Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional actions or remarks that communicate bias or negative attitudes towards a person or group, while macroaggressions are overt, intentional acts of discrimination or hostility that have a larger and more damaging impact. Explore this article to understand how recognizing both microaggressions and macroaggressions can improve relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
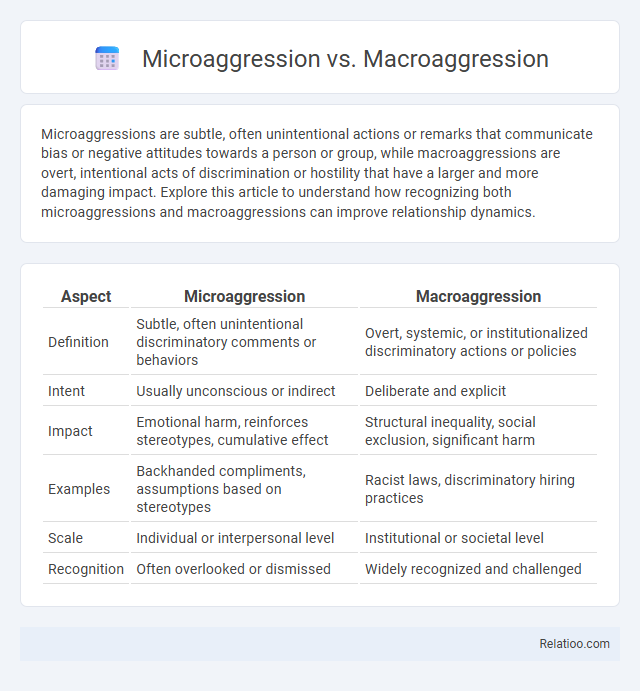
| Aspect | Microaggression | Macroaggression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Subtle, often unintentional discriminatory comments or behaviors | Overt, systemic, or institutionalized discriminatory actions or policies |
| Intent | Usually unconscious or indirect | Deliberate and explicit |
| Impact | Emotional harm, reinforces stereotypes, cumulative effect | Structural inequality, social exclusion, significant harm |
| Examples | Backhanded compliments, assumptions based on stereotypes | Racist laws, discriminatory hiring practices |
| Scale | Individual or interpersonal level | Institutional or societal level |
| Recognition | Often overlooked or dismissed | Widely recognized and challenged |
Understanding Microaggression: Subtle Everyday Slights
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, everyday slights or insults that communicate negative or derogatory messages to marginalized groups, impacting their psychological well-being. Macroaggressions refer to more overt, large-scale acts of discrimination or hostility that are easily recognizable and have immediate, significant consequences. Understanding microaggressions requires recognizing their covert nature and cumulative effects, which contribute to systemic inequality and reinforce harmful stereotypes over time.
Defining Macroaggression: Overt and Systemic Acts
Macroaggression refers to overt and systemic acts of discrimination or hostility that are easily recognizable and deeply embedded within institutions or societal structures. These aggressive behaviors exert widespread impact, influencing policies, organizational cultures, and social norms that perpetuate inequality. Understanding macroaggression helps you address the root causes of systemic oppression beyond individual microaggressions or subtle biases.
Key Differences Between Microaggression and Macroaggression
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, everyday slights or insults that communicate derogatory messages to marginalized groups, while macroaggressions are overt, deliberate, and systemic acts of discrimination or hostility. You can observe microaggressions in personal interactions, such as microinvalidations or microinsults, whereas macroaggressions manifest in broader social, institutional, or structural levels, including policies or explicit hate crimes. Understanding these key differences helps address both the nuanced and systemic impacts of aggression on individuals and communities.
Common Examples of Microaggression
Common examples of microaggressions include subtle comments or behaviors that unintentionally convey prejudice, such as asking someone "Where are you really from?" or assuming incompetence based on stereotypes. Macroaggressions, in contrast, involve overt and intentional acts of discrimination or hostility, like hate speech or systemic exclusion. Understanding how microaggressions affect your daily interactions can help you recognize and address these subtle forms of bias effectively.
Real-World Cases of Macroaggression
Macroaggressions are overt, large-scale acts of discrimination or hostility that often involve systemic policies or institutionalized practices, with real-world examples including widespread racial profiling, discriminatory immigration laws, and large-scale workplace harassment targeting specific groups. Unlike microaggressions, which involve subtle, often unconscious verbal or behavioral slights, macroaggressions produce visible, measurable harm and perpetuate structural inequality across societies. Understanding cases such as the impact of mass incarceration on communities of color or the enforcement of exclusionary voting laws highlights the extensive social and economic consequences driven by macroaggressions.
Psychological Impacts of Microaggression
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, verbal or behavioral slights that convey negative or derogatory messages to marginalized groups, causing cumulative psychological harm such as increased anxiety, depression, and lowered self-esteem. In contrast, macroaggressions are overt and explicit acts of discrimination or hostility that can lead to acute stress responses and trauma but are less frequent than microaggressions. The persistent exposure to microaggressions can result in a chronic stress burden, impairing mental health and well-being more insidiously over time than singular macroaggression instances.
Societal Consequences of Macroaggression
Macroaggressions, large-scale and overt discriminatory actions or policies, have profound societal consequences, including systemic inequality, marginalization, and entrenched social divisions. Unlike microaggressions, which are subtle and often unintentional, macroaggressions create structural barriers that impact access to education, healthcare, and employment for marginalized groups. These pervasive acts of discrimination perpetuate economic disparities and reinforce social hierarchies, hindering efforts toward equity and social cohesion.
Addressing Microaggressions in the Workplace
Addressing microaggressions in the workplace requires recognizing subtle, often unintentional discriminatory comments or behaviors that can create a hostile environment for marginalized groups. Unlike macroaggressions, which are overt and intentional acts of discrimination, microaggressions undermine employee well-being and productivity through repeated, everyday slights. Implementing comprehensive training programs, promoting open dialogue, and establishing clear policies are essential strategies for mitigating microaggressions and fostering an inclusive workplace culture.
Combating Macroaggressions Through Policy and Activism
Combating macroaggressions requires comprehensive policies and sustained activism targeting systemic inequalities and overt discrimination embedded in institutions and social structures. Your efforts should focus on enacting anti-discrimination laws, promoting inclusive workplace practices, and supporting advocacy groups that challenge large-scale social injustices. Addressing macroaggressions effectively also involves raising public awareness and mobilizing communities to demand accountability and equitable treatment at all levels.
Fostering Inclusive Environments: Prevention Strategies
Microaggressions, subtle everyday slights, and macroaggressions, overt and systemic discriminatory acts, both undermine inclusive environments by perpetuating bias and exclusion. Effective prevention strategies include ongoing education, clear policies, and active bystander intervention to address and reduce these behaviors, ensuring your workplace fosters respect and psychological safety. Prioritizing open dialogue and accountability creates a culture where diversity is valued and all individuals feel empowered.
Infographic: Microaggression vs Macroaggression
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com