Patriarchy enforces hierarchical gender roles privileging male authority, while egalitarianism promotes equal rights and shared power between genders. Explore this article to understand the impacts of these social systems on relationships.
Table of Comparison
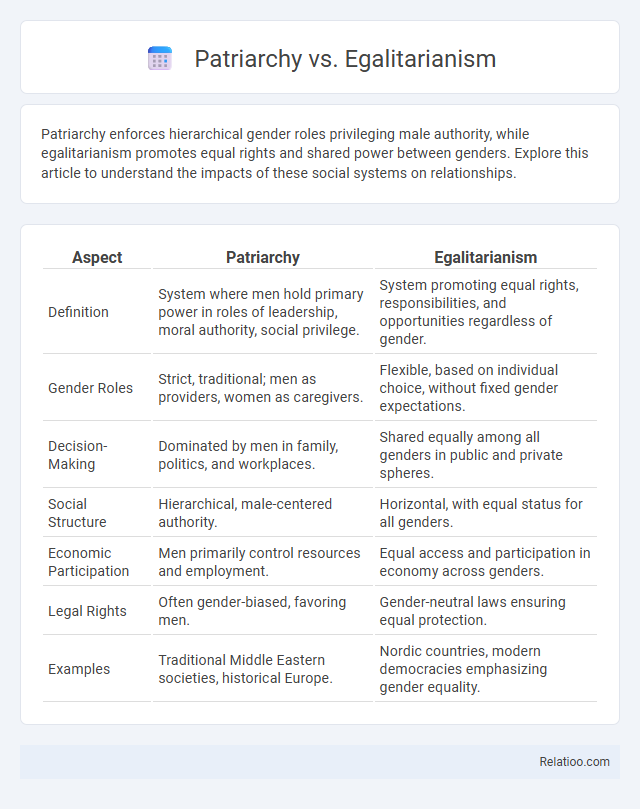
| Aspect | Patriarchy | Egalitarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System where men hold primary power in roles of leadership, moral authority, social privilege. | System promoting equal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities regardless of gender. |
| Gender Roles | Strict, traditional; men as providers, women as caregivers. | Flexible, based on individual choice, without fixed gender expectations. |
| Decision-Making | Dominated by men in family, politics, and workplaces. | Shared equally among all genders in public and private spheres. |
| Social Structure | Hierarchical, male-centered authority. | Horizontal, with equal status for all genders. |
| Economic Participation | Men primarily control resources and employment. | Equal access and participation in economy across genders. |
| Legal Rights | Often gender-biased, favoring men. | Gender-neutral laws ensuring equal protection. |
| Examples | Traditional Middle Eastern societies, historical Europe. | Nordic countries, modern democracies emphasizing gender equality. |
Understanding Patriarchy: Definition and Origins
Patriarchy is a social system in which men hold primary power and dominate roles in leadership, moral authority, and control over property, often traced back to early agricultural societies around 5,000 to 6,000 years ago. This hierarchical structure institutionalizes male dominance, shaping cultural norms, laws, and economic systems that marginalize women's influence. Understanding patriarchy involves exploring its deep-rooted origins linked to inheritance practices, militarization, and religious doctrines that perpetuate gender inequality across centuries.
Key Characteristics of Patriarchal Societies
Patriarchal societies are characterized by male dominance in political leadership, moral authority, social privilege, and control over property. Family structures in these societies often emphasize male authority, with inheritance and lineage traced through the male line. Gender roles are rigidly defined, limiting women's access to power and reinforcing systemic inequality.
Egalitarianism Explained: Principles and Values
Egalitarianism centers on the principle of equal rights, opportunities, and status for all individuals, rejecting hierarchical structures found in patriarchy where power is predominantly held by men. Core values include fairness, inclusivity, and respect for diversity, promoting gender equality in social, economic, and political spheres. This philosophy advocates dismantling systemic biases and embracing collaborative decision-making to achieve balanced representation and justice.
Historical Shifts from Patriarchy to Egalitarianism
Historical shifts from patriarchy to egalitarianism are marked by significant social and political transformations that challenge male-dominated power structures. Movements such as feminism, civil rights activism, and educational reforms have played crucial roles in promoting gender equality and dismantling patriarchal norms. These shifts reflect increasing recognition of individual rights and equal opportunities across gender lines in various societies worldwide.
Gender Roles in Patriarchal and Egalitarian Systems
In patriarchal systems, gender roles are strictly defined, often assigning men to leadership and economic roles while women are relegated to domestic and caregiving responsibilities. Egalitarian systems promote flexible gender roles where power, responsibilities, and opportunities are shared equally between men and women, fostering mutual respect and collaboration. Studies show that societies with egalitarian gender roles experience higher levels of social equality and economic development.
Social and Economic Impacts of Patriarchy
Patriarchy systematically limits women's access to economic resources and decision-making power, resulting in persistent gender wage gaps and reduced female labor force participation worldwide. Socially, it reinforces traditional gender roles that perpetuate inequality, restrict women's education and healthcare access, and increase vulnerabilities to gender-based violence. These patriarchal structures negatively affect overall economic growth by underutilizing half the population's potential and maintaining unequal power dynamics in both public and private spheres.
Benefits of Egalitarian Societies
Egalitarian societies promote equal rights, opportunities, and responsibilities for all individuals, regardless of gender, leading to increased social cohesion and cooperation. Your community benefits from diverse perspectives, fostering innovation and more equitable resource distribution. Research shows that egalitarianism correlates with lower rates of violence and higher overall well-being compared to patriarchal systems.
Myths and Misconceptions about Both Systems
Patriarchy is often misunderstood as solely oppressive toward women, ignoring its complex social roles and varied cultural contexts. Egalitarianism is frequently idealized as perfectly fair, yet it can mask ongoing power imbalances and structural inequalities. Your understanding improves by recognizing myths that oversimplify these systems, revealing the nuanced realities behind patriarchy and egalitarianism.
Contemporary Debates: Patriarchy vs. Egalitarianism
Contemporary debates on patriarchy versus egalitarianism center on power distribution and gender roles, with patriarchy upholding male dominance and hierarchical social structures, while egalitarianism advocates for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender. Research highlights how patriarchal systems perpetuate systemic inequalities in political representation, economic participation, and social norms. Egalitarian frameworks promote inclusive policies and cultural shifts aimed at dismantling gender biases entrenched in institutions and everyday interactions.
Future Trends: Moving Toward Gender Equality
Future trends indicate a global shift from rigid patriarchal systems toward more egalitarian societies, driven by increasing awareness of gender equality and inclusive policies. Technological advancements and education reforms empower marginalized genders, fostering balanced representation in leadership and decision-making roles. Continued progress depends on dismantling systemic biases and promoting cultural change that values diversity and equity.
Infographic: Patriarchy vs Egalitarianism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com