Legal polygamy is recognized and regulated by specific governments, allowing individuals to have multiple spouses within the boundaries of law, whereas illegal polygamy violates marital laws and may result in legal penalties. Explore this article to understand the distinctions, implications, and global perspectives on legal versus illegal polygamy.
Table of Comparison
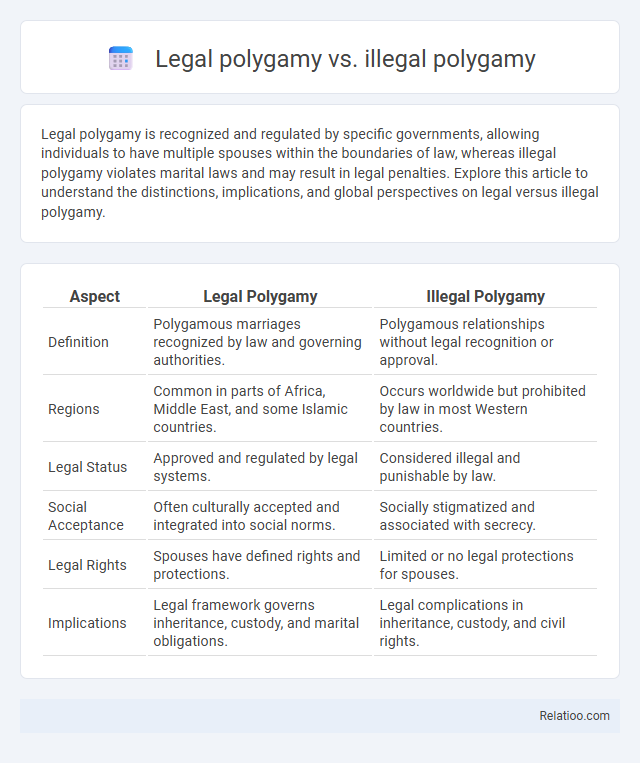
| Aspect | Legal Polygamy | Illegal Polygamy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Polygamous marriages recognized by law and governing authorities. | Polygamous relationships without legal recognition or approval. |
| Regions | Common in parts of Africa, Middle East, and some Islamic countries. | Occurs worldwide but prohibited by law in most Western countries. |
| Legal Status | Approved and regulated by legal systems. | Considered illegal and punishable by law. |
| Social Acceptance | Often culturally accepted and integrated into social norms. | Socially stigmatized and associated with secrecy. |
| Legal Rights | Spouses have defined rights and protections. | Limited or no legal protections for spouses. |
| Implications | Legal framework governs inheritance, custody, and marital obligations. | Legal complications in inheritance, custody, and civil rights. |
Definition of Legal and Illegal Polygamy
Legal polygamy refers to the practice of having multiple spouses simultaneously in jurisdictions where such marriages are officially recognized and regulated by law, often seen in countries with specific cultural or religious legal frameworks. Illegal polygamy involves entering into multiple marriages without legal recognition, violating national laws that mandate monogamy and can result in criminal penalties or annulment of subsequent unions. Understanding the distinction between legal and illegal polygamy is crucial for you to navigate marital rights and legal responsibilities effectively in different regions.
Historical Context of Polygamy Laws
Historical context of polygamy laws varies significantly across cultures and legal systems, with legal polygamy often rooted in religious or customary traditions permitted by certain governments, such as in parts of the Middle East and Africa. Illegal polygamy typically refers to marriages that contravene national laws prohibiting multiple simultaneous spouses, prominently enforced in Western countries where monogamy is the legal standard. Understanding the evolution of polygamy regulations highlights the complex interplay between cultural practices and legal frameworks shaped by colonial legacies, religious doctrines, and social norms.
Countries Where Polygamy Is Legal
Legal polygamy is permitted in countries such as Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Nigeria, where it is regulated by religious or civil laws allowing multiple spouses under specific conditions. Illegal polygamy occurs in nations like the United States and most European countries, where marrying multiple spouses violates marital laws and can result in criminal charges. Understanding your country's stance on polygamy is essential, especially if you are considering relationships involving multiple marriages or want to ensure compliance with local family laws.
Jurisdictions That Criminalize Polygamy
Legal polygamy occurs in jurisdictions such as parts of the Middle East, Africa, and Asia where multiple marriages are recognized under specific religious or cultural laws. Illegal polygamy is criminalized in many countries including the United States, Canada, and most European nations, where bigamy and multiple marriages violate legal statutes. Laws against polygamy aim to protect individual rights and maintain social order, with penalties ranging from fines to imprisonment in jurisdictions enforcing strict monogamy.
Social and Cultural Drivers of Polygamy
Legal polygamy is often shaped by religious beliefs and cultural traditions endorsing multiple spouses, commonly found in regions where it is formally recognized by law, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East. Illegal polygamy typically occurs in societies where monogamy is legally enforced but cultural or social norms continue to support plural marriages, leading to clandestine relationships and potential legal conflicts. The broader practice of polygamy is driven by factors like economic advantages, social status, gender dynamics, and the preservation of lineage, reflecting deep-rooted societal structures that influence its acceptance or prohibition.
Legal Rights in Recognized Polygamous Marriages
Legal polygamy refers to marriages recognized by law in certain countries or cultures, granting spouses official rights such as inheritance, spousal support, and parental responsibilities. Illegal polygamy occurs where multiple marriages are not sanctioned by law, often leading to lack of legal protections, social stigma, and potential criminal penalties for participants. Polygamy, in general, varies globally in legal recognition, with legal rights fully accessible only in jurisdictions that formally acknowledge multiple spouses within marriage frameworks.
Enforcement and Penalties for Illegal Polygamy
Legal polygamy, recognized in certain countries under specific religious or cultural laws, allows multiple marriages with government oversight, ensuring compliance and legitimacy. Illegal polygamy involves entering multiple marital contracts without legal consent, often resulting in criminal prosecution, fines, or imprisonment depending on jurisdictional statutes. Enforcement agencies prioritize investigations and legal actions against illegal polygamy to uphold civil codes, protect individual rights, and maintain accurate marital records.
Impacts on Women and Children
Legal polygamy often provides regulated protections for women and children, including rights to inheritance and custody, whereas illegal polygamy can expose them to risks such as domestic abuse, lack of legal recognition, and economic instability. The absence of legal oversight in illegal polygamous relationships frequently results in limited access to healthcare, education, and social services, undermining the well-being of those involved. You should be aware that the societal and psychological impacts on women and children vary greatly depending on the legal status of polygamy in their region.
Religious Perspectives on Polygamy Laws
Religious perspectives on polygamy significantly influence the distinction between legal and illegal polygamy, as many faiths such as Islam and certain African traditional religions permit polygamous marriages under specific conditions, leading to legal recognition in countries like Saudi Arabia and South Africa. In contrast, Judeo-Christian doctrines typically oppose polygamy, shaping Western legal frameworks that render such unions illegal, evident in countries including the United States and most of Europe. The conflict between religious acceptance and secular laws creates complex legal and social dynamics affecting polygamous families worldwide.
Future Trends: Global Legalization or Restriction
Legal polygamy is recognized and regulated in certain countries, providing frameworks for multiple marriages, while illegal polygamy occurs where such unions violate local laws and often face penalties. Polygamy's future trends show a complex global landscape with some regions considering legalization due to cultural acceptance or population dynamics, while others enforce stricter restrictions driven by human rights and gender equality concerns. Your understanding of these evolving legal statuses is crucial as international debates and policy reforms continue shaping the acceptance or prohibition of polygamous relationships worldwide.
Infographic: Legal polygamy vs Illegal polygamy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com