Public spaces foster social interaction and community engagement, while private spaces provide intimacy and personal comfort. Explore the dynamics between these environments and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
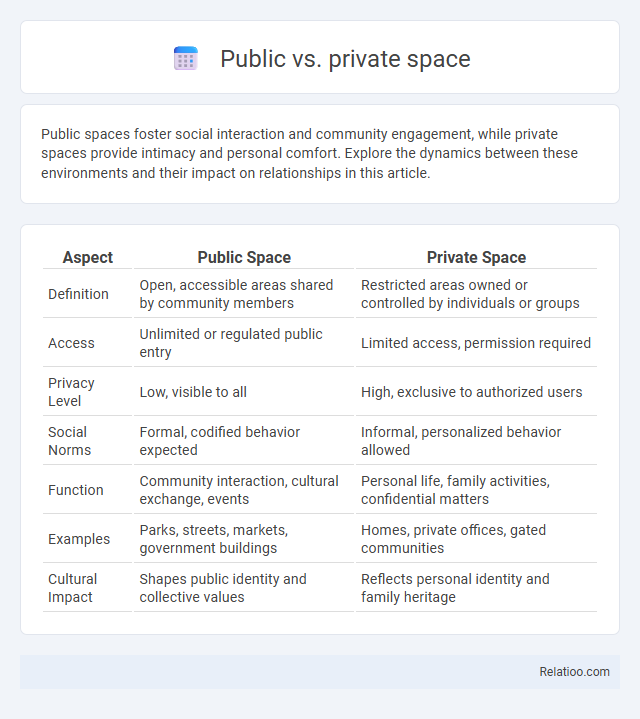
| Aspect | Public Space | Private Space |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Open, accessible areas shared by community members | Restricted areas owned or controlled by individuals or groups |
| Access | Unlimited or regulated public entry | Limited access, permission required |
| Privacy Level | Low, visible to all | High, exclusive to authorized users |
| Social Norms | Formal, codified behavior expected | Informal, personalized behavior allowed |
| Function | Community interaction, cultural exchange, events | Personal life, family activities, confidential matters |
| Examples | Parks, streets, markets, government buildings | Homes, private offices, gated communities |
| Cultural Impact | Shapes public identity and collective values | Reflects personal identity and family heritage |
Understanding Public and Private Spaces
Public spaces are areas accessible to all individuals, such as parks, streets, and plazas, where social interaction is common but privacy expectations are limited. Private spaces refer to locations like homes or offices, where access is restricted, and individuals have a higher right to control personal information and activities. Understanding the balance between public and private spaces is essential to respecting privacy norms, which guide appropriate behavior and data protection based on context and environment.
Defining the Boundaries: Public vs Private
Defining the boundaries between public and private space is crucial for understanding social behavior and privacy norms. Public spaces are areas accessible to everyone, such as parks and streets, where individual privacy is limited by default. Your privacy in private spaces, including homes and personal offices, is legally and socially protected, establishing clear limits on surveillance and intrusion.
Historical Evolution of Shared and Personal Areas
Public and private spaces have evolved through historical shifts in societal norms and urban development, reflecting changing attitudes toward shared and personal areas. Ancient civilizations often featured communal areas like agoras or forums, while private dwellings varied significantly in accessibility and design, influenced by class and cultural practices. Understanding this evolution helps you navigate contemporary privacy norms that balance collective interaction with individual boundaries.
Social Functions of Public Spaces
Public spaces serve as essential hubs for social interaction, community engagement, and civic participation, fostering inclusivity and cultural exchange. Private spaces prioritize individual control and intimacy, offering refuge from public scrutiny and enabling personal expression free from external observation. Privacy norms regulate behavior in both public and private realms, balancing the need for social connectivity with individual rights to confidentiality and autonomy.
Privacy Rights in Private Spaces
Privacy rights in private spaces are legally protected to ensure individuals have control over personal information and activities within their homes or designated private areas. Unlike public spaces, where there is limited expectation of privacy, your private environment safeguards against unauthorized surveillance, data collection, and intrusion. Understanding these rights is crucial for maintaining personal security and autonomy in both physical and digital private domains.
The Impact of Technology on Space Distinctions
Technology has significantly blurred the boundaries between public and private spaces, challenging traditional privacy norms through pervasive surveillance, social media, and location-based services. Digital platforms enable constant connectivity and data sharing, often resulting in the unintended exposure of personal information in what was once considered private environments. This shift necessitates updated privacy regulations and technological safeguards to protect individual autonomy within increasingly hybrid physical and virtual spaces.
Legal Frameworks Governing Public and Private Areas
Legal frameworks governing public and private spaces establish clear boundaries that define the extent of individual privacy rights and state authority. Public space regulations typically allow for greater state surveillance and limited privacy expectations, whereas private spaces are protected under laws ensuring personal privacy and restricted access. Privacy norms are codified in statutes such as the Fourth Amendment in the U.S. or the GDPR in the EU, which regulate data collection, surveillance, and the permissible scope of intrusion into private versus public domains.
Cultural Perspectives on Space Usage
Cultural perspectives on space usage significantly influence the distinctions between public and private spaces and the expectations of privacy norms. In collectivist societies, public spaces are often communal, fostering social interaction, while in individualistic cultures, private spaces are highly valued for personal autonomy and privacy. Understanding these cultural variations helps You navigate social boundaries and respect privacy expectations across different environments.
Challenges in Maintaining Boundaries
Balancing the boundaries between public and private spaces poses significant challenges as urbanization and digital surveillance blur traditional distinctions. Privacy norms are increasingly tested by the proliferation of cameras, social media, and data collection, complicating individuals' control over personal information and physical boundaries. Ensuring clear legal frameworks and social understanding is essential to protect privacy amid evolving technological and societal landscapes.
Future Trends: Blurring Lines Between Public and Private
Emerging technologies such as augmented reality and pervasive surveillance cameras are increasingly eroding the traditional boundaries between public and private spaces. Social media platforms and smart city infrastructures collect and analyze vast amounts of personal data, challenging established privacy norms and prompting debates over consent and data ownership. Future trends indicate a growing need for adaptive privacy regulations that address the dynamic interplay between public visibility and private autonomy in digital and physical environments.
Infographic: Public vs Private space
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com